Information designers focus on the visual representation and communication of data to make complex information easily understandable and accessible for users. Information modelers develop structured frameworks that define relationships and rules within data sets, enabling better organization and integration across systems. Both roles complement each other by combining clarity in presentation with disciplined data architecture to enhance decision-making processes.
Table of Comparison
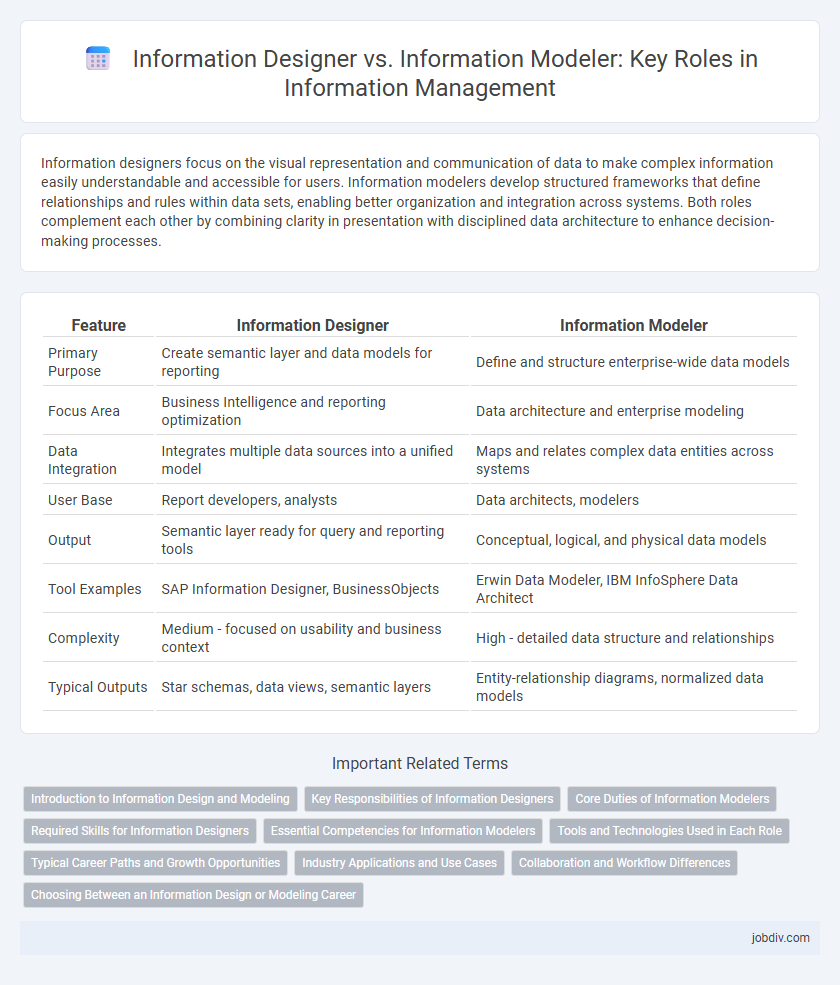
| Feature | Information Designer | Information Modeler |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Create semantic layer and data models for reporting | Define and structure enterprise-wide data models |
| Focus Area | Business Intelligence and reporting optimization | Data architecture and enterprise modeling |
| Data Integration | Integrates multiple data sources into a unified model | Maps and relates complex data entities across systems |
| User Base | Report developers, analysts | Data architects, modelers |
| Output | Semantic layer ready for query and reporting tools | Conceptual, logical, and physical data models |
| Tool Examples | SAP Information Designer, BusinessObjects | Erwin Data Modeler, IBM InfoSphere Data Architect |
| Complexity | Medium - focused on usability and business context | High - detailed data structure and relationships |
| Typical Outputs | Star schemas, data views, semantic layers | Entity-relationship diagrams, normalized data models |
Introduction to Information Design and Modeling
Information Design focuses on structuring and presenting data to enhance user understanding and decision-making through visual and textual elements. Information Modeling involves creating abstract representations of data and its relationships to enable accurate database planning and system development. Both disciplines are essential in translating complex information into accessible formats, optimizing communication and system efficiency.
