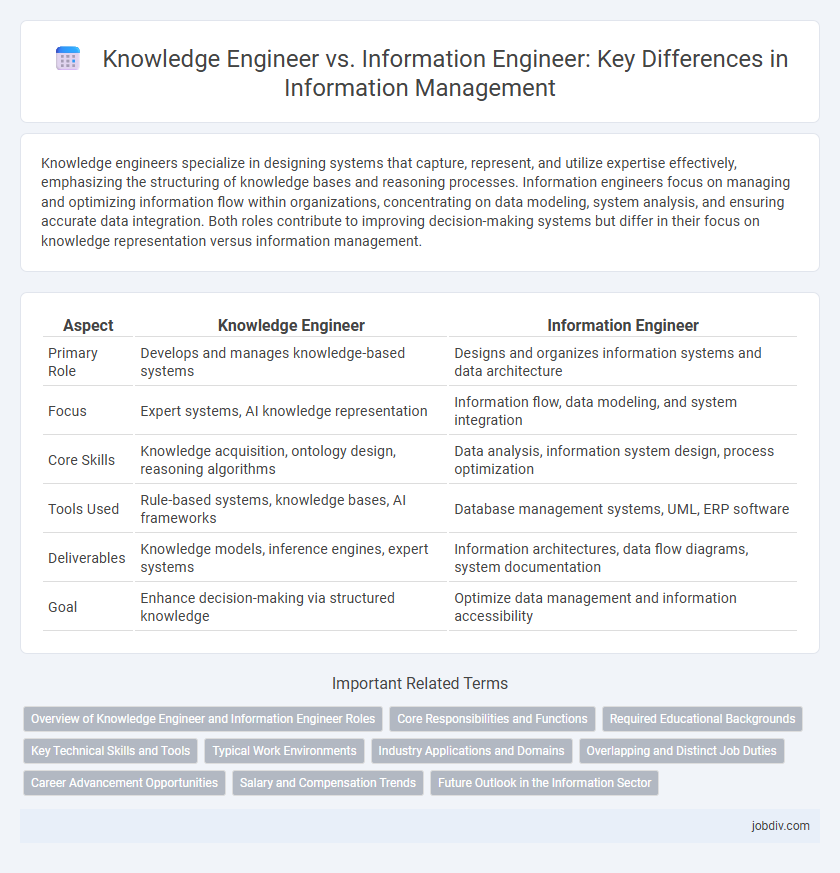
Knowledge engineers specialize in designing systems that capture, represent, and utilize expertise effectively, emphasizing the structuring of knowledge bases and reasoning processes. Information engineers focus on managing and optimizing information flow within organizations, concentrating on data modeling, system analysis, and ensuring accurate data integration. Both roles contribute to improving decision-making systems but differ in their focus on knowledge representation versus information management.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Knowledge Engineer | Information Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Develops and manages knowledge-based systems | Designs and organizes information systems and data architecture |
| Focus | Expert systems, AI knowledge representation | Information flow, data modeling, and system integration |
| Core Skills | Knowledge acquisition, ontology design, reasoning algorithms | Data analysis, information system design, process optimization |
| Tools Used | Rule-based systems, knowledge bases, AI frameworks | Database management systems, UML, ERP software |
| Deliverables | Knowledge models, inference engines, expert systems | Information architectures, data flow diagrams, system documentation |
| Goal | Enhance decision-making via structured knowledge | Optimize data management and information accessibility |
Overview of Knowledge Engineer and Information Engineer Roles
Knowledge Engineers specialize in designing and managing knowledge-based systems, focusing on capturing, structuring, and implementing expert knowledge into artificial intelligence applications. Information Engineers concentrate on the analysis, design, and management of information systems, ensuring effective data flow, storage, and retrieval within organizations. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but Knowledge Engineers prioritize cognitive modeling and rule-based reasoning, while Information Engineers emphasize database design, information architecture, and system integration.
