A Finance Manager oversees the financial planning, analysis, and reporting processes to drive strategic decision-making and ensure organizational growth. In contrast, a Controller focuses on maintaining accurate financial records, internal controls, and compliance with accounting standards. Both roles are essential for effective financial management, with the Finance Manager emphasizing strategy and forecasting, while the Controller prioritizes operational accuracy and regulatory adherence.
Table of Comparison
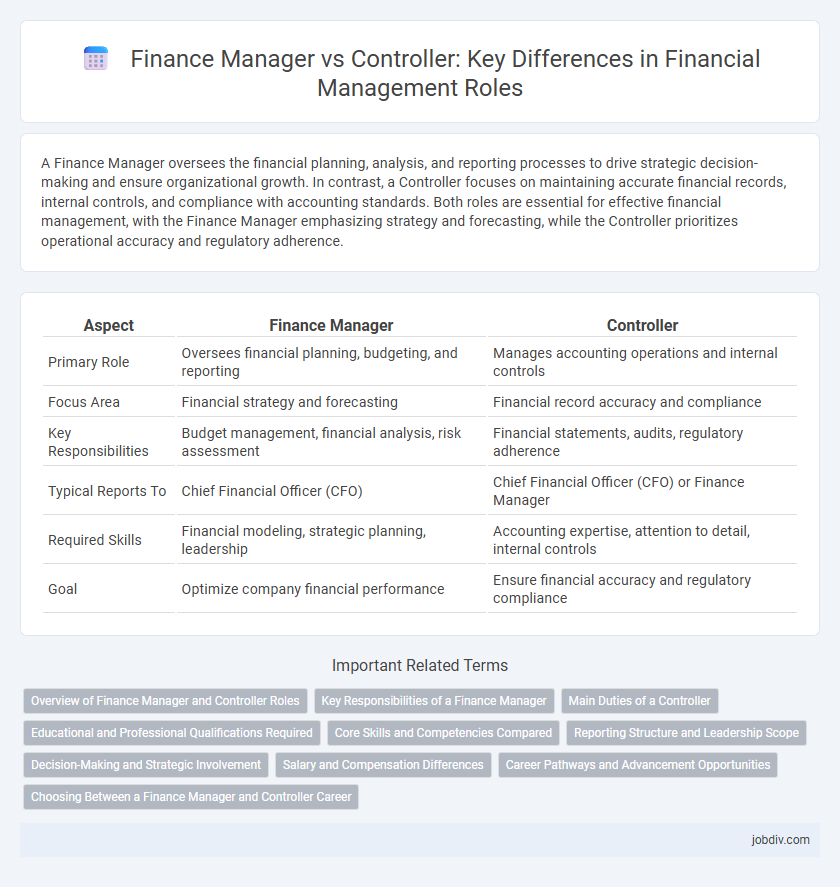
| Aspect | Finance Manager | Controller |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Oversees financial planning, budgeting, and reporting | Manages accounting operations and internal controls |
| Focus Area | Financial strategy and forecasting | Financial record accuracy and compliance |
| Key Responsibilities | Budget management, financial analysis, risk assessment | Financial statements, audits, regulatory adherence |
| Typical Reports To | Chief Financial Officer (CFO) | Chief Financial Officer (CFO) or Finance Manager |
| Required Skills | Financial modeling, strategic planning, leadership | Accounting expertise, attention to detail, internal controls |
| Goal | Optimize company financial performance | Ensure financial accuracy and regulatory compliance |
Overview of Finance Manager and Controller Roles
Finance Managers oversee an organization's financial health by managing budgeting, forecasting, and financial reporting to drive strategic decision-making. Controllers focus on maintaining accurate financial records, ensuring compliance with accounting standards, and supervising internal audits. Both roles play crucial parts in financial management, with Finance Managers concentrating on forward-looking strategies and Controllers emphasizing accuracy and regulatory adherence.
Key Responsibilities of a Finance Manager
A Finance Manager oversees budgeting, forecasting, and financial analysis to drive strategic decision-making and ensure organizational profitability. They manage cash flow, prepare financial reports, and coordinate with other departments to align financial goals with business objectives. Their key responsibilities also include risk management, compliance with financial regulations, and optimizing resource allocation to enhance operational efficiency.
Main Duties of a Controller
A Controller primarily oversees the accounting functions, ensuring accurate financial reporting, compliance with regulatory standards, and internal controls. They manage budgeting processes, financial audits, and the preparation of financial statements to provide key insights for strategic decision-making. Controllers also coordinate closely with finance managers to align operational finance activities with overall company goals.
Educational and Professional Qualifications Required
A Finance Manager typically requires a bachelor's degree in finance, accounting, or business administration, with many holding CPA or CFA certifications to enhance analytical skills. Controllers often need a similar educational background but emphasize extensive experience in accounting, usually possessing a CPA credential due to their focus on regulatory compliance and financial reporting. Both roles benefit from advanced degrees like an MBA, though controllers prioritize expertise in internal controls and audit processes, while finance managers focus more on financial strategy and investment analysis.
Core Skills and Competencies Compared
Finance Managers excel in strategic financial planning, budgeting, and analysis, leveraging strong leadership and communication skills to align financial goals with business objectives. Controllers focus on meticulous financial reporting, regulatory compliance, and internal controls, requiring expertise in accounting standards, risk management, and audit processes. Both roles demand proficiency in financial software, data analytics, and problem-solving, but Finance Managers prioritize growth-oriented decision-making while Controllers emphasize accuracy and financial governance.
Reporting Structure and Leadership Scope
A Finance Manager typically reports to the Controller or Chief Financial Officer (CFO), overseeing financial analysis, budgeting, and day-to-day financial operations. In contrast, the Controller holds a higher leadership position with broader responsibility, managing the entire accounting department and ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance. The Controller's leadership scope includes strategic financial planning and internal controls, while the Finance Manager focuses more on operational finance and team supervision.
Decision-Making and Strategic Involvement
Finance Managers play a critical role in decision-making by analyzing financial data to guide budgeting, forecasting, and investment strategies that align with organizational goals. Controllers focus more on ensuring accurate financial reporting, compliance, and internal controls, which provide a reliable foundation for strategic decisions. While Finance Managers engage deeply in shaping long-term financial strategies, Controllers maintain the integrity of financial operations essential for informed executive decisions.
Salary and Compensation Differences
Finance Managers typically earn a higher average salary than Controllers, reflecting their broader strategic role in financial planning and analysis. Finance Manager salaries range from $85,000 to $140,000 annually, while Controllers generally earn between $75,000 and $130,000 depending on company size and industry. Compensation packages for Finance Managers often include performance bonuses and stock options, whereas Controllers may receive more stable, fixed salary structures with potential profit-sharing incentives.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Finance Managers typically advance by developing strategic financial planning skills and gaining expertise in budgeting, forecasting, and team leadership, often progressing to roles like Director of Finance or Chief Financial Officer. Controllers focus on mastering accounting processes, regulatory compliance, and internal controls, positioning themselves for promotion to Senior Controller or Vice President of Finance roles. Both career paths offer advancement opportunities in executive management, with Finance Managers leaning toward strategic decision-making and Controllers specializing in financial reporting and audit functions.
Choosing Between a Finance Manager and Controller Career
Choosing between a Finance Manager and Controller career depends on your preference for strategic planning versus financial oversight. Finance Managers typically focus on budgeting, forecasting, and aligning financial goals with business strategies. Controllers emphasize accuracy in financial reporting, compliance, and internal control systems, making them essential for auditing and regulatory requirements.
Finance Manager vs Controller Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com