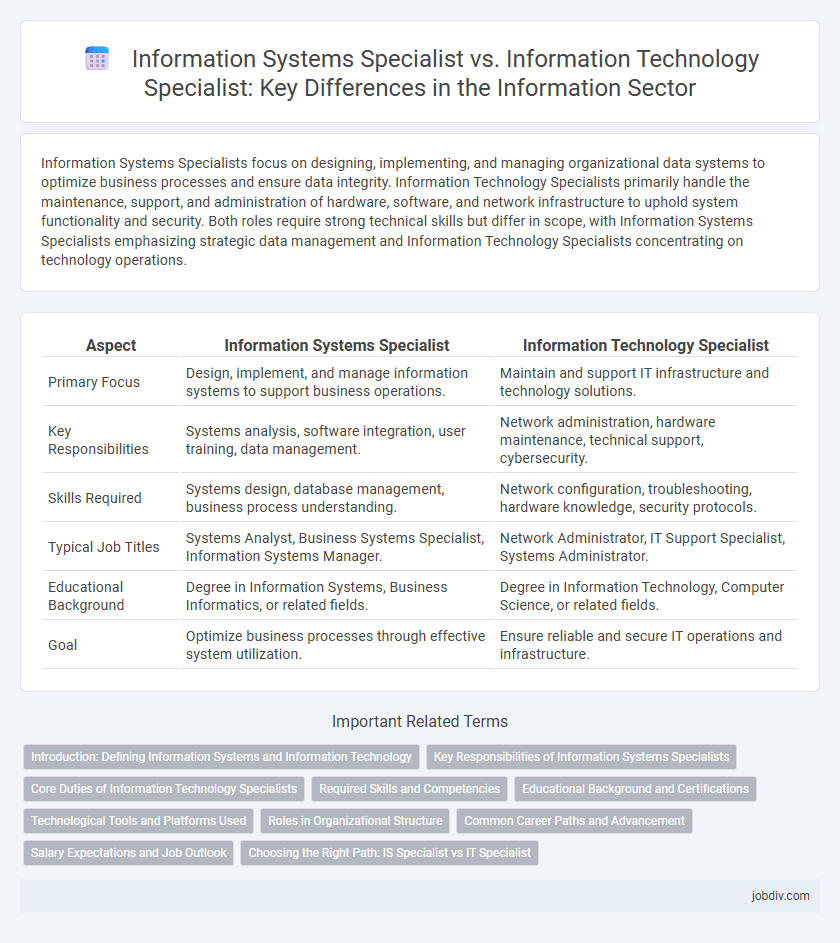
Information Systems Specialists focus on designing, implementing, and managing organizational data systems to optimize business processes and ensure data integrity. Information Technology Specialists primarily handle the maintenance, support, and administration of hardware, software, and network infrastructure to uphold system functionality and security. Both roles require strong technical skills but differ in scope, with Information Systems Specialists emphasizing strategic data management and Information Technology Specialists concentrating on technology operations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Information Systems Specialist | Information Technology Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Design, implement, and manage information systems to support business operations. | Maintain and support IT infrastructure and technology solutions. |
| Key Responsibilities | Systems analysis, software integration, user training, data management. | Network administration, hardware maintenance, technical support, cybersecurity. |
| Skills Required | Systems design, database management, business process understanding. | Network configuration, troubleshooting, hardware knowledge, security protocols. |
| Typical Job Titles | Systems Analyst, Business Systems Specialist, Information Systems Manager. | Network Administrator, IT Support Specialist, Systems Administrator. |
| Educational Background | Degree in Information Systems, Business Informatics, or related fields. | Degree in Information Technology, Computer Science, or related fields. |
| Goal | Optimize business processes through effective system utilization. | Ensure reliable and secure IT operations and infrastructure. |
Introduction: Defining Information Systems and Information Technology
Information Systems Specialists focus on the design, implementation, and management of systems that collect, process, and distribute data to support organizational goals. Information Technology Specialists specialize in the hardware, software, and networks that enable computing infrastructure and technology solutions. Both roles are essential in leveraging technology to improve business processes and information flow.
