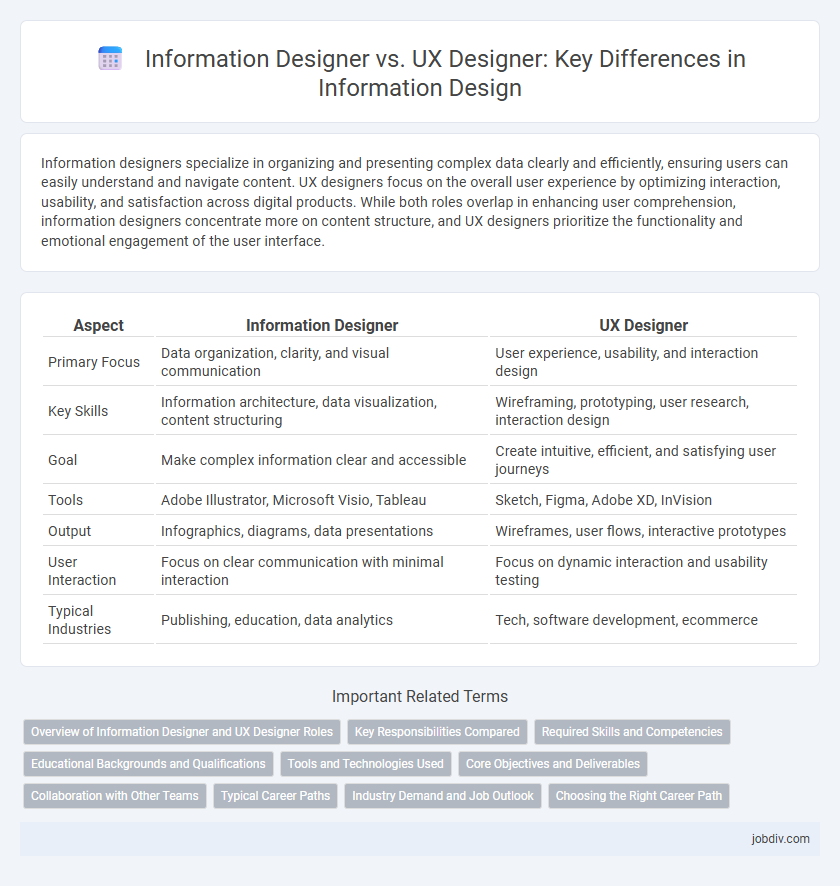
Information designers specialize in organizing and presenting complex data clearly and efficiently, ensuring users can easily understand and navigate content. UX designers focus on the overall user experience by optimizing interaction, usability, and satisfaction across digital products. While both roles overlap in enhancing user comprehension, information designers concentrate more on content structure, and UX designers prioritize the functionality and emotional engagement of the user interface.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Information Designer | UX Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Data organization, clarity, and visual communication | User experience, usability, and interaction design |
| Key Skills | Information architecture, data visualization, content structuring | Wireframing, prototyping, user research, interaction design |
| Goal | Make complex information clear and accessible | Create intuitive, efficient, and satisfying user journeys |
| Tools | Adobe Illustrator, Microsoft Visio, Tableau | Sketch, Figma, Adobe XD, InVision |
| Output | Infographics, diagrams, data presentations | Wireframes, user flows, interactive prototypes |
| User Interaction | Focus on clear communication with minimal interaction | Focus on dynamic interaction and usability testing |
| Typical Industries | Publishing, education, data analytics | Tech, software development, ecommerce |
Overview of Information Designer and UX Designer Roles
Information Designers specialize in organizing and structuring content to ensure clarity, usability, and effective communication of data. UX Designers focus on creating intuitive and engaging user experiences by addressing user needs, behaviors, and interactions across digital platforms. Both roles involve user-centered design principles, but Information Designers prioritize content hierarchy while UX Designers emphasize overall usability and interface design.
Key Responsibilities Compared
Information Designers specialize in organizing and structuring content to enhance clarity and accessibility, focusing primarily on information architecture, data visualization, and content strategy. UX Designers concentrate on user experience, emphasizing interaction design, usability testing, and user research to create intuitive and engaging digital interfaces. Both roles require collaboration with cross-functional teams but differ in their core objectives: Information Designers optimize content delivery, while UX Designers improve overall user interaction.
Required Skills and Competencies
Information Designers excel in data visualization, content strategy, and taxonomy development, ensuring information is structured for clarity and accessibility. UX Designers prioritize user research, interaction design, and usability testing to create seamless and intuitive digital experiences. Both roles demand proficiency in design tools, analytical thinking, and a deep understanding of user behavior and cognitive processes.
Educational Backgrounds and Qualifications
Information Designers typically hold degrees in graphic design, communication, or information science, emphasizing data visualization and information architecture skills. UX Designers often possess backgrounds in human-computer interaction, psychology, or computer science, focusing on user research, interaction design, and usability testing. Both roles benefit from certifications in design tools and methodologies, but UX Designers generally require stronger knowledge of user-centered design principles and prototyping techniques.
Tools and Technologies Used
Information Designers utilize tools such as Adobe Illustrator, Microsoft Visio, and Tableau to create clear visualizations and data representations, focusing on information structure and clarity. UX Designers rely heavily on software like Sketch, Figma, Adobe XD, and InVision to design interactive user interfaces, prototype workflows, and conduct usability testing. Both roles integrate analytics platforms and user research tools, but UX Designers emphasize tools that support user experience optimization and iterative design processes.
Core Objectives and Deliverables
Information Designers focus on structuring and presenting data clearly through content hierarchy, visual organization, and effective communication strategies to enhance information accessibility. UX Designers prioritize optimizing user interactions and experiences by conducting user research, creating personas, wireframes, and prototypes to ensure intuitive and satisfying product usability. Both roles deliver actionable insights, but Information Designers emphasize clarity and content flow, while UX Designers concentrate on user behavior and interface functionality.
Collaboration with Other Teams
Information Designers and UX Designers collaborate closely with product managers, developers, and marketing teams to ensure cohesive user experiences. Information Designers focus on structuring content and data visualization, while UX Designers prioritize interaction flows and usability testing. Effective teamwork between these roles enhances design consistency and aligns user needs with business goals.
Typical Career Paths
Information Designers often start their careers in graphic design, content strategy, or technical writing before specializing in structuring data and visual communication. UX Designers typically progress from roles in interaction design, psychology, or product management, focusing on user research and interface optimization. Both paths emphasize cross-disciplinary skills, but Information Designers lean more toward data presentation while UX Designers prioritize user experience and usability testing.
Industry Demand and Job Outlook
Information Designers and UX Designers both play crucial roles in tech and design industries, but the demand for UX Designers is experiencing faster growth due to the increasing emphasis on user-centered digital experiences. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, UX Design jobs are projected to grow by 13% through 2031, reflecting strong industry demand driven by e-commerce and app development. Information Designers remain essential in organizing complex data and improving communication, but their job growth is more moderate, often linked to specialized sectors like education and publishing.
Choosing the Right Career Path
Information Designers specialize in organizing and presenting data clearly, ensuring users understand complex content through visual hierarchy and structure. UX Designers focus on enhancing user experience by optimizing usability, interaction, and accessibility across digital products. Choosing the right career path depends on your passion for data visualization versus user-centered design and whether you prefer working with information architecture or interactive interface development.
Information Designer vs UX Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com