Information engineers specialize in designing and managing data architectures, ensuring efficient information flow and storage across systems. Systems engineers focus on integrating complex hardware and software components to create cohesive, reliable operational systems. Both roles require interdisciplinary knowledge but differ in their primary emphasis on data versus overall system functionality.
Table of Comparison
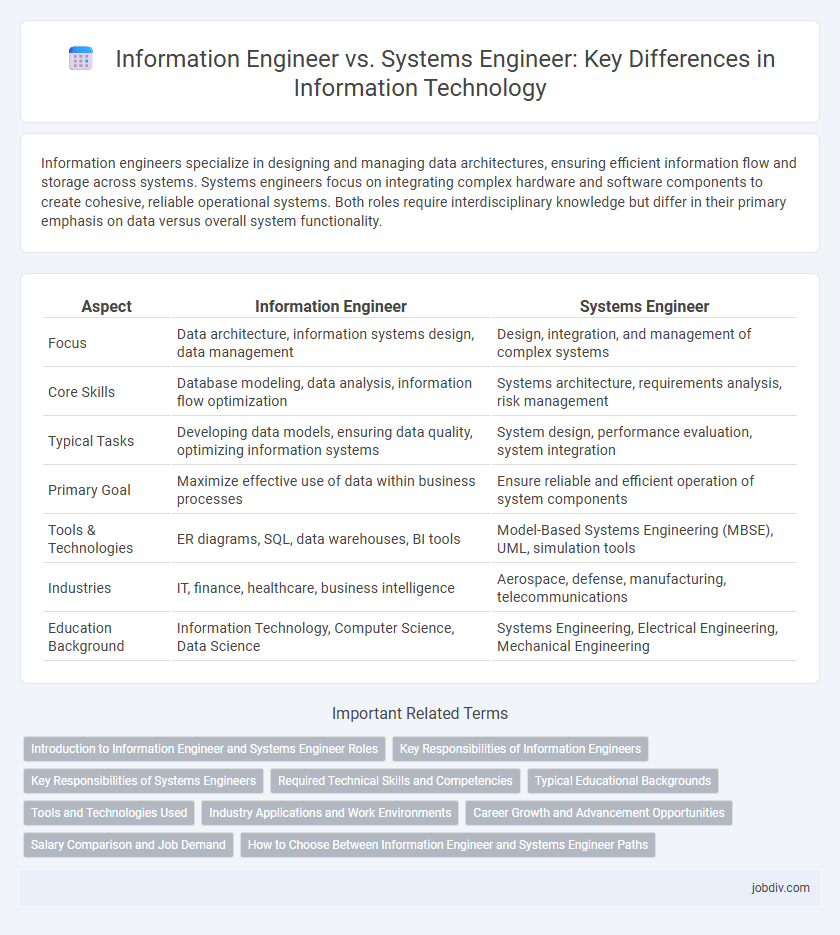
| Aspect | Information Engineer | Systems Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Data architecture, information systems design, data management | Design, integration, and management of complex systems |
| Core Skills | Database modeling, data analysis, information flow optimization | Systems architecture, requirements analysis, risk management |
| Typical Tasks | Developing data models, ensuring data quality, optimizing information systems | System design, performance evaluation, system integration |
| Primary Goal | Maximize effective use of data within business processes | Ensure reliable and efficient operation of system components |
| Tools & Technologies | ER diagrams, SQL, data warehouses, BI tools | Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE), UML, simulation tools |
| Industries | IT, finance, healthcare, business intelligence | Aerospace, defense, manufacturing, telecommunications |
| Education Background | Information Technology, Computer Science, Data Science | Systems Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Mechanical Engineering |
Introduction to Information Engineer and Systems Engineer Roles
Information engineers design, manage, and optimize data systems to ensure efficient information flow and accuracy across organizational platforms. Systems engineers focus on the integration, development, and maintenance of complex systems, ensuring all components function cohesively within operational environments. Both roles require expertise in system architecture, but information engineers prioritize data management while systems engineers emphasize overall system performance and reliability.
