Information librarians specialize in organizing, managing, and facilitating access to physical and digital information resources, ensuring users can efficiently locate relevant data. Digital archivists concentrate on preserving, curating, and providing long-term access to digital records and archives, often dealing with issues of digital preservation and metadata standards. Both roles require expertise in information management but differ in scope, with librarians focusing on information retrieval and digital archivists on safeguarding digital heritage.
Table of Comparison
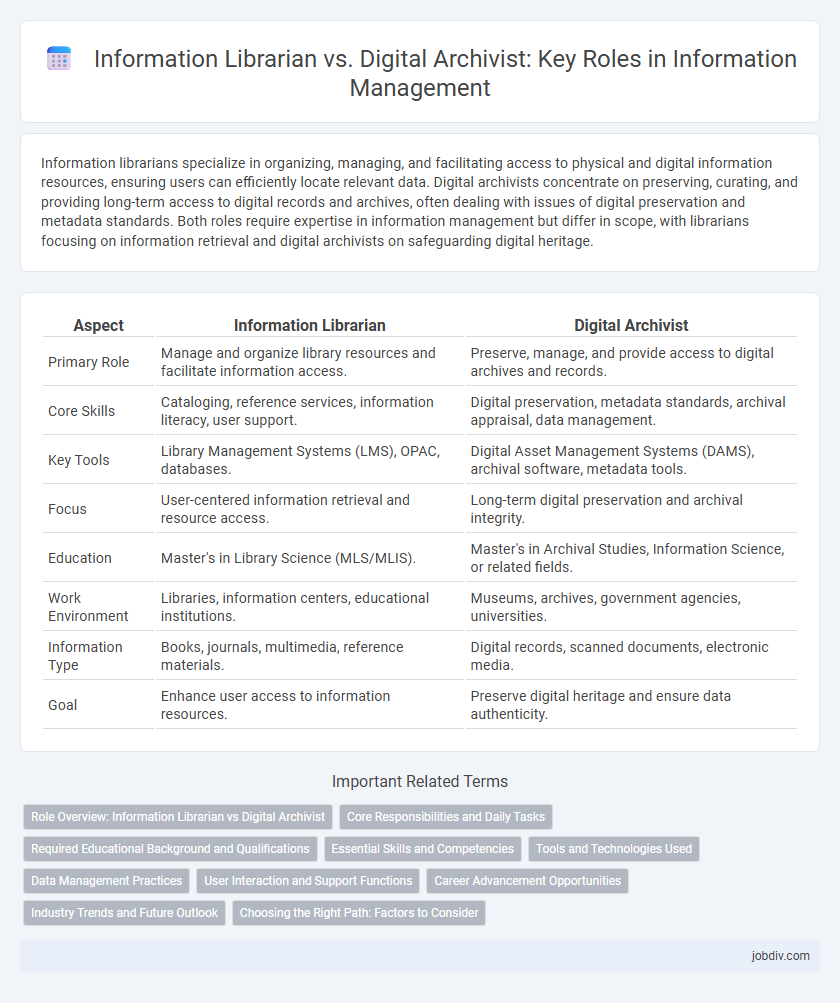
| Aspect | Information Librarian | Digital Archivist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage and organize library resources and facilitate information access. | Preserve, manage, and provide access to digital archives and records. |
| Core Skills | Cataloging, reference services, information literacy, user support. | Digital preservation, metadata standards, archival appraisal, data management. |
| Key Tools | Library Management Systems (LMS), OPAC, databases. | Digital Asset Management Systems (DAMS), archival software, metadata tools. |
| Focus | User-centered information retrieval and resource access. | Long-term digital preservation and archival integrity. |
| Education | Master's in Library Science (MLS/MLIS). | Master's in Archival Studies, Information Science, or related fields. |
| Work Environment | Libraries, information centers, educational institutions. | Museums, archives, government agencies, universities. |
| Information Type | Books, journals, multimedia, reference materials. | Digital records, scanned documents, electronic media. |
| Goal | Enhance user access to information resources. | Preserve digital heritage and ensure data authenticity. |
Role Overview: Information Librarian vs Digital Archivist
Information librarians manage, organize, and facilitate access to physical and digital information resources, supporting research and learning in libraries and institutions. Digital archivists specialize in preserving, curating, and maintaining digital records and archives to ensure long-term accessibility and authenticity. Both roles require expertise in information management, but digital archivists focus more on digital preservation technologies and metadata standards.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Information librarians primarily manage and organize physical and digital information resources, assist users in research, and maintain cataloging systems to ensure efficient information retrieval. Digital archivists specialize in preserving, curating, and managing digital records and archives, focusing on metadata standards, digital preservation techniques, and long-term access to electronic documents. Both roles require expertise in information management, but librarians emphasize user support and resource organization, while archivists concentrate on digital asset preservation and archival integrity.
