Information Security Analysts specialize in protecting an organization's data and systems from cyber threats by monitoring security measures, identifying vulnerabilities, and responding to breaches. Information Systems Analysts focus on improving business processes through the analysis, design, and implementation of information systems to enhance organizational efficiency and productivity. Both roles require strong technical skills, but the former emphasizes cybersecurity, while the latter prioritizes system optimization and integration.
Table of Comparison
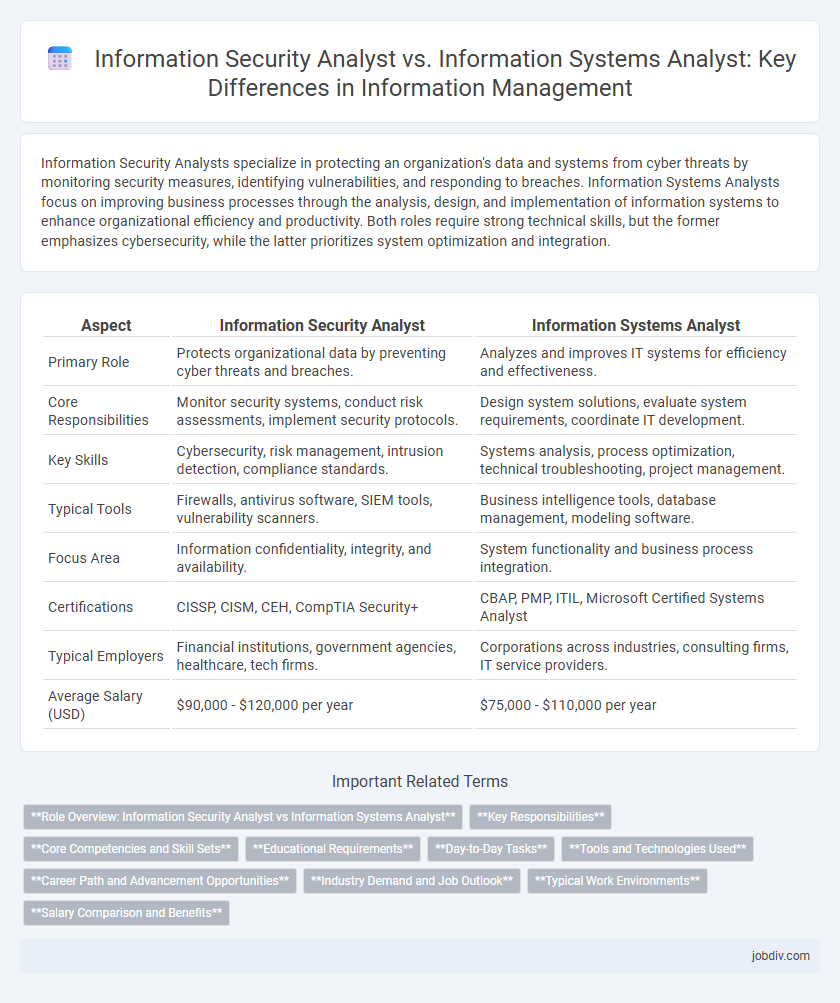
| Aspect | Information Security Analyst | Information Systems Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Protects organizational data by preventing cyber threats and breaches. | Analyzes and improves IT systems for efficiency and effectiveness. |
| Core Responsibilities | Monitor security systems, conduct risk assessments, implement security protocols. | Design system solutions, evaluate system requirements, coordinate IT development. |
| Key Skills | Cybersecurity, risk management, intrusion detection, compliance standards. | Systems analysis, process optimization, technical troubleshooting, project management. |
| Typical Tools | Firewalls, antivirus software, SIEM tools, vulnerability scanners. | Business intelligence tools, database management, modeling software. |
| Focus Area | Information confidentiality, integrity, and availability. | System functionality and business process integration. |
| Certifications | CISSP, CISM, CEH, CompTIA Security+ | CBAP, PMP, ITIL, Microsoft Certified Systems Analyst |
| Typical Employers | Financial institutions, government agencies, healthcare, tech firms. | Corporations across industries, consulting firms, IT service providers. |
| Average Salary (USD) | $90,000 - $120,000 per year | $75,000 - $110,000 per year |
Role Overview: Information Security Analyst vs Information Systems Analyst
Information Security Analysts focus on protecting an organization's computer systems and networks from cyber threats by implementing security measures, monitoring for vulnerabilities, and responding to breaches. Information Systems Analysts evaluate and improve IT systems to enhance business processes, aligning technology solutions with organizational goals. Both roles require strong analytical skills but differ in their primary objectives: security-focused protection versus systems optimization.
