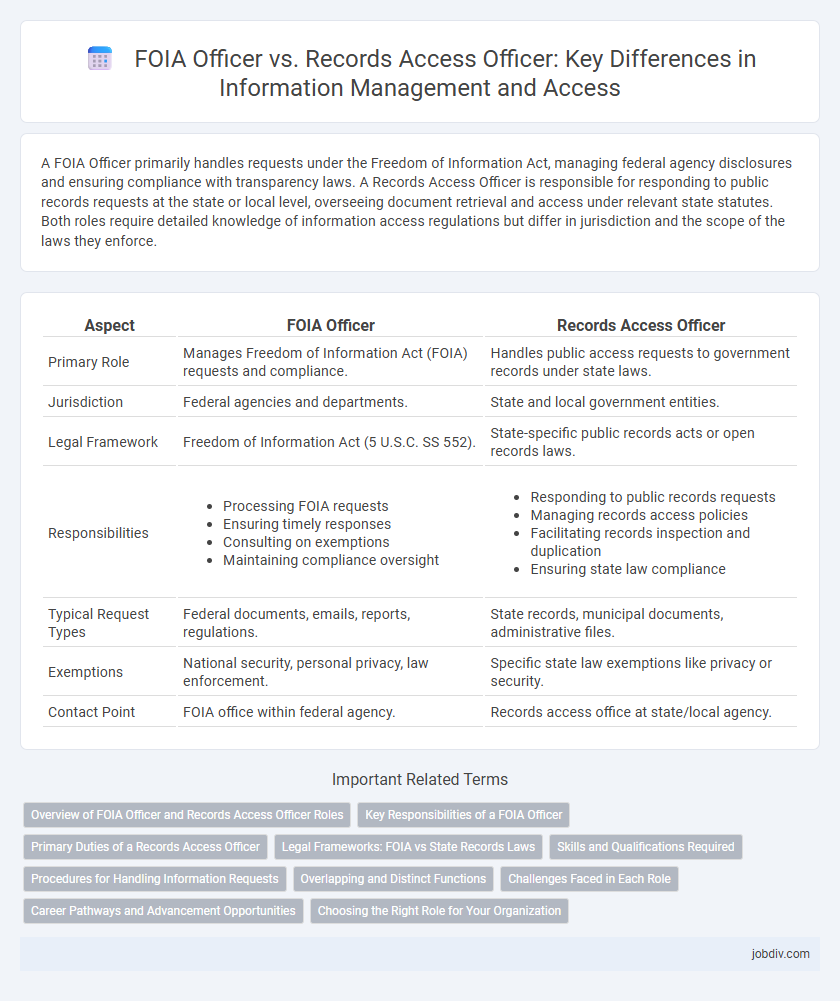
A FOIA Officer primarily handles requests under the Freedom of Information Act, managing federal agency disclosures and ensuring compliance with transparency laws. A Records Access Officer is responsible for responding to public records requests at the state or local level, overseeing document retrieval and access under relevant state statutes. Both roles require detailed knowledge of information access regulations but differ in jurisdiction and the scope of the laws they enforce.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | FOIA Officer | Records Access Officer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manages Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) requests and compliance. | Handles public access requests to government records under state laws. |
| Jurisdiction | Federal agencies and departments. | State and local government entities. |
| Legal Framework | Freedom of Information Act (5 U.S.C. SS 552). | State-specific public records acts or open records laws. |
| Responsibilities |
|
|
| Typical Request Types | Federal documents, emails, reports, regulations. | State records, municipal documents, administrative files. |
| Exemptions | National security, personal privacy, law enforcement. | Specific state law exemptions like privacy or security. |
| Contact Point | FOIA office within federal agency. | Records access office at state/local agency. |
Overview of FOIA Officer and Records Access Officer Roles
FOIA Officers are responsible for processing Freedom of Information Act requests, ensuring compliance with federal regulations by reviewing documents for release, and coordinating with agency departments to respond accurately and timely. Records Access Officers handle state and local public records requests, manage document retention policies, and oversee the accessibility and confidentiality of records within their jurisdiction. Both roles require knowledge of transparency laws, but FOIA Officers focus on federal information disclosure while Records Access Officers deal with broader public records management.