Key Responsibilities of Information Engineers
Information Engineers specialize in designing and managing data architectures, focusing on data modeling, database integration, and optimizing information flow within organizations. They develop systems that ensure accurate data collection, storage, and retrieval to support decision-making processes. Their key responsibilities include creating information systems frameworks, aligning data strategies with business goals, and enhancing data quality and accessibility.
Key Responsibilities of Systems Engineers
Systems Engineers focus on designing, integrating, and managing complex systems throughout their life cycles, ensuring all components work seamlessly together. They develop system architectures, conduct risk analyses, and coordinate multidisciplinary teams to optimize performance and reliability. Their responsibilities also include system testing, validation, and maintenance to meet operational requirements and support long-term sustainability.
Required Technical Skills and Competencies
Information engineers require strong expertise in data modeling, database design, and software development, emphasizing proficiency in programming languages such as SQL, Python, and Java. Systems engineers focus on systems integration, network architecture, and project management, with competencies in system lifecycle processes, configuration management, and tools like MATLAB and SysML. Both roles demand analytical problem-solving skills and familiarity with cybersecurity principles to design robust, scalable solutions.
Typical Educational Backgrounds
Information Engineers typically hold degrees in information technology, computer science, or information systems, emphasizing data management, software development, and network design. Systems Engineers often graduate with backgrounds in systems engineering, electrical engineering, or industrial engineering, focusing on system integration, optimization, and lifecycle management. Both roles require strong analytical and technical skills but differ in their core educational focus on data versus system architecture.
Tools and Technologies Used
Information engineers utilize data modeling tools, database management systems, and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) technologies to design and manage information flow within organizations. Systems engineers employ system simulation software, requirements management tools, and integration platforms to develop and maintain complex engineering systems. Both roles rely on programming languages like Python and Java, but information engineers emphasize data-centric technologies while systems engineers focus more on system architecture and interoperability solutions.
Industry Applications and Work Environments
Information engineers specialize in designing and managing data systems that optimize information flow across industries such as telecommunications, finance, and healthcare. Systems engineers focus on integrating complex systems and ensuring operational efficiency in sectors like aerospace, manufacturing, and defense. Both roles collaborate in environments ranging from corporate IT departments to large-scale industrial automation projects, emphasizing cross-disciplinary problem solving and technological innovation.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Information Engineers often specialize in data management, analytics, and information systems design, positioning them for advanced roles in data architecture and business intelligence leadership. Systems Engineers focus on integrating complex systems and managing infrastructure, which can lead to senior roles in systems design, project management, and enterprise architecture. Both careers offer robust advancement opportunities, but Information Engineers tend to advance in domains centered on data strategy and innovation, while Systems Engineers progress toward overseeing large-scale system implementations and operational efficiencies.
Salary Comparison and Job Demand
Information engineers typically earn salaries ranging from $70,000 to $110,000 annually, while systems engineers command slightly higher pay, often between $80,000 and $120,000 depending on experience and location. Job demand for systems engineers is growing by 7% annually due to increased reliance on integrated technology solutions, whereas information engineers see steady demand with a 5% growth linked to data management and analytics. Both roles require strong technical skills, but systems engineers tend to have broader responsibilities involving system design and integration, influencing their higher salary and demand.
How to Choose Between Information Engineer and Systems Engineer Paths
Choosing between Information Engineer and Systems Engineer paths depends on your focus: Information Engineers specialize in data architecture, management, and analytics, while Systems Engineers emphasize designing, integrating, and maintaining complex systems and infrastructure. Consider your skill set and career goals--Information Engineering suits those passionate about data flow optimization and database systems, whereas Systems Engineering aligns with interests in hardware-software integration and process engineering. Evaluate job market demand, required certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) for systems or Certified Information Engineer (CIE) credentials, and industry sectors like IT services, telecommunications, or software development to make an informed decision.
Information Engineer vs Systems Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com