Required Educational Background and Qualifications
Information Librarians typically require a Master's degree in Library and Information Science (MLIS) accredited by the American Library Association, with coursework emphasizing cataloging, reference services, and information management. Digital Archivists often hold advanced degrees in archival studies, information science, or related fields, supplemented by specialized training in digital preservation technologies, metadata standards, and records management. Professional certifications such as the Certified Archivist credential or Digital Archives Specialist certificate enhance qualifications for digital archivist roles, while Information Librarians may pursue credentials like the Library Support Staff Certification or subject-specific certificates.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Information librarians excel in skills such as cataloging, information retrieval, and user services, ensuring efficient access to physical and digital resources. Digital archivists specialize in digital preservation, metadata standards like Dublin Core, and managing digital asset management systems to safeguard electronic records. Both roles require strong competencies in information organization, critical thinking, and technological proficiency to support knowledge management and data accessibility.
Tools and Technologies Used
Information librarians primarily use integrated library systems (ILS), metadata standards like MARC and Dublin Core, and digital cataloging tools to organize and manage physical and digital collections. Digital archivists rely on digital preservation software such as Archivematica, content management systems (CMS), and file format validation tools to ensure long-term access and authenticity of digital assets. Both professionals utilize advanced search algorithms, database management systems, and data curation technologies tailored to their specific roles in information stewardship.
Data Management Practices
Information librarians specialize in organizing, cataloging, and providing access to physical and digital information resources using metadata standards like Dublin Core, enhancing discoverability and user retrieval. Digital archivists focus on preserving digital records through data integrity checks, format migrations, and adherence to archival standards such as OAIS and PREMIS to ensure long-term accessibility. Both roles implement structured data management practices, but information librarians emphasize user-centered access while digital archivists prioritize digital preservation and authenticity.
User Interaction and Support Functions
Information librarians prioritize direct user interaction by assisting with research inquiries, curating relevant resources, and offering personalized support to enhance knowledge discovery. Digital archivists focus on managing, preserving, and providing access to digital records and collections, ensuring long-term usability and authenticity for users. Both roles support users, but librarians emphasize immediate information retrieval while archivists concentrate on safeguarding digital content for future research.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Information librarians typically advance by gaining expertise in metadata standards, digital curation, and user experience design, often moving into roles such as head librarian or information management consultant. Digital archivists progress through specialization in digital preservation technologies, data forensics, and archival standards, with career trajectories leading to senior archivist, digital preservation manager, or chief information officer positions. Both careers benefit from continuous professional development and certification in digital tools and data management to enhance leadership prospects.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
Information librarians are increasingly integrating artificial intelligence and data analytics to enhance information retrieval and user experience, reflecting a trend towards more technology-driven services. Digital archivists are focusing on preserving digital assets through advanced metadata standards and blockchain for ensuring long-term authenticity and accessibility. Both professions are expected to grow as organizations prioritize digital transformation and information governance in data-intensive industries.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
When choosing between a career as an Information Librarian or a Digital Archivist, consider factors such as the work environment, with librarians typically engaging in public-facing roles in libraries and archives focusing on preserving digital records. Evaluate your interest in managing traditional catalog systems versus curating digital assets and metadata using advanced technologies. Career growth opportunities, required technical skills like digital preservation software, and personal inclination towards user interaction or digital curation play critical roles in making the right decision.
Information Librarian vs Digital Archivist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com