Content Managers oversee the creation, organization, and publication of digital content to ensure consistent messaging and brand alignment across platforms. Digital Asset Managers specialize in organizing, storing, and retrieving digital files such as images, videos, and documents to streamline workflows and maintain version control. Both roles are essential for efficient digital content strategy but focus on different aspects of content lifecycle management.
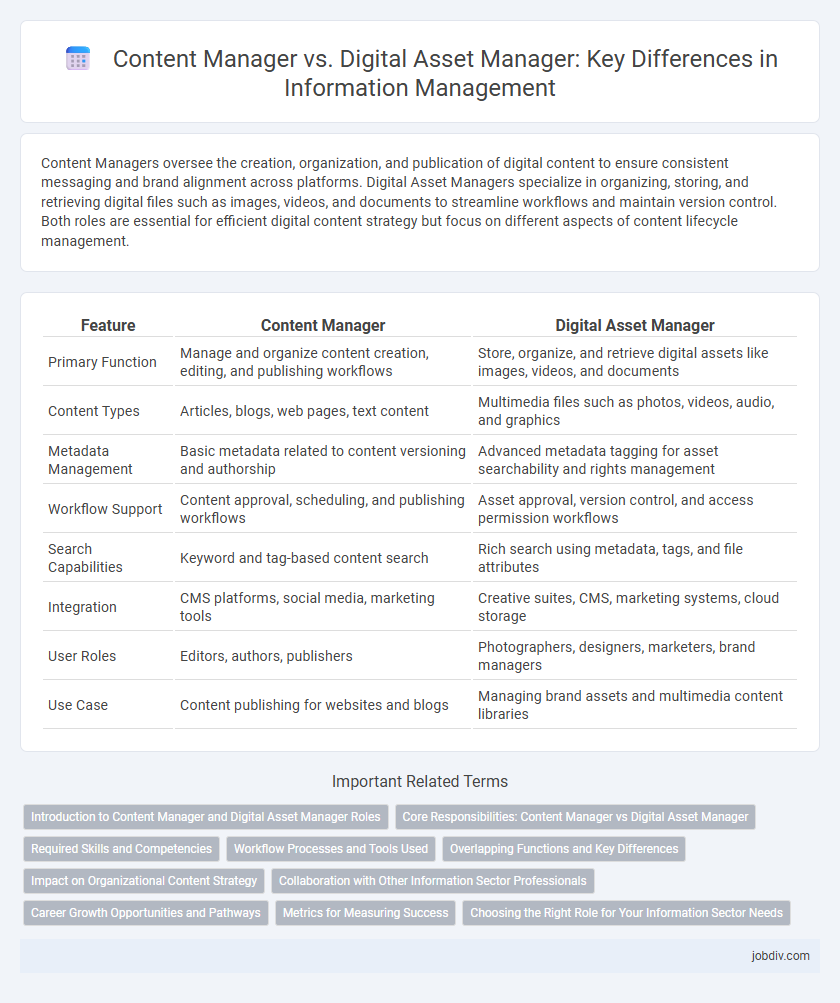
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Content Manager | Digital Asset Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manage and organize content creation, editing, and publishing workflows | Store, organize, and retrieve digital assets like images, videos, and documents |
| Content Types | Articles, blogs, web pages, text content | Multimedia files such as photos, videos, audio, and graphics |
| Metadata Management | Basic metadata related to content versioning and authorship | Advanced metadata tagging for asset searchability and rights management |
| Workflow Support | Content approval, scheduling, and publishing workflows | Asset approval, version control, and access permission workflows |
| Search Capabilities | Keyword and tag-based content search | Rich search using metadata, tags, and file attributes |
| Integration | CMS platforms, social media, marketing tools | Creative suites, CMS, marketing systems, cloud storage |
| User Roles | Editors, authors, publishers | Photographers, designers, marketers, brand managers |
| Use Case | Content publishing for websites and blogs | Managing brand assets and multimedia content libraries |
Introduction to Content Manager and Digital Asset Manager Roles
Content Managers oversee the creation, organization, and publication of digital content across various platforms, ensuring consistency and engagement with target audiences. Digital Asset Managers specialize in organizing, storing, and retrieving digital media assets such as images, videos, and documents to streamline workflow and maintain brand integrity. Both roles are essential for effective digital strategy but focus on distinct aspects of content lifecycle management.
