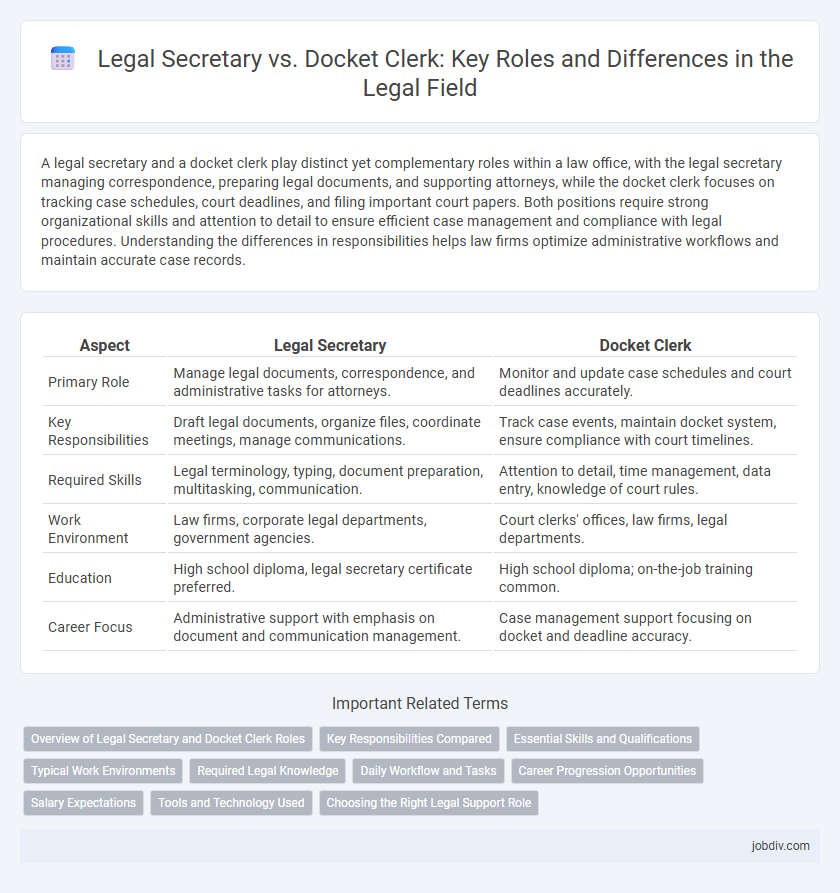
A legal secretary and a docket clerk play distinct yet complementary roles within a law office, with the legal secretary managing correspondence, preparing legal documents, and supporting attorneys, while the docket clerk focuses on tracking case schedules, court deadlines, and filing important court papers. Both positions require strong organizational skills and attention to detail to ensure efficient case management and compliance with legal procedures. Understanding the differences in responsibilities helps law firms optimize administrative workflows and maintain accurate case records.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Legal Secretary | Docket Clerk |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage legal documents, correspondence, and administrative tasks for attorneys. | Monitor and update case schedules and court deadlines accurately. |
| Key Responsibilities | Draft legal documents, organize files, coordinate meetings, manage communications. | Track case events, maintain docket system, ensure compliance with court timelines. |
| Required Skills | Legal terminology, typing, document preparation, multitasking, communication. | Attention to detail, time management, data entry, knowledge of court rules. |
| Work Environment | Law firms, corporate legal departments, government agencies. | Court clerks' offices, law firms, legal departments. |
| Education | High school diploma, legal secretary certificate preferred. | High school diploma; on-the-job training common. |
| Career Focus | Administrative support with emphasis on document and communication management. | Case management support focusing on docket and deadline accuracy. |
Overview of Legal Secretary and Docket Clerk Roles
Legal Secretaries manage correspondence, prepare legal documents, and assist lawyers with case preparation, ensuring accuracy and adherence to legal procedures. Docket Clerks maintain and update court calendars, track case deadlines, and organize filings to facilitate efficient courtroom scheduling. Both roles are essential for supporting legal operations, with Legal Secretaries focused on documentation and administrative tasks while Docket Clerks prioritize case tracking and deadline management.