Key Responsibilities
Information Security Analysts primarily focus on protecting an organization's computer systems and networks by monitoring for security breaches, implementing protective measures such as firewalls and encryption, and responding to cyber threats. Information Systems Analysts concentrate on optimizing and maintaining business IT infrastructures, analyzing system requirements, designing solutions to improve efficiency, and coordinating system upgrades or integrations. Both roles require a deep understanding of information technology but differ significantly in their focus on security versus system performance and functionality.
Core Competencies and Skill Sets
Information Security Analysts specialize in cybersecurity measures, risk assessment, and incident response, emphasizing expertise in threat detection, encryption, and vulnerability management. Information Systems Analysts focus on designing, implementing, and optimizing IT systems, requiring skills in systems analysis, business process integration, and software development lifecycles. Both roles demand strong analytical skills, but Information Security Analysts prioritize protective technologies while Information Systems Analysts concentrate on improving system efficiency and functionality.
Educational Requirements
Information Security Analysts typically require a bachelor's degree in cybersecurity, information technology, or computer science, often supplemented with certifications such as CISSP or CEH to enhance expertise in protecting digital assets. In contrast, Information Systems Analysts generally hold a degree in information systems, computer science, or business administration, with an emphasis on analyzing and optimizing IT systems for business efficiency. Both roles value strong analytical skills, but Information Security Analysts prioritize specialized security training, whereas Information Systems Analysts focus on system integration and management knowledge.
Day-to-Day Tasks
Information Security Analysts primarily monitor networks for security breaches, implement security measures, and respond to cyber threats daily. Information Systems Analysts focus on analyzing and improving IT systems, troubleshooting software issues, and coordinating system upgrades to enhance organizational efficiency. Both roles require daily collaboration with IT teams, but their core tasks differ significantly in security versus system optimization.
Tools and Technologies Used
Information Security Analysts primarily utilize tools such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), antivirus software, and encryption technologies to protect organizational data from cyber threats. In contrast, Information Systems Analysts employ database management systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, and business intelligence tools to optimize and streamline IT infrastructure and workflows. Both roles leverage advanced analytics platforms and scripting languages like Python or SQL for system monitoring and data analysis but apply them to different core objectives.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Information Security Analysts often advance toward roles such as Security Architect, Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), or Cybersecurity Consultant, capitalizing on expertise in threat detection, risk management, and compliance. Information Systems Analysts typically progress into positions like IT Project Manager, Systems Architect, or Business Systems Analyst, leveraging skills in system integration, software development, and process optimization. Both career paths demand continuous learning and certifications such as CISSP for Security Analysts and CBAP or PMP for Systems Analysts to enhance advancement opportunities.
Industry Demand and Job Outlook
Information Security Analysts are experiencing robust industry demand due to escalating cyber threats, with the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projecting a 35% employment growth from 2021 to 2031. Information Systems Analysts also face strong job prospects, driven by organizations' need to optimize IT infrastructure and enhance system integration, with a projected 21% growth rate in the same period. Both roles offer competitive salaries and job stability, but Information Security Analysts tend to command higher compensation linked to the critical nature of cybersecurity in protecting sensitive data.
Typical Work Environments
Information Security Analysts typically work in corporate IT departments, government agencies, and financial institutions, where they focus on protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. Information Systems Analysts are often found in healthcare organizations, manufacturing companies, and consulting firms, analyzing and improving IT systems to enhance operational efficiency. Both roles commonly operate in office settings but may also require remote work or on-site visits for system assessments and security audits.
Salary Comparison and Benefits
Information Security Analysts typically earn higher salaries than Information Systems Analysts due to their specialized role in protecting organizational data from cyber threats, with average annual wages ranging from $95,000 to $120,000 compared to $75,000 to $95,000 for Information Systems Analysts. Benefits for Information Security Analysts often include cybersecurity certifications reimbursement, comprehensive health insurance, and performance bonuses tied to risk mitigation success. Information Systems Analysts receive competitive benefits focusing on system optimization training, flexible work arrangements, and technology stipends enhancing their operational efficiency.
Information Security Analyst vs Information Systems Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com