Information Security Analysts focus on protecting an organization's data by identifying vulnerabilities, monitoring networks, and implementing security measures. Cybersecurity Specialists have a broader role that includes threat intelligence, incident response, and advanced defense strategies against cyber attacks. Both roles require strong knowledge of security protocols and continuous adaptation to evolving cyber threats.
Table of Comparison
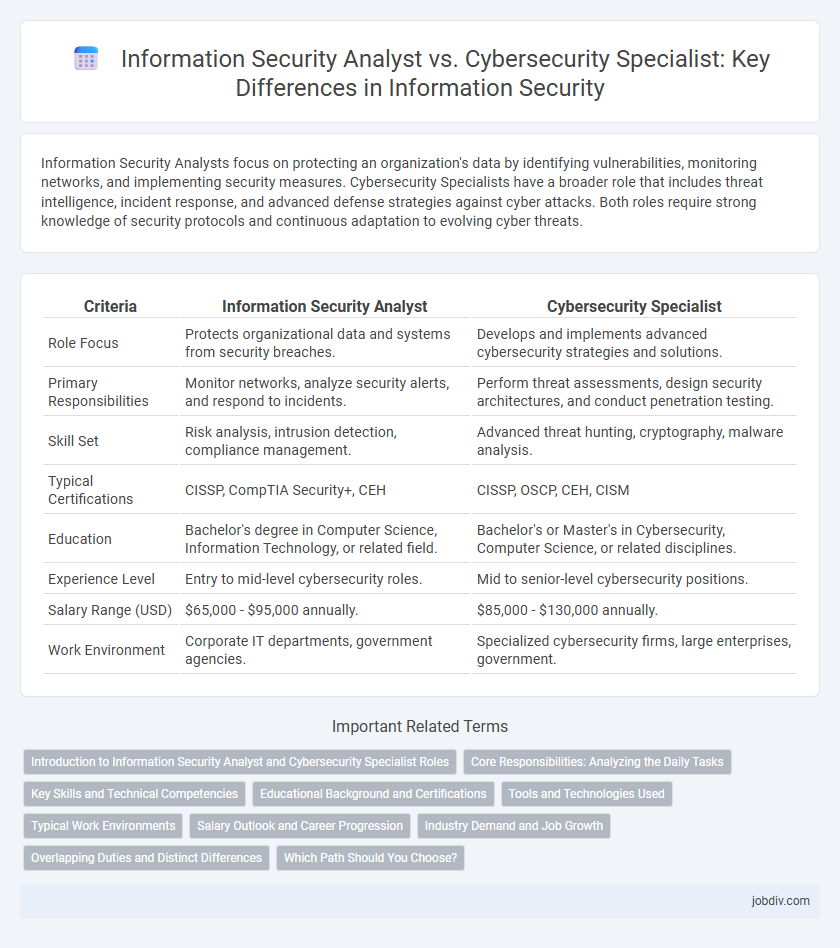
| Criteria | Information Security Analyst | Cybersecurity Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Protects organizational data and systems from security breaches. | Develops and implements advanced cybersecurity strategies and solutions. |
| Primary Responsibilities | Monitor networks, analyze security alerts, and respond to incidents. | Perform threat assessments, design security architectures, and conduct penetration testing. |
| Skill Set | Risk analysis, intrusion detection, compliance management. | Advanced threat hunting, cryptography, malware analysis. |
| Typical Certifications | CISSP, CompTIA Security+, CEH | CISSP, OSCP, CEH, CISM |
| Education | Bachelor's degree in Computer Science, Information Technology, or related field. | Bachelor's or Master's in Cybersecurity, Computer Science, or related disciplines. |
| Experience Level | Entry to mid-level cybersecurity roles. | Mid to senior-level cybersecurity positions. |
| Salary Range (USD) | $65,000 - $95,000 annually. | $85,000 - $130,000 annually. |
| Work Environment | Corporate IT departments, government agencies. | Specialized cybersecurity firms, large enterprises, government. |
Introduction to Information Security Analyst and Cybersecurity Specialist Roles
Information Security Analysts focus on protecting an organization's data by monitoring networks, managing security software, and responding to breaches to prevent unauthorized access. Cybersecurity Specialists design and implement advanced security systems, conduct vulnerability assessments, and develop strategies to safeguard complex infrastructure against cyber threats. Both roles collaborate to enhance organizational cybersecurity posture, emphasizing proactive risk management and incident response.
