A Lease Analyst evaluates lease agreements to ensure compliance with accounting standards and helps optimize lease portfolios. A Lease Accountant, on the other hand, focuses on recording lease transactions accurately and preparing financial statements in accordance with relevant regulations. Both roles are essential for effective lease management and financial reporting accuracy.
Table of Comparison
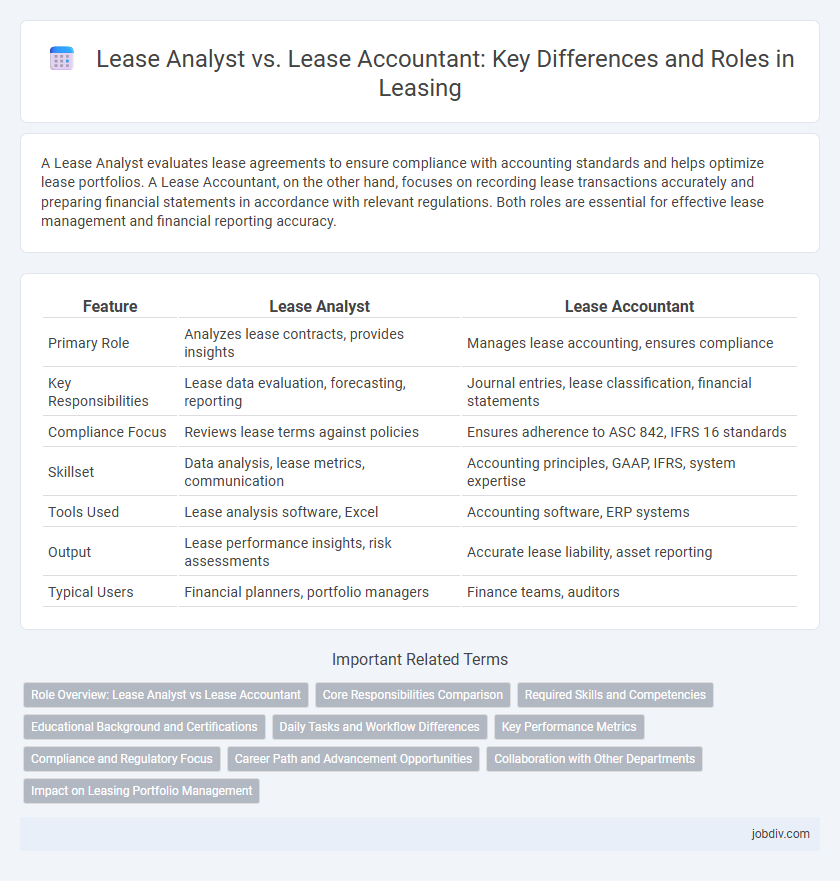
| Feature | Lease Analyst | Lease Accountant |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Analyzes lease contracts, provides insights | Manages lease accounting, ensures compliance |
| Key Responsibilities | Lease data evaluation, forecasting, reporting | Journal entries, lease classification, financial statements |
| Compliance Focus | Reviews lease terms against policies | Ensures adherence to ASC 842, IFRS 16 standards |
| Skillset | Data analysis, lease metrics, communication | Accounting principles, GAAP, IFRS, system expertise |
| Tools Used | Lease analysis software, Excel | Accounting software, ERP systems |
| Output | Lease performance insights, risk assessments | Accurate lease liability, asset reporting |
| Typical Users | Financial planners, portfolio managers | Finance teams, auditors |
Role Overview: Lease Analyst vs Lease Accountant
Lease Analysts evaluate lease agreements and market data to provide insights on lease terms, ensuring optimal financial and operational outcomes. Lease Accountants focus on the accurate recording, reporting, and compliance of lease transactions in financial statements according to lease accounting standards like ASC 842 or IFRS 16. Both roles collaborate to maintain alignment between lease strategy and accounting accuracy, but Lease Analysts emphasize analysis and negotiation while Lease Accountants prioritize financial compliance and reporting.