Key Responsibilities Compared
Legal Secretaries handle correspondence, document preparation, and client communication to support attorneys efficiently. Docket Clerks focus on managing court schedules, filing deadlines, and case tracking to ensure compliance with judicial timelines. Both roles require attention to detail but differ in administrative versus calendaring priorities within legal operations.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
Legal Secretaries require strong proficiency in legal terminology, document preparation, and effective communication skills to support attorneys and manage confidential legal documents accurately. Docket Clerks must excel in data entry, calendar management, and attention to detail to track court dates, deadlines, and case statuses precisely. Both roles demand organizational skills, familiarity with legal software, and discretion, but Legal Secretaries often require higher-level administrative capabilities and knowledge of legal procedures.
Typical Work Environments
Legal secretaries typically work in law firms, corporate legal departments, and government agencies, handling document preparation, correspondence, and client communication. Docket clerks are primarily found in courts, law offices, and administrative agencies, where they manage case schedules, track filings, and update court dockets. Both roles require proficiency with legal software and adherence to strict confidentiality standards in high-pressure environments.
Required Legal Knowledge
Legal secretaries require a comprehensive understanding of legal terminology, court procedures, and document preparation essential for supporting attorneys effectively. Docket clerks must be proficient in case management systems and calendaring rules to accurately track deadlines and court dates. Both roles demand familiarity with jurisdiction-specific legal regulations to ensure compliance and efficient case handling.
Daily Workflow and Tasks
Legal secretaries manage correspondence, draft legal documents, and coordinate schedules to support attorneys efficiently, ensuring case preparation and court deadlines are met. Docket clerks maintain and update court case calendars, track filing deadlines, and organize court records to prevent missed submissions or hearings. Both roles require meticulous attention to detail, but legal secretaries engage more directly with client communication and document drafting, whereas docket clerks focus primarily on case tracking and schedule management.
Career Progression Opportunities
Legal Secretaries typically have broader career progression opportunities, advancing to roles such as Legal Assistant, Paralegal, or Office Manager due to their comprehensive understanding of legal documentation and client interaction. Docket Clerks often transition into specialized positions like Court Clerk or Legal Records Manager, leveraging their expertise in case management and calendar coordination. Both roles offer pathways to higher administrative and legal support positions, but Legal Secretaries generally access more diverse advancement options within law firms and corporate legal departments.
Salary Expectations
Legal secretaries typically earn higher salaries than docket clerks, with average annual wages ranging between $45,000 and $60,000 depending on experience and location. Docket clerks generally have a lower salary range, often between $35,000 and $50,000 annually, reflecting their more specialized focus on case scheduling and court filings. Salary expectations for both roles can increase with additional certifications, expertise in complex legal areas, and employment at larger law firms or corporate legal departments.
Tools and Technology Used
Legal secretaries utilize advanced word processing software such as Microsoft Word and legal document management systems including Clio or MyCase to efficiently draft, edit, and organize legal documents. Docket clerks primarily rely on court docketing software like Odyssey, PACER, or Juris for managing case schedules, filing deadlines, and tracking electronic court records. Both roles require proficiency in electronic filing systems (e-filing) and secure communication platforms to ensure compliance with legal protocols and streamline workflow management.
Choosing the Right Legal Support Role
Choosing the right legal support role depends on the specific responsibilities and skills required; legal secretaries focus on document preparation, client communication, and managing schedules, while docket clerks specialize in maintaining accurate court case records and tracking important deadlines. Legal secretaries often possess strong typing and proofreading capabilities, whereas docket clerks require meticulous attention to detail and knowledge of court procedures. Evaluating your strengths in organization, communication, and legal terminology helps determine the best fit between these essential legal support positions.
Legal Secretary vs Docket Clerk Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com