Core Responsibilities: Analyzing the Daily Tasks
Information Security Analysts focus on monitoring networks, identifying vulnerabilities, and implementing security measures to protect organizational data from cyber threats. Cybersecurity Specialists perform advanced threat analysis, develop security protocols, and manage incident response to mitigate complex cyber attacks. Both roles require continuous assessment of system defenses and collaboration with IT teams to ensure comprehensive protection of information assets.
Key Skills and Technical Competencies
Information Security Analysts excel in vulnerability assessment, risk management, and incident response, with strong skills in encryption, firewall management, and compliance frameworks such as NIST and ISO 27001. Cybersecurity Specialists possess advanced expertise in penetration testing, threat modeling, and malware analysis, along with proficiency in tools like SIEM, IDS/IPS, and advanced scripting languages. Both roles require a solid understanding of network security protocols, but Cybersecurity Specialists often engage more deeply with proactive threat hunting and advanced threat mitigation techniques.
Educational Background and Certifications
Information Security Analysts typically hold a bachelor's degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field, with certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) and CompTIA Security+ enhancing their credentials. Cybersecurity Specialists often possess similar academic qualifications but may also focus on specialized certifications like Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) and Cisco Certified CyberOps Associate to demonstrate expertise in threat detection and incident response. Both roles value continuous education in emerging security technologies and standards to maintain effective protection strategies.
Tools and Technologies Used
Information Security Analysts primarily use tools like intrusion detection systems (IDS), vulnerability assessment software, and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms to monitor network activity and protect organizational assets. Cybersecurity Specialists often leverage advanced technologies such as threat intelligence platforms, endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, and encryption software to proactively defend against sophisticated cyber threats. Both roles require expertise in firewall management, antivirus solutions, and incident response tools, but Cybersecurity Specialists tend to work more closely with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence-based security systems and penetration testing frameworks.
Typical Work Environments
Information Security Analysts typically work in corporate IT departments, government agencies, and financial institutions where they monitor and protect organizational data from potential breaches. Cybersecurity Specialists often operate in specialized security firms, consulting companies, and tech startups, focusing on proactive threat detection and incident response. Both roles require collaboration in secure, technology-driven environments prioritizing data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Salary Outlook and Career Progression
Information Security Analysts typically earn a median annual salary of around $103,590, with opportunities for advancement into managerial roles or specialized fields such as risk assessment. Cybersecurity Specialists, often commanding higher salaries averaging $110,000 to $120,000 annually, benefit from rapid career progression into positions like cybersecurity architect or chief information security officer (CISO). Both roles offer robust growth prospects driven by increasing cyber threats and expanding digital infrastructures.
Industry Demand and Job Growth
Information Security Analysts and Cybersecurity Specialists experience significant industry demand driven by increasing cyber threats and regulatory requirements. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 35% job growth for Information Security Analysts from 2021 to 2031, far exceeding average occupational growth rates. Demand in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and government fuels rapid expansion, with Cybersecurity Specialists often filling specialized roles in threat detection and incident response.
Overlapping Duties and Distinct Differences
Information Security Analysts and Cybersecurity Specialists both focus on protecting digital assets, yet Analysts primarily develop and enforce security policies, conduct risk assessments, and monitor systems for vulnerabilities. Cybersecurity Specialists emphasize hands-on defense tactics, including intrusion detection, malware analysis, and incident response. Despite overlaps in threat prevention, Analysts take a strategic, policy-driven approach, whereas Specialists concentrate on tactical technical operations.
Which Path Should You Choose?
Choosing between an Information Security Analyst and a Cybersecurity Specialist depends on your career goals and skill set, as both roles focus on protecting digital assets but differ in scope and methods. Information Security Analysts emphasize monitoring and analyzing security measures to prevent data breaches, while Cybersecurity Specialists often engage in proactive threat hunting and incident response to combat cyberattacks. Evaluating your preference for strategic oversight versus hands-on technical defense will help determine the optimal path in the evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Information Security Analyst vs Cybersecurity Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com