Data curators manage the organization, quality, and usability of data by ensuring it is accurate, consistent, and properly documented for analysis and decision-making. Data custodians are responsible for the technical environment, maintaining data storage, security, and access controls to protect data integrity. Together, curators and custodians collaborate to ensure reliable and secure data management throughout its lifecycle.
Table of Comparison
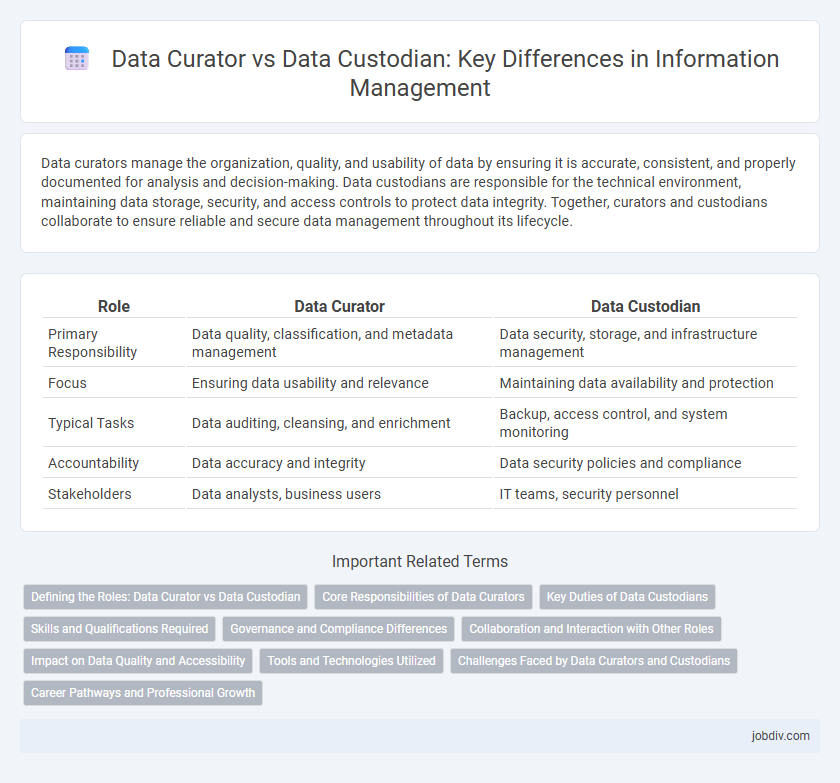
| Role | Data Curator | Data Custodian |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Data quality, classification, and metadata management | Data security, storage, and infrastructure management |
| Focus | Ensuring data usability and relevance | Maintaining data availability and protection |
| Typical Tasks | Data auditing, cleansing, and enrichment | Backup, access control, and system monitoring |
| Accountability | Data accuracy and integrity | Data security policies and compliance |
| Stakeholders | Data analysts, business users | IT teams, security personnel |
Defining the Roles: Data Curator vs Data Custodian
Data Curators design and manage data frameworks by organizing, annotating, and maintaining datasets to ensure quality, accuracy, and usability for analysis. Data Custodians oversee technical infrastructure, handling data storage, security, and access control to maintain data integrity and compliance with organizational policies. Clear role differentiation enables efficient data governance by aligning data curation's focus on content with custodianship's emphasis on infrastructure management.
Core Responsibilities of Data Curators
Data Curators are responsible for organizing, maintaining, and ensuring the quality and usability of datasets by applying metadata standards and data governance policies. They validate data accuracy, enrich datasets through annotation and classification, and facilitate data accessibility for analysis and decision-making. Their core responsibilities include data stewardship, lifecycle management, and compliance with regulatory requirements to maintain the integrity and relevance of information assets.
Key Duties of Data Custodians
Data Custodians are primarily responsible for implementing data security measures, managing access controls, and maintaining data storage infrastructure to ensure data integrity and availability. They handle routine data backups, disaster recovery processes, and monitor data usage to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches. Emphasizing operational data management, Data Custodians collaborate closely with IT teams to enforce compliance with organizational policies and regulatory standards.
Skills and Qualifications Required
Data Curators require strong expertise in data management, metadata standards, and domain-specific knowledge to ensure data quality and usability. Data Custodians need technical skills in database administration, cybersecurity, and access control to maintain and protect the data infrastructure. Both roles benefit from proficiency in data governance frameworks and compliance regulations to support effective data stewardship.
Governance and Compliance Differences
Data Curators oversee the accuracy, quality, and usability of datasets, ensuring compliance with data governance policies and regulatory standards. Data Custodians manage the technical environment and security controls needed to store and protect data, maintaining adherence to compliance frameworks and access protocols. The governance role of Data Curators centers on data stewardship and policy enforcement, while Data Custodians focus on infrastructure management and operational compliance.
Collaboration and Interaction with Other Roles
Data Curators collaborate closely with Data Scientists and Analysts to ensure data quality, relevance, and compliance with regulatory standards, facilitating accurate and trustworthy insights. Data Custodians interact primarily with IT teams and Security Officers to maintain data infrastructure, enforce access controls, and safeguard data integrity throughout its lifecycle. Effective collaboration between Data Curators and Custodians ensures seamless data governance, combining strategic data management with robust technical oversight.
Impact on Data Quality and Accessibility
Data Curators enhance data quality by applying rigorous validation and metadata standards, ensuring accurate and reliable datasets for analysis. Data Custodians maintain data accessibility and security, managing rights and infrastructure to safeguard data availability for authorized users. Their combined roles are critical in sustaining high-quality, accessible data ecosystems that drive effective decision-making.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
Data Curators leverage advanced data cataloging tools and metadata management platforms such as Alation and Collibra to ensure data quality and accessibility. Data Custodians utilize security and access control technologies like Microsoft Azure Active Directory and AWS Identity and Access Management to maintain data protection and compliance. Both roles rely on data governance frameworks and collaboration through platforms like Jira and Confluence to coordinate data stewardship effectively.
Challenges Faced by Data Curators and Custodians
Data curators face challenges in ensuring data quality, metadata accuracy, and compliance with evolving data standards, requiring continuous validation and updates. Data custodians struggle with maintaining data security, access controls, and infrastructure reliability to prevent breaches and downtime. Both roles demand clear communication and coordination to manage data lifecycle risks effectively.
Career Pathways and Professional Growth
Data Curators focus on organizing, validating, and enriching data to ensure its accuracy and usability across business functions, typically advancing into roles such as Data Scientists or Analytics Managers. Data Custodians specialize in the technical management, security, and maintenance of data infrastructure, often progressing toward IT governance or data engineering leadership positions. Both career pathways emphasize increasing expertise in data governance frameworks, regulatory compliance, and cross-functional collaboration, essential for professional growth in data-centric industries.
Data Curator vs Data Custodian Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com