Core Responsibilities Comparison
Lease analysts focus on evaluating lease agreements, conducting financial analysis, and ensuring compliance with lease standards such as IFRS 16 and ASC 842. Lease accountants are responsible for recording lease transactions, managing lease accounting entries, and preparing lease-related financial reports in accordance with GAAP or IFRS. While lease analysts emphasize analytical assessments of lease terms and financial impact, lease accountants prioritize accurate lease data entry and financial statement integration.
Required Skills and Competencies
A Lease Analyst requires expertise in financial modeling, lease portfolio analysis, and knowledge of lease accounting standards such as ASC 842 and IFRS 16, with strong analytical and problem-solving skills. A Lease Accountant must have proficiency in lease data management, journal entries, and compliance reporting, coupled with advanced Excel skills and familiarity with ERP systems like SAP or Oracle. Both roles demand attention to detail, understanding of lease contracts, and the ability to interpret complex leasing arrangements to ensure accurate financial reporting.
Educational Background and Certifications
Lease Analysts typically hold a bachelor's degree in finance, accounting, or business administration, with certifications such as Certified Lease Analyst (CLA) enhancing their expertise in lease agreement evaluation and compliance. Lease Accountants usually possess a degree in accounting or finance and often pursue professional certifications like Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or Chartered Accountant (CA) to ensure proficiency in financial reporting and lease accounting standards like ASC 842 or IFRS 16. The distinction in educational background and certifications reflects the Lease Analyst's focus on lease data analysis versus the Lease Accountant's emphasis on financial accuracy and regulatory adherence.
Daily Tasks and Workflow Differences
Lease analysts primarily focus on reviewing and interpreting lease agreements, extracting critical data to ensure compliance and accuracy in lease recordings. Lease accountants handle the financial aspects, such as preparing journal entries, reconciling lease liabilities, and ensuring adherence to accounting standards like ASC 842 or IFRS 16. The workflow of a lease analyst revolves around data analysis and contract assessment, while lease accountants emphasize financial reporting and audit readiness.
Key Performance Metrics
Lease analysts focus on evaluating lease agreements, identifying risks, and ensuring compliance with accounting standards such as ASC 842 or IFRS 16, emphasizing metrics like lease data accuracy, variance analysis, and lease classification precision. Lease accountants prioritize the accurate recording of lease transactions, lease payment schedules, and depreciation calculations, with key performance indicators including timeliness of lease reporting, reconciliation accuracy, and adherence to lease accounting policies. Both roles contribute to optimal lease portfolio management by improving financial transparency and regulatory compliance through their complementary performance metrics.
Compliance and Regulatory Focus
Lease Analysts concentrate on evaluating lease agreements to ensure compliance with relevant accounting standards like ASC 842 and IFRS 16, identifying discrepancies and potential risks in lease data. Lease Accountants focus on maintaining accurate lease financial records, ensuring regulatory adherence through precise journal entries, and supporting audit processes to verify compliance with tax laws and reporting requirements. Both roles are crucial for organizations to mitigate lease-related financial risks and uphold regulatory standards.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Lease Analysts focus on data review, lease compliance, and financial reporting, providing critical insights that support strategic lease decisions. Lease Accountants specialize in lease accounting standards such as ASC 842 and IFRS 16, managing lease financials, journal entries, and audit preparation. Career advancement for Lease Analysts often leads to roles in real estate management or finance strategy, while Lease Accountants progress towards senior accounting positions, financial controllers, or compliance specialists.
Collaboration with Other Departments
Lease Analysts collaborate closely with finance, legal, and property management teams to ensure accurate lease data collection and compliance with accounting standards. Lease Accountants work with auditors, controllers, and tax departments to verify lease reporting, reconciliations, and financial statement accuracy. Effective communication between Lease Analysts and Lease Accountants enhances lease administration, reduces errors, and improves regulatory compliance.
Impact on Leasing Portfolio Management
Lease analysts focus on evaluating lease terms, market trends, and financial data to identify cost-saving opportunities and optimize portfolio performance. Lease accountants ensure accurate lease accounting, compliance with ASC 842 and IFRS 16 standards, and proper financial reporting, directly impacting lease liability and asset valuation. Together, their collaboration enhances strategic decision-making and improves the financial health of the leasing portfolio.
Lease Analyst vs Lease Accountant Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com