A Business Intelligence Analyst transforms raw data into actionable insights through data visualization and reporting, enabling informed decision-making. A Data Engineer designs, builds, and maintains the data infrastructure and pipelines that ensure data is accessible, reliable, and optimized for analysis. Both roles are essential in leveraging data strategically, with analysts focusing on interpretation and engineers on data architecture.
Table of Comparison
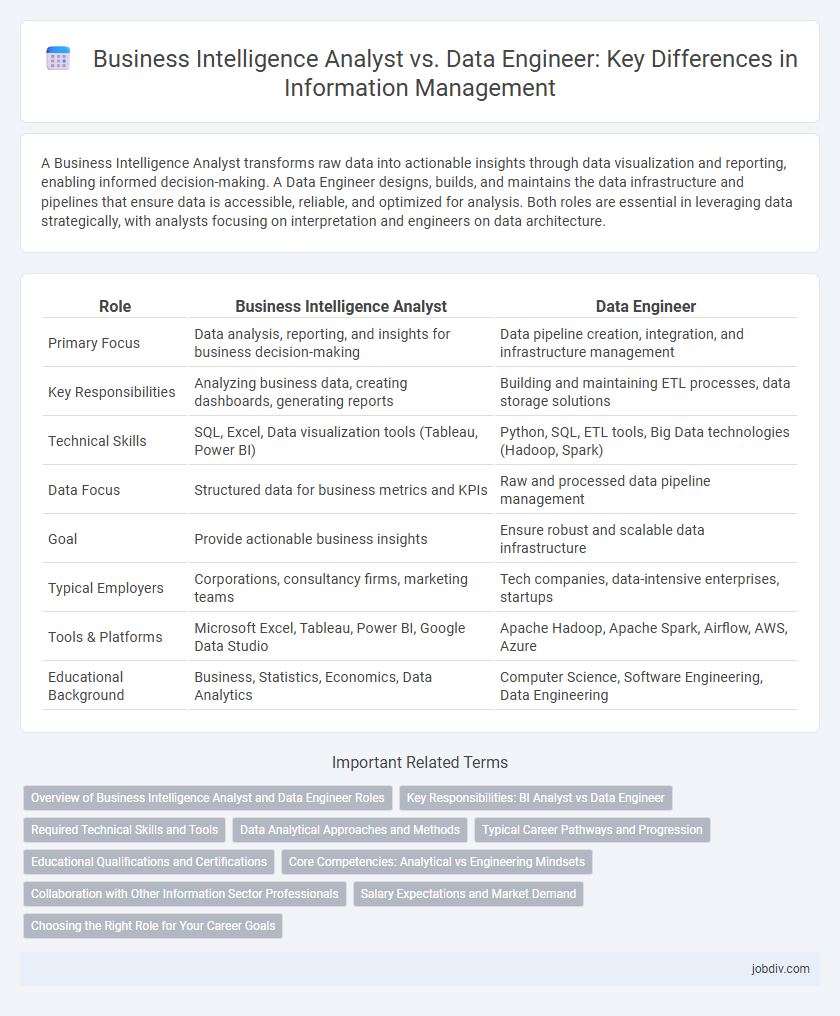
| Role | Business Intelligence Analyst | Data Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Data analysis, reporting, and insights for business decision-making | Data pipeline creation, integration, and infrastructure management |
| Key Responsibilities | Analyzing business data, creating dashboards, generating reports | Building and maintaining ETL processes, data storage solutions |
| Technical Skills | SQL, Excel, Data visualization tools (Tableau, Power BI) | Python, SQL, ETL tools, Big Data technologies (Hadoop, Spark) |
| Data Focus | Structured data for business metrics and KPIs | Raw and processed data pipeline management |
| Goal | Provide actionable business insights | Ensure robust and scalable data infrastructure |
| Typical Employers | Corporations, consultancy firms, marketing teams | Tech companies, data-intensive enterprises, startups |
| Tools & Platforms | Microsoft Excel, Tableau, Power BI, Google Data Studio | Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Airflow, AWS, Azure |
| Educational Background | Business, Statistics, Economics, Data Analytics | Computer Science, Software Engineering, Data Engineering |
Overview of Business Intelligence Analyst and Data Engineer Roles
Business Intelligence Analysts interpret complex data sets to provide actionable insights that drive strategic business decisions, utilizing tools like SQL, Tableau, and Power BI. Data Engineers design, build, and maintain scalable data pipelines and infrastructure, ensuring data is reliable and accessible for analysis using technologies such as Hadoop, Spark, and AWS. Both roles require strong programming skills but focus respectively on data analysis and data architecture within an organization's data ecosystem.
