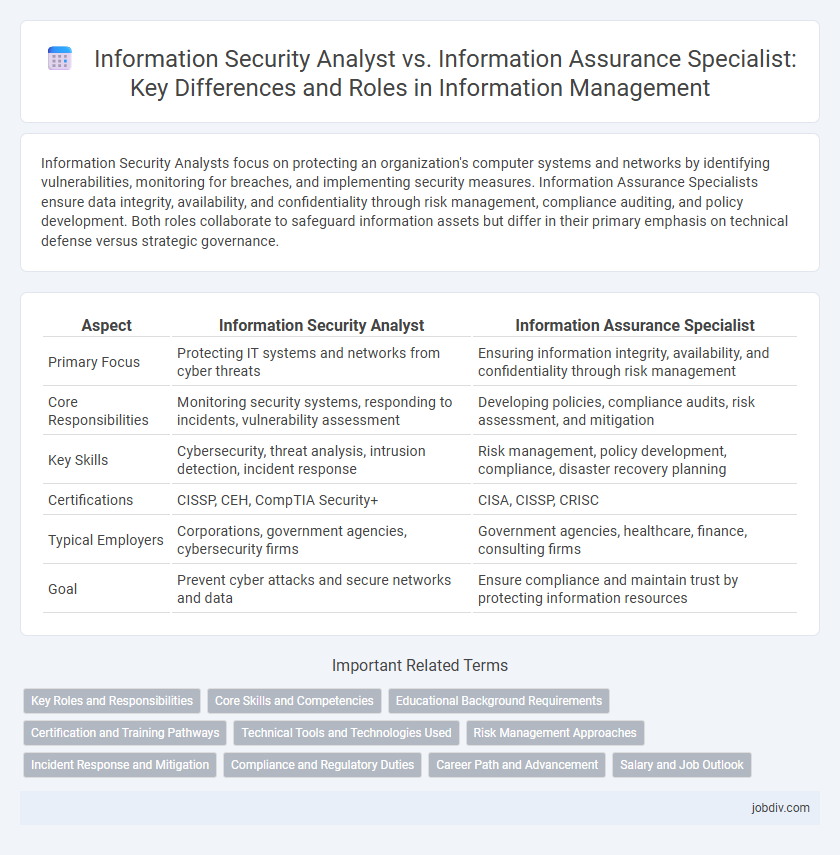
Information Security Analysts focus on protecting an organization's computer systems and networks by identifying vulnerabilities, monitoring for breaches, and implementing security measures. Information Assurance Specialists ensure data integrity, availability, and confidentiality through risk management, compliance auditing, and policy development. Both roles collaborate to safeguard information assets but differ in their primary emphasis on technical defense versus strategic governance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Information Security Analyst | Information Assurance Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Protecting IT systems and networks from cyber threats | Ensuring information integrity, availability, and confidentiality through risk management |
| Core Responsibilities | Monitoring security systems, responding to incidents, vulnerability assessment | Developing policies, compliance audits, risk assessment, and mitigation |
| Key Skills | Cybersecurity, threat analysis, intrusion detection, incident response | Risk management, policy development, compliance, disaster recovery planning |
| Certifications | CISSP, CEH, CompTIA Security+ | CISA, CISSP, CRISC |
| Typical Employers | Corporations, government agencies, cybersecurity firms | Government agencies, healthcare, finance, consulting firms |
| Goal | Prevent cyber attacks and secure networks and data | Ensure compliance and maintain trust by protecting information resources |
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Information Security Analysts focus on protecting an organization's computer systems and networks by identifying vulnerabilities, implementing security measures, and monitoring for breaches. Information Assurance Specialists ensure the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of data by developing and enforcing policies, managing risk assessments, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Both roles collaborate to safeguard information assets but differ in emphasis, with Analysts concentrating on technical defenses and Assurance Specialists prioritizing governance and risk management.
