Information Security Analysts concentrate on protecting organizational data from cyber threats by implementing security measures, monitoring systems, and responding to breaches. Information Privacy Analysts focus on ensuring compliance with privacy laws and regulations, managing data usage policies, and safeguarding personal information from unauthorized access. Both roles play complementary parts in maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information within an organization.
Table of Comparison
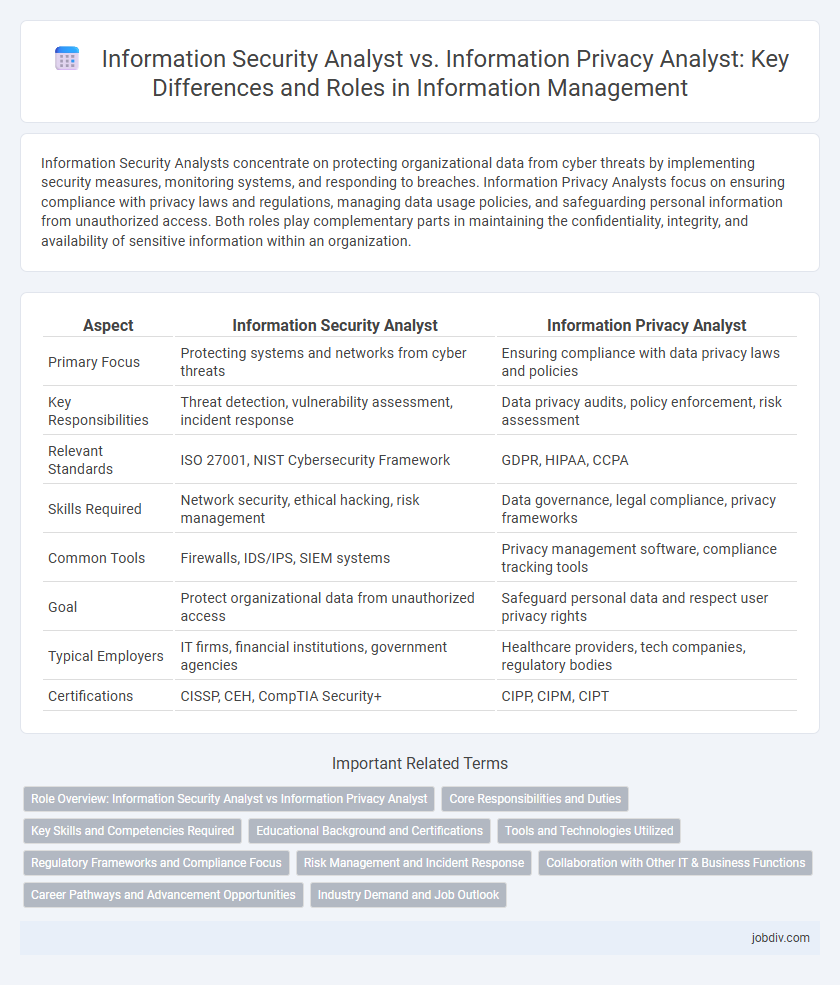
| Aspect | Information Security Analyst | Information Privacy Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Protecting systems and networks from cyber threats | Ensuring compliance with data privacy laws and policies |
| Key Responsibilities | Threat detection, vulnerability assessment, incident response | Data privacy audits, policy enforcement, risk assessment |
| Relevant Standards | ISO 27001, NIST Cybersecurity Framework | GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA |
| Skills Required | Network security, ethical hacking, risk management | Data governance, legal compliance, privacy frameworks |
| Common Tools | Firewalls, IDS/IPS, SIEM systems | Privacy management software, compliance tracking tools |
| Goal | Protect organizational data from unauthorized access | Safeguard personal data and respect user privacy rights |
| Typical Employers | IT firms, financial institutions, government agencies | Healthcare providers, tech companies, regulatory bodies |
| Certifications | CISSP, CEH, CompTIA Security+ | CIPP, CIPM, CIPT |
Role Overview: Information Security Analyst vs Information Privacy Analyst
Information Security Analysts focus on protecting an organization's computer systems and networks from cyber threats by implementing and monitoring security measures such as firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems. Information Privacy Analysts ensure compliance with data privacy regulations by managing personal and sensitive information, developing privacy policies, and conducting risk assessments related to data handling. Both roles require a strong understanding of regulatory frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA, but Security Analysts emphasize technical defense mechanisms while Privacy Analysts specialize in legal compliance and data governance.