Core Responsibilities and Functions
Knowledge Engineers specialize in designing and maintaining knowledge-based systems, focusing on capturing, structuring, and utilizing expert knowledge to create intelligent applications and decision support systems. Information Engineers concentrate on analyzing, modeling, and managing data flows and information systems to optimize organizational processes and ensure accurate data integration across platforms. Both roles require strong analytical skills, with Knowledge Engineers emphasizing semantic representation and inference mechanisms, while Information Engineers prioritize information architecture and data lifecycle management.
Required Educational Backgrounds
Knowledge engineers typically require a background in artificial intelligence, computer science, or cognitive science, with expertise in knowledge representation, reasoning, and ontology development. Information engineers often hold degrees in information technology, computer science, or information systems, emphasizing data management, database design, and system architecture. Both roles benefit from advanced degrees, but knowledge engineers focus more on AI-related disciplines while information engineers prioritize information systems and technology frameworks.
Key Technical Skills and Tools
Knowledge Engineers specialize in ontology development, semantic modeling, and natural language processing using tools like Protege, RDF, and OWL for creating structured knowledge bases. Information Engineers focus on data architecture, database design, and information systems using SQL, ER modeling, and data integration platforms to optimize information flow. Both roles require expertise in data analytics and software engineering, but Knowledge Engineers emphasize AI-driven knowledge representation while Information Engineers prioritize system-level data management.
Typical Work Environments
Knowledge Engineers typically work in research labs, AI development companies, and academic institutions where they design and implement knowledge-based systems. Information Engineers are commonly found in IT departments, enterprise architecture teams, and business analysis units, focusing on managing data flow and system integration. Both roles operate in technology-driven environments but differ in their emphasis on knowledge representation versus information systems management.
Industry Applications and Domains
Knowledge Engineers specialize in designing expert systems and ontologies primarily for artificial intelligence and decision support applications in healthcare, finance, and manufacturing industries. Information Engineers focus on structuring, modeling, and managing data flows and information systems critical to enterprise architecture, software development, and telecommunications sectors. Both roles overlap in domains like data analytics and IT consulting, but Knowledge Engineers emphasize semantic reasoning while Information Engineers prioritize data integration and system optimization.
Overlapping and Distinct Job Duties
Knowledge Engineers primarily focus on designing and maintaining systems that organize and utilize structured knowledge for decision-making, emphasizing knowledge representation and reasoning. Information Engineers concentrate on managing and optimizing data flow, system architecture, and information integration within organizations to enhance data accessibility and usability. Both roles overlap in areas like system analysis and data modeling but differ in that Knowledge Engineers specialize in capturing expert knowledge, while Information Engineers address broader information systems and infrastructure challenges.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Knowledge Engineers specialize in designing systems that manage and utilize organizational knowledge, offering career advancement opportunities in AI development, semantic web technologies, and expert systems. Information Engineers focus on structuring and optimizing data flow and systems architecture, leading to roles in data management, enterprise systems design, and IT consultancy. Both career paths provide strong growth potential, but Knowledge Engineers often advance into roles involving artificial intelligence and cognitive computing, while Information Engineers typically progress toward strategic IT and data governance leadership positions.
Salary and Compensation Trends
Knowledge engineers command higher salary ranges due to their specialized skills in artificial intelligence and semantic analysis, with median annual earnings often exceeding $100,000 in top tech markets. Information engineers, focusing on data management and system integration, typically earn between $80,000 and $95,000, reflecting the demand for expertise in database architecture and network optimization. Compensation trends indicate that knowledge engineers experience faster salary growth driven by advancements in AI technologies and increased enterprise adoption of intelligent systems.
Future Outlook in the Information Sector
Knowledge Engineers will play a pivotal role in developing AI systems that simulate human expertise, enhancing decision-making processes across various industries. Information Engineers are expected to advance data management architectures, optimizing the flow and storage of big data to support intelligent systems. Both roles will be critical in shaping the future information sector by integrating artificial intelligence and sophisticated data infrastructure for smarter, more efficient knowledge ecosystems.
Knowledge Engineer vs Information Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com