Core Skills and Competencies
Information Security Analysts specialize in threat detection, risk assessment, and incident response, emphasizing technical skills such as cybersecurity protocols, vulnerability management, and security architecture. Information Assurance Specialists focus on policy development, compliance, and risk management frameworks like NIST, ISO 27001, and governance, requiring expertise in audit processes and regulatory standards. Both roles demand strong analytical abilities, attention to detail, and knowledge of encryption, but Information Security Analysts lean more towards hands-on technical defense, while Information Assurance Specialists prioritize strategic oversight and assurance of information integrity.
Educational Background Requirements
Information Security Analysts typically require a bachelor's degree in computer science, information technology, or cybersecurity, with a strong emphasis on technical skills such as threat analysis and risk management. Information Assurance Specialists often pursue degrees in information assurance, cybersecurity policy, or management, focusing on governance, compliance, and risk assessment frameworks. Both roles benefit from certifications like CISSP or CISA, but Information Assurance Specialists may prioritize knowledge in audit and regulatory standards more heavily.
Certification and Training Pathways
Information Security Analysts often pursue certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), and CompTIA Security+ to validate expertise in threat detection, risk management, and incident response. Information Assurance Specialists typically focus on certifications like Certified Information Assurance Manager (CIAM), Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), and Certified Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) that emphasize risk assessment, compliance, and governance. Training pathways for both roles include hands-on labs, industry-specific workshops, and continuing education programs designed to keep pace with evolving cybersecurity standards and regulatory requirements.
Technical Tools and Technologies Used
Information Security Analysts utilize advanced tools such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), security information and event management (SIEM) platforms, and endpoint protection solutions to monitor and defend networks. Information Assurance Specialists focus on risk management frameworks, compliance software, and data encryption technologies to ensure information integrity and regulatory adherence. Both roles leverage vulnerability assessment tools and firewall configurations, but analysts emphasize real-time threat mitigation while assurance specialists prioritize policy enforcement and system audits.
Risk Management Approaches
Information Security Analysts focus on identifying vulnerabilities and implementing technical controls to prevent data breaches, often utilizing frameworks like NIST SP 800-53 for risk mitigation. Information Assurance Specialists adopt a broader risk management approach by ensuring policy compliance, conducting audits, and integrating business continuity planning to safeguard information integrity and availability. Both roles emphasize risk assessment but differ in scope, with analysts concentrating on operational defenses and specialists overseeing strategic risk governance.
Incident Response and Mitigation
Information Security Analysts specialize in incident response by identifying, analyzing, and mitigating cyber threats and breaches to protect organizational data. Information Assurance Specialists focus on ensuring the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of information through risk management, compliance, and system controls, playing a proactive role in preventing incidents. Both roles collaborate closely to develop and implement incident mitigation strategies that minimize damage and restore normal operations efficiently.
Compliance and Regulatory Duties
Information Security Analysts focus on implementing security measures to protect systems and ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS by monitoring and analyzing security incidents. Information Assurance Specialists concentrate on developing and enforcing policies and frameworks to maintain regulatory compliance, risk management, and data integrity across the organization. Both roles require deep knowledge of standards like NIST, ISO 27001, and SOX to ensure robust information protection and regulatory adherence.
Career Path and Advancement
Information Security Analysts typically advance by acquiring certifications such as CISSP or CISM and gaining expertise in threat detection, risk management, and incident response. Information Assurance Specialists progress by mastering compliance frameworks like NIST and ISO 27001, focusing on policy development and risk assessment to ensure organizational data integrity. Both career paths offer growth into senior roles such as Security Manager, Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), or Risk Manager, emphasizing different aspects of cybersecurity governance and technical security management.
Salary and Job Outlook
Information Security Analysts earn a median annual salary of approximately $103,590, with a projected job growth rate of 35% through 2031, reflecting high demand due to increasing cyber threats. Information Assurance Specialists typically command salaries ranging from $75,000 to $120,000, depending on experience and certification, with steady employment growth driven by the need for compliance and risk management. Both professions offer strong job security and competitive pay, but Information Security Analysts generally experience faster employment growth and higher average salaries.
Information Security Analyst vs Information Assurance Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com