Key Responsibilities of Information Designers
Information Designers focus on creating clear, user-centric visual representations of data and content to enhance understanding and communication. They develop infographics, user interfaces, and communication materials that translate complex information into accessible formats using design principles and storytelling techniques. Their key responsibilities include analyzing audience needs, structuring content logically, and collaborating with stakeholders to ensure clarity and usability in information delivery.
Core Duties of Information Modelers
Information Modelers focus on creating structured representations of data, defining relationships, entities, and rules that govern information flow within a system. Their core duties include developing data models, ensuring data integrity, and collaborating with stakeholders to align models with business requirements. They play a crucial role in designing scalable, efficient information architectures that enable accurate data analysis and decision-making.
Required Skills for Information Designers
Information Designers require strong skills in data visualization, user experience (UX) design, and effective communication to transform complex data into clear, accessible formats. Proficiency in design software like Adobe Creative Suite and tools such as Tableau or Power BI is essential for creating engaging and informative visual content. Knowledge of information architecture, cognitive psychology, and audience analysis enhances their ability to deliver intuitive and impactful information presentations.
Essential Competencies for Information Modelers
Information Modelers require strong proficiency in data analysis, conceptual modeling, and database design to create accurate and scalable information structures. They must demonstrate expertise in semantic modeling, metadata management, and aligning models with business requirements to ensure data integrity and usability. Mastery of tools such as UML, ER diagrams, and ontology frameworks is essential for translating complex information into understandable and functional models.
Tools and Technologies Used in Each Role
Information Designers primarily use tools like Adobe Creative Suite, Sketch, and Figma to create visual representations and user interfaces, emphasizing user experience and clarity. Information Modelers rely on technologies such as UML, ER diagrams, and modeling software like Sparx Systems Enterprise Architect or IBM InfoSphere Data Architect to define data structures and relationships. Both roles utilize specialized software tailored to their focus: design for visual communication and modeling for data organization and system architecture.
Typical Career Paths and Growth Opportunities
Information Designers typically advance into roles such as User Experience (UX) Lead, Content Strategist, or Digital Product Manager, capitalizing on their expertise in visual communication and user interaction. Information Modelers often progress towards Data Architect, Systems Analyst, or Enterprise Architect positions, leveraging their skills in structuring data frameworks and optimizing information systems. Both career paths offer growth opportunities that emphasize increasing specialization and leadership in information management and technology domains.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Information Designers specialize in structuring content for user-friendly interfaces across digital platforms, enhancing user experience in industries like e-commerce, media, and education. Information Modelers focus on creating data frameworks and organizational models used in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and telecommunications to improve data integrity and interoperability. Both roles drive effective communication of complex information but differ in application: Designers optimize usability and clarity, while Modelers ensure robust data architecture and system integration.
Collaboration and Workflow Differences
Information Designers focus on creating clear, user-friendly representations of data, emphasizing visual communication and user experience to ensure information is easily understood. Information Modelers develop structured frameworks that define data relationships and semantics, enabling consistent data integration and management across systems. Collaboration between these roles often involves Information Designers translating complex models from Information Modelers into accessible formats, streamlining workflows through iterative feedback and alignment on data interpretation.
Choosing Between an Information Design or Modeling Career
Choosing between an Information Designer and Information Modeler career hinges on whether you prefer crafting user-centric data presentations or structuring complex data architectures. Information Designers excel in creating intuitive visuals and content flows for enhanced user comprehension, while Information Modelers specialize in developing data frameworks and schemas to support database integrity and system interoperability. Career success depends on your strengths in creative communication versus analytical data structuring within information management.
Information Designer vs Information Modeler Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com