Key Responsibilities of a FOIA Officer
FOIA Officers manage Freedom of Information Act requests by coordinating document searches, reviewing records for sensitive information, and ensuring timely responses in compliance with legal standards. They serve as the primary liaison between the public and federal agencies, facilitating transparency and accountability. FOIA Officers also train staff on FOIA procedures and maintain records of all requests and disclosures.
Primary Duties of a Records Access Officer
Records Access Officers (RAOs) primarily manage public access requests for agency records under the Freedom of Information Act (FOIA), ensuring compliance with statutory timelines and proper classification of documents. RAOs coordinate the retrieval, review, and release of records while maintaining privacy and exemption protocols to protect sensitive information. Their duties also include tracking request status, responding to public inquiries, and providing guidance on information disclosure policies within the agency.
Legal Frameworks: FOIA vs State Records Laws
FOIA Officers operate under the federal Freedom of Information Act, guiding access to federal agency records with a legal framework emphasizing transparency and public right to information. Records Access Officers enforce state-specific records laws, which vary widely and dictate how state and local government documents are managed, disclosed, and preserved. These roles differ legally as FOIA has uniform federal standards, while state records laws reflect diverse statutory requirements, affecting the scope and limitations of public records access.
Skills and Qualifications Required
FOIA Officers require expertise in federal transparency laws, strong analytical skills to interpret requests, and experience in government compliance and recordkeeping. Records Access Officers are skilled in managing public records, possess detailed knowledge of local and state record retention policies, and excel in organizing and retrieving document archives efficiently. Both roles benefit from excellent communication abilities, attention to detail, and proficiency with information management systems.
Procedures for Handling Information Requests
FOIA Officers handle Freedom of Information Act requests by processing, reviewing, and responding to public inquiries in compliance with federal regulations. Records Access Officers manage the retrieval and disclosure of agency records, ensuring timely and accurate fulfillment of information requests under applicable state or organizational policies. Both roles implement structured procedures to verify request validity, redact sensitive data, and maintain proper documentation throughout the information access process.
Overlapping and Distinct Functions
FOIA Officers primarily manage Freedom of Information Act requests, ensuring compliance with federal transparency laws and processing public inquiries for government-held information. Records Access Officers focus on facilitating public access to official records, maintaining records management systems, and enforcing policies related to record retention and release. Both roles overlap in handling requests for information, but FOIA Officers specialize in statutory regulations for disclosure, while Records Access Officers emphasize administrating and preserving records integrity.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
FOIA Officers face challenges in managing timely responses to Freedom of Information Act requests while ensuring compliance with privacy laws and handling high volumes of sensitive information. Records Access Officers must navigate complex record-keeping systems and maintain data accuracy, often contending with inconsistent classification standards and evolving regulations. Both roles require balancing transparency with legal constraints, but FOIA Officers primarily focus on information release processes, whereas Records Access Officers prioritize secure data access and preservation.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
FOIA Officers specialize in managing Freedom of Information Act requests, ensuring legal compliance and timely responses, which often leads to roles in government transparency and compliance management. Records Access Officers focus on the systematic organization, retrieval, and protection of public records, providing a pathway to careers in records management and archival administration. Advancement opportunities for FOIA Officers typically involve senior government positions or legal advisory roles, while Records Access Officers can progress into information governance or data management leadership.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Organization
Selecting the appropriate role between a FOIA Officer and a Records Access Officer depends on the organization's specific needs for handling public information requests and managing records compliance. A FOIA Officer primarily manages Freedom of Information Act requests, ensuring transparency and timely disclosure of government-held data. In contrast, a Records Access Officer focuses on maintaining and providing access to organizational records, emphasizing internal recordkeeping accuracy and regulatory adherence.
FOIA Officer vs Records Access Officer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com