Key Responsibilities of Information Systems Specialists
Information Systems Specialists focus on managing and optimizing organizational data systems, ensuring seamless integration between software applications and user needs. Their key responsibilities include analyzing system requirements, designing custom solutions, maintaining databases, and providing user training to enhance system efficiency. They often collaborate with IT teams to troubleshoot issues, streamline workflows, and support business objectives through technology.
Core Duties of Information Technology Specialists
Information Technology Specialists primarily focus on managing and maintaining an organization's IT infrastructure, including hardware, software, and networks. Their core duties involve troubleshooting technical issues, implementing security measures, and ensuring system reliability to support business operations. They also configure servers, manage databases, and provide technical support to end-users, enhancing overall information technology performance.
Required Skills and Competencies
Information Systems Specialists require strong analytical skills, proficiency in database management, and expertise in systems analysis and design to optimize organizational workflows. Information Technology Specialists must demonstrate technical proficiency in network administration, cybersecurity, and hardware troubleshooting to ensure robust IT infrastructure. Both roles demand problem-solving abilities and knowledge of software applications, but Information Systems Specialists focus more on aligning technology solutions with business needs, while IT Specialists emphasize maintaining and supporting technology systems.
Educational Background and Certifications
An Information Systems Specialist typically holds a degree in Information Systems, Computer Science, or Business Administration, emphasizing system analysis, data management, and organizational technology integration. An Information Technology Specialist often has a background in Computer Science, Information Technology, or Network Administration, focusing on technical support, hardware, and software maintenance. Common certifications for Information Systems Specialists include Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) and Certified Information Systems Manager (CISM), while IT Specialists often pursue CompTIA A+, Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE), and Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certifications.
Technological Tools and Platforms Used
Information Systems Specialists primarily utilize enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, database management platforms like Oracle and SQL Server, and business intelligence tools such as Tableau or Power BI to optimize organizational workflows. In contrast, Information Technology Specialists focus on network infrastructure technologies, cybersecurity tools like firewalls and antivirus software, and system administration platforms including Windows Server and Linux distributions. Both roles require proficiency in cloud services such as AWS or Azure, but their core technological expertise targets distinct operational areas within IT environments.
Roles in Organizational Structure
Information Systems Specialists primarily focus on designing, implementing, and managing organizational data systems to support business operations and decision-making processes. Information Technology Specialists concentrate on maintaining and optimizing the technical infrastructure, including hardware, software, and networks, to ensure operational continuity and security. Both roles are critical in the organizational structure, with IS Specialists aligning technology solutions with strategic goals and IT Specialists providing the technical support necessary for system reliability.
Common Career Paths and Advancement
Information Systems Specialists often advance by focusing on roles such as systems analyst, database administrator, and enterprise architect, leveraging expertise in analyzing and optimizing organizational information flows. Information Technology Specialists typically pursue careers in network administration, cybersecurity, and IT project management, emphasizing technical infrastructure and security. Both career paths offer opportunities for progression into managerial positions, such as IT director or chief information officer, by developing a blend of technical knowledge and leadership skills.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Information Systems Specialists typically earn a median salary of around $88,000 annually, while Information Technology Specialists often have a slightly lower median salary near $75,000, reflecting differences in specialization and industry demand. The job outlook for both roles remains strong, with an expected growth rate of approximately 11% through 2031, driven by increasing reliance on digital infrastructure and cybersecurity needs. Organizations prioritize Information Systems Specialists for strategic system management, whereas Information Technology Specialists focus on technical support and infrastructure maintenance, influencing salary and employment opportunities.
Choosing the Right Path: IS Specialist vs IT Specialist
Information Systems Specialists focus on analyzing, designing, and managing organizational data systems to improve business processes and decision-making. Information Technology Specialists concentrate on implementing, maintaining, and supporting hardware, software, and network infrastructure to ensure operational efficiency. Choosing the right path depends on whether you prefer strategic system integration and business analysis (IS Specialist) or technical support and infrastructure management (IT Specialist).
Information Systems Specialist vs Information Technology Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com