Core Responsibilities: Content Manager vs Digital Asset Manager
Content Managers oversee the creation, editing, publishing, and strategy of digital content to ensure alignment with marketing goals and audience engagement. Digital Asset Managers specialize in organizing, storing, and managing digital files such as images, videos, and documents to provide easy retrieval and maintain brand consistency. Both roles enhance digital workflows but differ in focus: Content Managers prioritize content lifecycle management, while Digital Asset Managers emphasize asset organization and accessibility.
Required Skills and Competencies
Content Managers require strong editorial skills, proficiency in content strategy, and experience with CMS platforms like WordPress or Drupal. Digital Asset Managers need expertise in metadata standards, digital rights management, and familiarity with DAM systems such as Adobe Experience Manager or Bynder. Both roles demand project management skills and the ability to analyze user engagement metrics for optimizing digital content.
Workflow Processes and Tools Used
Content Managers optimize workflow processes by coordinating content creation, approval, and publishing through tools like CMS platforms such as WordPress or Drupal. Digital Asset Managers streamline asset organization, metadata tagging, and version control using specialized DAM systems like Adobe Experience Manager or Bynder. Both roles rely on integration capabilities with marketing automation and collaboration tools to enhance productivity and maintain consistent digital experiences.
Overlapping Functions and Key Differences
Content Managers and Digital Asset Managers both streamline digital workflows by organizing and distributing media assets, but their core functions differ significantly. Content Managers focus on content creation, editorial workflows, and publishing schedules, while Digital Asset Managers emphasize the storage, tagging, and retrieval of multimedia files such as images, videos, and audio. Overlapping functions include metadata management and version control, yet Content Managers prioritize content lifecycle management whereas Digital Asset Managers excel in asset preservation and rights management.
Impact on Organizational Content Strategy
Content managers focus on organizing, creating, and distributing textual and multimedia content to engage target audiences effectively. Digital asset managers specialize in storing, categorizing, and retrieving digital files such as images, videos, and documents, ensuring seamless access and brand consistency. Integrating both roles enhances organizational content strategy by optimizing workflow efficiency, improving content quality, and enabling cohesive brand messaging across platforms.
Collaboration with Other Information Sector Professionals
Content Managers streamline workflows by coordinating with marketers, editors, and SEO specialists to ensure cohesive messaging across platforms. Digital Asset Managers facilitate collaboration by centralizing multimedia resources, allowing designers, developers, and legal teams quick access to approved assets. Both roles require seamless integration with IT professionals to optimize content delivery and digital asset management systems.
Career Growth Opportunities and Pathways
Content Managers typically advance into roles such as Director of Content or Chief Content Officer, leveraging skills in strategy, SEO, and cross-platform storytelling. Digital Asset Managers often progress to positions like Digital Asset Management Lead or Chief Digital Officer, emphasizing expertise in metadata management, digital rights, and workflow optimization. Both career pathways offer growth through specialization and leadership within marketing, media, and IT sectors.
Metrics for Measuring Success
Content Manager success is typically measured by user engagement metrics such as page views, bounce rates, and content accuracy. Digital Asset Manager effectiveness is gauged through asset retrieval times, metadata completeness, and the frequency of asset reuse across campaigns. Both rely heavily on system performance and user satisfaction metrics to optimize content delivery and asset management workflows.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Information Sector Needs
Content Managers oversee the creation, organization, and publication of digital content, ensuring brand consistency and effective communication across platforms. Digital Asset Managers focus on storing, categorizing, and retrieving digital assets such as images, videos, and documents to optimize workflow and asset utilization. Selecting the right role depends on your organization's priority: content strategy and customer engagement favor Content Managers, while asset organization and efficient digital resource management require Digital Asset Managers.
Content Manager vs Digital Asset Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com