Key Responsibilities: BI Analyst vs Data Engineer
Business Intelligence Analysts focus on interpreting complex data sets to provide actionable insights through dashboards and reports, enabling strategic business decisions. Data Engineers specialize in designing, building, and maintaining data pipelines and architectures to ensure reliable data flow and storage for analytical use. Both roles are essential for data-driven organizations but differ in their emphasis on analysis versus infrastructure development.
Required Technical Skills and Tools
Business Intelligence Analysts require proficiency in SQL, data visualization tools like Tableau and Power BI, and strong knowledge of data modeling and reporting techniques to transform data into actionable insights. Data Engineers need expertise in programming languages such as Python and Java, experience with big data technologies like Apache Hadoop and Spark, and skills in building and maintaining data pipelines and databases including SQL and NoSQL systems. Both roles demand familiarity with cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud to manage and analyze large-scale datasets efficiently.
Data Analytical Approaches and Methods
Business Intelligence Analysts specialize in interpreting data through dashboards, reports, and visualization tools, emphasizing descriptive and diagnostic analytics to provide actionable insights for strategic decision-making. Data Engineers focus on building and maintaining scalable data pipelines, employing ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes and cloud-based architectures to facilitate data availability and quality for analytical consumption. Both roles utilize SQL, Python, and data warehousing concepts, but Business Intelligence Analysts prioritize data interpretation methods while Data Engineers concentrate on data infrastructure and processing frameworks.
Typical Career Pathways and Progression
Business Intelligence Analysts often progress from roles in data analysis or reporting, advancing to senior analyst positions and eventually into BI management or consultancy, leveraging strong skills in SQL, data visualization, and business strategy. Data Engineers typically begin as junior engineers or data technicians, moving towards senior engineer roles, lead engineering positions, and specialized domains like data architecture or machine learning infrastructure, with expertise in programming, ETL processes, and big data technologies. Both career paths emphasize continuous skill enhancement in data handling, but BI Analysts focus more on interpreting data insights for decision-making, while Data Engineers concentrate on building and optimizing data pipelines and systems.
Educational Qualifications and Certifications
Business Intelligence Analysts typically hold degrees in business, information technology, or data analytics, complemented by certifications like Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate or Certified Business Intelligence Professional (CBIP). Data Engineers often possess degrees in computer science, software engineering, or related fields, alongside certifications such as Google Cloud Professional Data Engineer, AWS Certified Big Data - Specialty, or Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Engineer Associate. Both roles benefit from continuous learning through specialized courses in SQL, Python, data warehousing, and ETL processes to enhance technical proficiency and industry relevance.
Core Competencies: Analytical vs Engineering Mindsets
Business Intelligence Analysts excel in data interpretation, leveraging analytical minds to transform data into actionable business insights, skilled in querying, visualization, and reporting tools like SQL and Tableau. Data Engineers possess engineering mindsets focused on building and maintaining data pipelines, ensuring data quality, scalability, and integration using technologies such as Apache Spark, Hadoop, and Python. The core competency difference lies in BI Analysts prioritizing analysis and decision support, while Data Engineers emphasize data infrastructure and engineering efficiency.
Collaboration with Other Information Sector Professionals
Business Intelligence Analysts collaborate closely with Data Engineers to translate raw data into actionable insights by leveraging expertly engineered data pipelines. Data Engineers provide robust, scalable infrastructure and ensure data quality, enabling Analysts to develop comprehensive reports and dashboards for stakeholders. This collaboration enhances decision-making processes across information management, data science, and IT departments, ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
Salary Expectations and Market Demand
Business Intelligence Analysts typically earn between $70,000 and $110,000 annually, reflecting strong market demand driven by companies seeking actionable insights from data. Data Engineers command higher salaries, ranging from $90,000 to $140,000, due to their critical role in building and maintaining complex data infrastructure. The job market shows accelerated growth for Data Engineers, fueled by increased data volume and the need for scalable pipelines, while Business Intelligence Analysts remain essential for data interpretation and strategic decision-making.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Career Goals
A Business Intelligence Analyst focuses on interpreting data to provide actionable insights, using tools like SQL, Tableau, and Excel to support decision-making and strategy. Data Engineers build and maintain data infrastructure, ensuring data flow and integrity by utilizing technologies such as Hadoop, Apache Spark, and Python for developing scalable pipelines. Choosing the right role depends on your strengths: analysts thrive on data interpretation and visualization, while engineers excel in data architecture and programming for large-scale data management.
Business Intelligence Analyst vs Data Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com