Information designers create visual representations that simplify complex data, making it easily understandable and accessible for users. Information curators gather, organize, and maintain relevant content from diverse sources, ensuring accuracy and coherence. Both roles are essential for effective knowledge management but focus on different aspects of handling information.
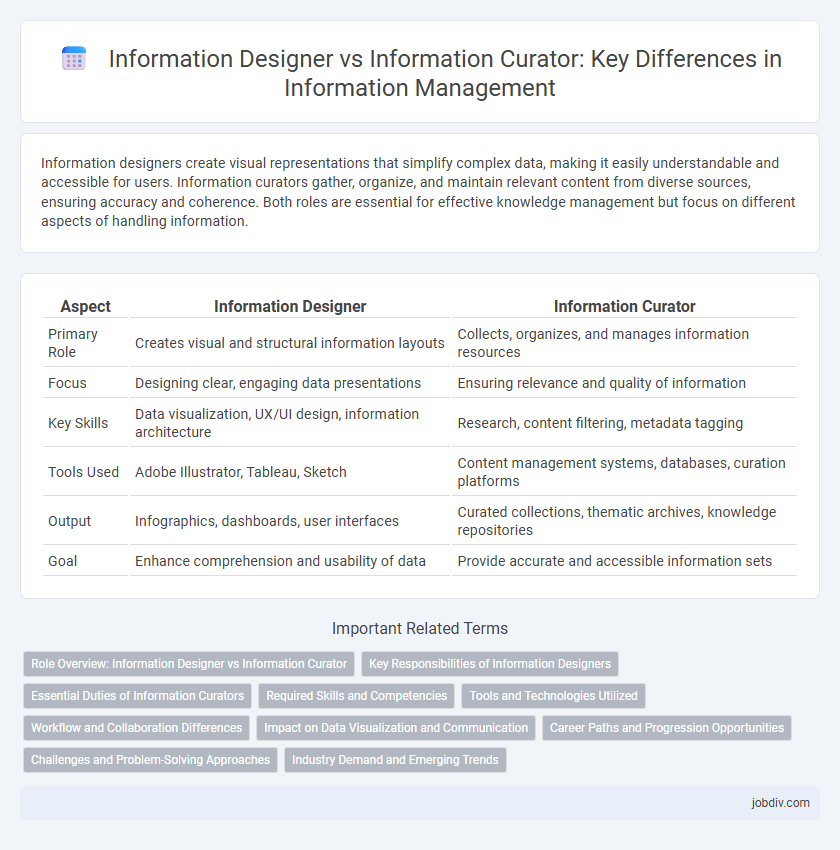
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Information Designer | Information Curator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Creates visual and structural information layouts | Collects, organizes, and manages information resources |
| Focus | Designing clear, engaging data presentations | Ensuring relevance and quality of information |
| Key Skills | Data visualization, UX/UI design, information architecture | Research, content filtering, metadata tagging |
| Tools Used | Adobe Illustrator, Tableau, Sketch | Content management systems, databases, curation platforms |
| Output | Infographics, dashboards, user interfaces | Curated collections, thematic archives, knowledge repositories |
| Goal | Enhance comprehension and usability of data | Provide accurate and accessible information sets |
Role Overview: Information Designer vs Information Curator
Information Designers specialize in structuring and visualizing data to enhance user comprehension through intuitive layouts, infographics, and interactive elements. Information Curators focus on gathering, organizing, and maintaining relevant content from diverse sources to ensure accuracy and accessibility for target audiences. Both roles prioritize clarity and usability but differ in their approach--Designers emphasize presentation while Curators concentrate on content selection and management.
Key Responsibilities of Information Designers
Information Designers specialize in structuring and presenting data in a clear, accessible format to enhance user comprehension and decision-making. Key responsibilities include creating visual representations such as infographics, diagrams, and data dashboards that simplify complex information. They collaborate closely with stakeholders to ensure the content aligns with user needs and supports effective communication strategies.
Essential Duties of Information Curators
Information Curators are responsible for organizing, managing, and maintaining accurate and relevant data collections to ensure easy access and usability. They evaluate content sources, classify information according to predefined standards, and update digital repositories to reflect current and valuable insights. Their essential duties also include ensuring data integrity, improving metadata quality, and facilitating seamless information retrieval for diverse user needs.
Required Skills and Competencies
Information Designers require strong skills in data visualization, user experience design, and information architecture to create clear and engaging presentations of complex data. Information Curators must excel in content evaluation, data classification, and metadata management to organize and maintain relevant and accurate information repositories. Both roles demand proficiency in digital tools, critical thinking, and a deep understanding of audience needs to enhance information accessibility and usability.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
Information Designers primarily utilize graphic design software like Adobe Illustrator, Sketch, and data visualization tools such as Tableau and Power BI to create visually compelling and easy-to-understand representations of data. Information Curators rely on content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Drupal, and digital asset management platforms, alongside data aggregation tools including RSS feeds, APIs, and specialized software like Evernote or Zotero for collecting, organizing, and maintaining accurate information repositories. Both roles leverage collaboration tools such as Slack and Trello, but their core technologies differ significantly based on their focus on creation versus organization.
Workflow and Collaboration Differences
Information Designers focus on structuring and presenting data visually, using tools like wireframes and prototypes to enhance user understanding, while Information Curators prioritize collecting, organizing, and verifying data from multiple sources to ensure accuracy and relevance. The designer's workflow involves iterative design phases and collaboration with UX/UI teams to optimize user experience, whereas curators work closely with content creators, researchers, and database managers to maintain data integrity and accessibility. Collaboration in design centers on creative ideation and user feedback, contrasting with curation's emphasis on data validation and knowledge management frameworks.
Impact on Data Visualization and Communication
Information Designers specialize in creating clear, visually engaging representations of complex data to enhance comprehension and decision-making. Information Curators focus on selecting, organizing, and maintaining high-quality data sets that ensure accuracy and relevance for visualization projects. Their combined efforts significantly improve the effectiveness of data communication by blending precision in data management with innovative design techniques.
Career Paths and Progression Opportunities
Information Designers specialize in creating visually engaging and user-friendly data presentations, often progressing towards roles like UX Designer or Creative Director with a focus on information architecture. Information Curators focus on collecting, organizing, and maintaining data sets for accessibility and accuracy, with career advancement typically leading to Data Manager or Digital Asset Manager positions. Both career paths emphasize expertise in data handling but diverge in application, with designers prioritizing visualization and curators emphasizing content management and metadata optimization.
Challenges and Problem-Solving Approaches
Information Designers face challenges in translating complex data into clear, user-friendly visuals, requiring strong skills in data visualization and user experience design to solve communication barriers. Information Curators contend with filtering, organizing, and validating vast amounts of data from varied sources, emphasizing expertise in metadata management and data governance to ensure accuracy and relevance. Both roles rely on collaborative problem-solving approaches, integrating technology tools and user feedback to enhance information accessibility and usability.
Industry Demand and Emerging Trends
Information Designers specialize in visualizing complex data to enhance user comprehension, with growing demand in sectors like UX/UI design, data analytics, and digital marketing. Information Curators focus on organizing and managing digital content, crucial for industries emphasizing knowledge management, content strategy, and archival systems. Emerging trends highlight increased integration of AI tools, emphasizing the need for both roles to adapt to automated data processing and dynamic content delivery environments.
Information Designer vs Information Curator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com