In-house counsel offers companies dedicated legal expertise with deep understanding of internal operations, enabling faster decision-making and cost efficiency. Outside counsel provides specialized knowledge and impartial advice on complex or niche legal matters, often benefiting from extensive experience across diverse industries. Choosing between in-house and outside counsel depends on the organization's legal needs, budget, and desire for internal integration versus external perspective.
Table of Comparison
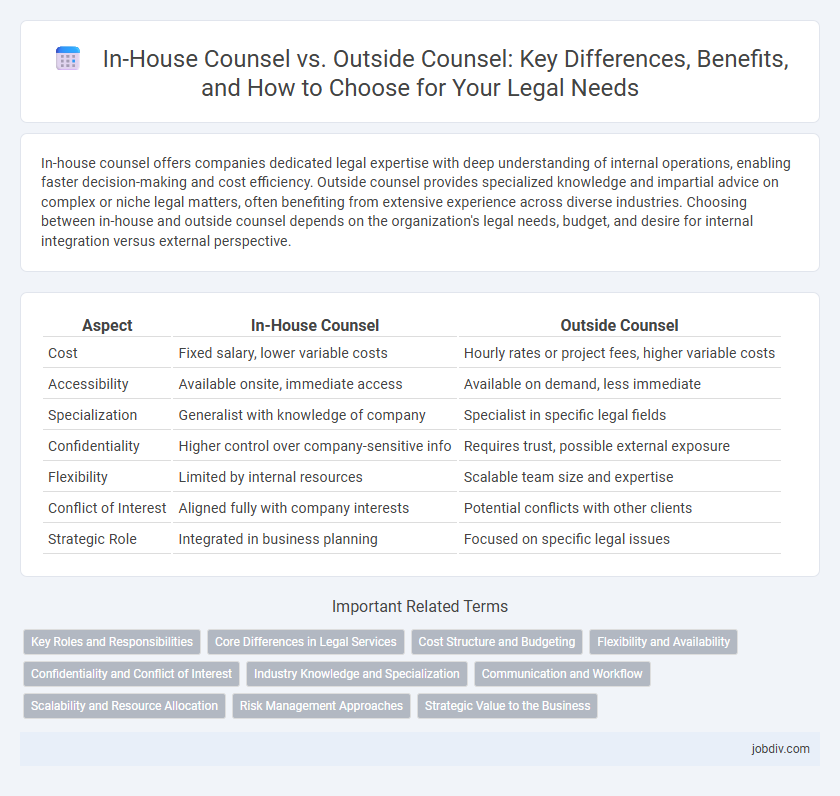
| Aspect | In-House Counsel | Outside Counsel |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Fixed salary, lower variable costs | Hourly rates or project fees, higher variable costs |
| Accessibility | Available onsite, immediate access | Available on demand, less immediate |
| Specialization | Generalist with knowledge of company | Specialist in specific legal fields |
| Confidentiality | Higher control over company-sensitive info | Requires trust, possible external exposure |
| Flexibility | Limited by internal resources | Scalable team size and expertise |
| Conflict of Interest | Aligned fully with company interests | Potential conflicts with other clients |
| Strategic Role | Integrated in business planning | Focused on specific legal issues |
Key Roles and Responsibilities
In-house counsel primarily manage a company's legal matters, offering continuous advice on compliance, contracts, risk management, and corporate governance tailored to the business's strategic objectives. Outside counsel provide specialized expertise and represent clients in litigation, complex transactions, and regulatory issues that exceed the scope of internal legal resources. Both roles collaborate to protect the organization's legal interests, with in-house counsel overseeing daily legal operations and outside counsel delivering subject-matter expertise and advocacy.
Core Differences in Legal Services
In-house counsel provide continuous, integrated legal support tailored to the specific needs and strategic goals of a single organization, fostering deep institutional knowledge and immediate accessibility. Outside counsel offers specialized expertise and a broad range of legal services on a case-by-case basis, often bringing experience from multiple industries and jurisdictions. Key differences include cost structure, with in-house counsel typically salaried and outside counsel billed hourly or per project, and the scope of service, where in-house handles routine legal matters and compliance while outside counsel manages complex litigation or specialized transactions.
Cost Structure and Budgeting
In-house counsel typically offer a fixed salary cost structure, providing predictable budgeting for ongoing legal needs and internal advisory services. Outside counsel usually operates on hourly billing or retainer fees, which can lead to fluctuating expenses based on the complexity and volume of legal matters. Effective cost management often involves blending in-house resources for routine tasks and outside firms for specialized, high-stakes litigation or compliance issues.
Flexibility and Availability
In-house counsel offers greater flexibility and immediate availability, facilitating real-time legal support tailored to the company's evolving needs. Outside counsel provides specialized expertise for complex cases but may face constraints due to billable hours and scheduling conflicts. Balancing these factors, organizations often rely on in-house teams for routine legal matters and outside counsel for niche or high-stakes issues.
Confidentiality and Conflict of Interest
In-house counsel often faces unique confidentiality challenges due to their dual role within the company, which can blur the lines between legal advice and business interests. Outside counsel typically provides greater protection against conflicts of interest by maintaining independence from the client's daily operations. Both arrangements demand rigorous adherence to ethical standards to safeguard privileged communication and ensure unbiased legal representation.
Industry Knowledge and Specialization
In-house counsel possess deep industry knowledge and an intimate understanding of their company's business operations, enabling tailored legal strategies that align closely with corporate goals. Outside counsel offer specialized expertise in complex or niche legal areas, providing access to broad experience across multiple industries and jurisdictions. The choice between in-house and outside counsel hinges on balancing the need for specialized legal skills with the value of embedded industry insight.
Communication and Workflow
Effective communication between in-house counsel and outside counsel is critical for streamlined workflow and risk mitigation. In-house counsel provide deeper organizational context and ongoing collaboration, enhancing decision-making and strategic alignment. Outside counsel bring specialized expertise and external perspective, requiring clear, concise communication protocols to ensure timely, accurate exchange of information and efficient case management.
Scalability and Resource Allocation
In-house counsel offers scalable legal support by integrating directly within the company, enabling efficient resource allocation tailored to ongoing business needs and controlling costs. Outside counsel provides flexible scalability for specialized or high-volume matters without long-term commitments, allowing companies to access diverse expertise on demand. Strategic use of both models optimizes legal resource management, balancing fixed internal capacity with variable external expertise.
Risk Management Approaches
In-house counsel integrates risk management strategies directly with business operations, enabling proactive identification and mitigation of legal risks tailored to company objectives. Outside counsel offers specialized expertise and impartial risk assessments, often supporting complex or high-stakes matters beyond internal resources. Combining in-house insights with external perspectives enhances comprehensive risk management and legal compliance across diverse regulatory environments.
Strategic Value to the Business
In-house counsel offers strategic value by aligning legal advice directly with business objectives, ensuring immediate access to company-specific insights and faster decision-making. Outside counsel provides specialized expertise and an external perspective, aiding complex transactions or litigation beyond the scope of internal resources. Balancing in-house efficiency with outside counsel's depth enhances overall legal strategy and risk management.
In-House Counsel vs Outside Counsel Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com