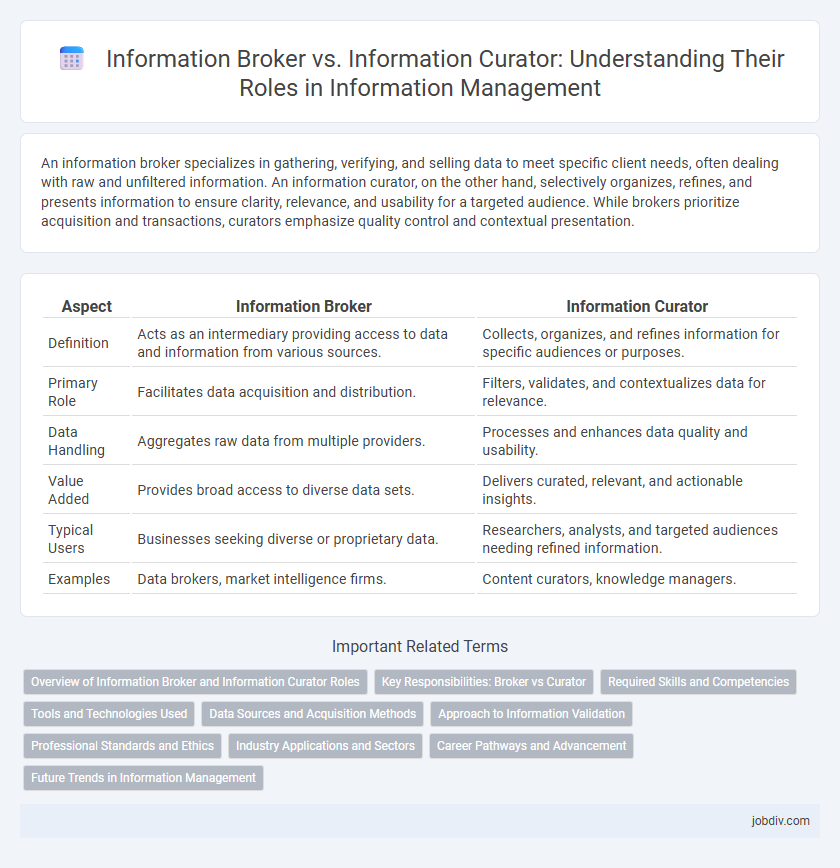
An information broker specializes in gathering, verifying, and selling data to meet specific client needs, often dealing with raw and unfiltered information. An information curator, on the other hand, selectively organizes, refines, and presents information to ensure clarity, relevance, and usability for a targeted audience. While brokers prioritize acquisition and transactions, curators emphasize quality control and contextual presentation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Information Broker | Information Curator |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acts as an intermediary providing access to data and information from various sources. | Collects, organizes, and refines information for specific audiences or purposes. |
| Primary Role | Facilitates data acquisition and distribution. | Filters, validates, and contextualizes data for relevance. |
| Data Handling | Aggregates raw data from multiple providers. | Processes and enhances data quality and usability. |
| Value Added | Provides broad access to diverse data sets. | Delivers curated, relevant, and actionable insights. |
| Typical Users | Businesses seeking diverse or proprietary data. | Researchers, analysts, and targeted audiences needing refined information. |
| Examples | Data brokers, market intelligence firms. | Content curators, knowledge managers. |
Overview of Information Broker and Information Curator Roles
Information brokers specialize in gathering, analyzing, and distributing data from diverse sources to provide actionable insights for decision-making. Information curators focus on organizing, validating, and maintaining accurate, relevant content to ensure high-quality knowledge dissemination. Both roles are crucial in managing information flow, with brokers emphasizing data acquisition and analysts, while curators prioritize content quality and contextual relevance.
Key Responsibilities: Broker vs Curator
Information brokers specialize in gathering, verifying, and distributing data to meet client needs, often operating in diverse industries for strategic decision-making. Information curators focus on organizing, categorizing, and maintaining data collections to ensure accessibility, relevance, and accuracy for targeted audiences or platforms. While brokers actively source and negotiate information, curators streamline and contextualize data for efficient consumption and long-term value.
Required Skills and Competencies
Information brokers excel in data acquisition, requiring strong research skills, database management, and advanced analytical abilities to source and verify accurate information efficiently. Information curators need competencies in content organization, metadata tagging, and critical evaluation to transform raw data into structured, accessible knowledge. Both roles demand proficiency in digital tools, attention to detail, and a deep understanding of information ethics and privacy regulations.
Tools and Technologies Used
Information brokers utilize advanced data aggregation platforms, web scraping tools, and proprietary databases to collect and analyze vast amounts of raw data efficiently. Information curators rely on content management systems, AI-driven filtering algorithms, and metadata tagging technologies to organize, contextualize, and present refined information to targeted audiences. Both professionals leverage cloud storage solutions and analytics software, but brokers emphasize data acquisition tools while curators focus on enhancing accessibility and relevance.
Data Sources and Acquisition Methods
Information brokers specialize in acquiring data from diverse sources such as public records, proprietary databases, and online platforms using advanced search techniques and data purchasing agreements. Information curators focus on collecting, organizing, and verifying data from trusted, often niche-specific sources like academic journals, expert networks, and curated content repositories. While brokers emphasize broad data acquisition, curators prioritize the quality and relevance of information through meticulous vetting and contextualization.
Approach to Information Validation
Information brokers prioritize extensive data acquisition from diverse sources, applying standardized verification techniques to ensure accuracy. Information curators emphasize selective content gathering coupled with rigorous contextual analysis to validate relevance and credibility. Both roles employ fact-checking, yet brokers focus on breadth while curators prioritize depth in information validation.
Professional Standards and Ethics
Information brokers and information curators both handle data access and dissemination, but their professional standards and ethics differ significantly. Information brokers prioritize accuracy, confidentiality, and compliance with data protection laws to maintain trust and legality when acquiring and distributing data. Information curators emphasize ethical content selection, unbiased presentation, and intellectual property rights, ensuring responsible curation that respects source integrity and user privacy.
Industry Applications and Sectors
Information brokers specialize in aggregating and selling data across sectors such as finance, healthcare, and marketing, enabling businesses to gain competitive insights and identify market trends. Information curators focus on organizing, validating, and contextualizing data primarily for industries like education, research, and media, enhancing accessibility and relevance for decision-makers. Both roles are critical in sectors like technology and government, where accurate data management drives strategic planning and operational efficiency.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Information Brokers specialize in acquiring and distributing data to meet client needs, often advancing into roles like data consultants or market analysts by developing expertise in research and negotiation. Information Curators focus on organizing, managing, and preserving digital content, progressing towards careers such as digital librarians, content strategists, or knowledge managers through skills in metadata and content lifecycle management. Both career paths emphasize continuing education in data management technologies and industry-specific knowledge to enhance advancement opportunities.
Future Trends in Information Management
Information brokers specialize in acquiring and distributing data, while information curators focus on organizing and contextualizing content for specific audiences. Future trends in information management emphasize integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance data discovery, personalization, and quality control. This evolution will blur the lines between brokering and curating roles, driving more dynamic and user-centric information ecosystems.
Information Broker vs Information Curator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com