Core Responsibilities and Duties
Information Security Analysts focus on protecting an organization's computer systems and networks from cyber threats through risk assessment, threat monitoring, and implementation of security measures. Information Privacy Analysts concentrate on ensuring compliance with data protection laws, managing personal data policies, conducting privacy impact assessments, and safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access. Both roles require expertise in identifying vulnerabilities, but Information Security emphasizes technical defenses while Information Privacy prioritizes regulatory adherence and data confidentiality.
Key Skills and Competencies Required
Information Security Analysts require expertise in risk assessment, intrusion detection, and cybersecurity frameworks like NIST and ISO 27001, emphasizing technical skills such as network security, encryption, and incident response. Information Privacy Analysts focus on data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA, with competencies in privacy impact assessments, compliance audits, and knowledge of legal and ethical standards surrounding personal data. Both roles demand strong analytical abilities, attention to detail, and proficiency in communication to effectively manage and safeguard organizational information assets.
Educational Background and Certifications
Information Security Analysts typically hold degrees in computer science, cybersecurity, or information technology, complemented by certifications such as CISSP, CISM, or CompTIA Security+. Information Privacy Analysts often possess educational backgrounds in law, information management, or data governance, with certifications like CIPP, CIPM, or CIPT emphasizing privacy frameworks and regulatory compliance. Both roles demand specialized knowledge, but Security Analysts focus on protecting digital assets, while Privacy Analysts ensure adherence to data privacy laws and policies.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
Information Security Analysts primarily utilize tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), encryption software, and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms to protect organizational data from cyber threats. In contrast, Information Privacy Analysts focus on technologies such as data loss prevention (DLP) software, privacy compliance management tools, and consent management platforms to ensure personal data is handled according to privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA. Both roles leverage risk assessment tools and audit technologies but apply them differently to secure information integrity versus ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance Focus
Information Security Analysts concentrate on implementing and monitoring cybersecurity measures aligned with regulatory frameworks such as NIST, ISO 27001, and GDPR to ensure data protection and compliance. Information Privacy Analysts emphasize compliance with privacy-specific regulations, including CCPA, HIPAA, and GDPR, focusing on data subject rights and privacy impact assessments. Both roles require thorough knowledge of legal requirements but differ in prioritizing cybersecurity controls versus privacy policies and data governance.
Risk Management and Incident Response
Information Security Analysts focus on risk management by identifying vulnerabilities and implementing controls to protect organizational assets from cyber threats. Information Privacy Analysts specialize in mitigating risks related to data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws such as GDPR and HIPAA to prevent data breaches. Both roles are critical in incident response, with Security Analysts handling technical containment and recovery, while Privacy Analysts manage legal notifications and stakeholder communication.
Collaboration with Other IT & Business Functions
Information Security Analysts collaborate closely with IT teams, risk management, and compliance departments to safeguard systems against cyber threats and ensure regulatory adherence. Information Privacy Analysts work alongside legal, compliance, and data governance units to implement privacy policies, manage data protection frameworks, and oversee user consent practices. Both roles require strong coordination with business stakeholders to align security and privacy strategies with organizational objectives and regulatory requirements.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Information Security Analysts focus on protecting organizational data through risk assessment, threat mitigation, and compliance with cybersecurity standards, often advancing towards roles like cybersecurity manager or chief information security officer (CISO). Information Privacy Analysts specialize in managing data privacy policies, ensuring regulatory compliance such as GDPR or CCPA, and typically progress into positions such as privacy officer or data protection officer (DPO). Both career pathways offer growth opportunities in increasingly specialized fields driven by the expanding importance of data protection and privacy laws.
Industry Demand and Job Outlook
Information Security Analysts are experiencing high industry demand due to the increasing frequency of cyberattacks, with job growth projected at 35% through 2031 according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Information Privacy Analysts also see robust demand, driven by stricter data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA, with employment expected to grow about 15% over the same period. Organizations across finance, healthcare, and technology sectors prioritize these roles to safeguard sensitive data and ensure regulatory compliance.
Information Security Analyst vs Information Privacy Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com