Line managers directly oversee employee performance and daily operations, ensuring team productivity and alignment with organizational goals. Staff managers provide specialized support and expertise, advising line managers without direct authority over frontline employees. Clear role differentiation between line and staff managers enhances decision-making efficiency and operational effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
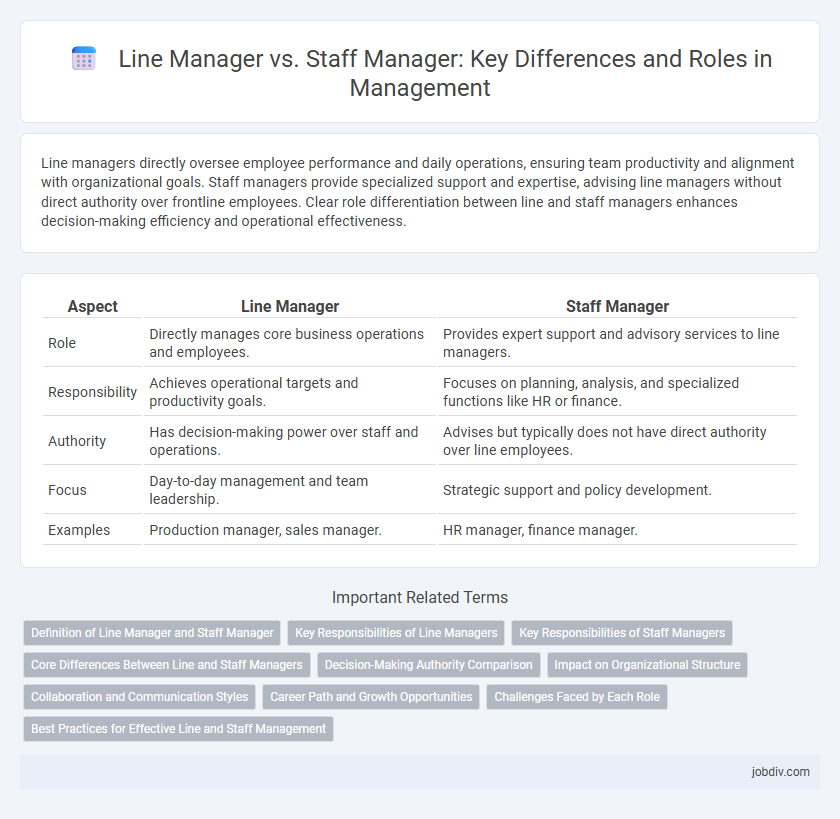
| Aspect | Line Manager | Staff Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Directly manages core business operations and employees. | Provides expert support and advisory services to line managers. |
| Responsibility | Achieves operational targets and productivity goals. | Focuses on planning, analysis, and specialized functions like HR or finance. |
| Authority | Has decision-making power over staff and operations. | Advises but typically does not have direct authority over line employees. |
| Focus | Day-to-day management and team leadership. | Strategic support and policy development. |
| Examples | Production manager, sales manager. | HR manager, finance manager. |
Definition of Line Manager and Staff Manager
A line manager is responsible for directly overseeing employees who are involved in the core business activities, ensuring operational tasks are completed efficiently. Staff managers provide specialized support and advisory services to line managers, focusing on areas such as human resources, finance, or legal compliance without direct authority over production employees. The distinction lies in line managers' direct control over workflow and staff managers' role in strategic guidance and functional expertise.
Key Responsibilities of Line Managers
Line managers hold primary accountability for direct operational functions, including task delegation, performance monitoring, and team motivation to achieve organizational goals. They serve as the critical link between senior management and frontline employees, ensuring effective communication and resource allocation. Their role encompasses problem-solving, staff development, and enforcing company policies to maintain productivity and operational efficiency.
Key Responsibilities of Staff Managers
Staff managers primarily focus on developing and implementing policies that support the overall organizational goals, ensuring operational efficiency across various departments. They oversee specialized functions such as human resources, finance, or marketing, providing expert guidance and facilitating resource allocation. Their key responsibilities include strategic planning, staff training, performance evaluation, and maintaining compliance with regulatory standards.
Core Differences Between Line and Staff Managers
Line managers have direct authority over employees and are responsible for achieving organizational goals through operational tasks, whereas staff managers provide specialized advisory support without direct control over production activities. Line managers focus on day-to-day management and decision-making within the primary workflow, while staff managers influence strategic planning by offering expertise in areas such as human resources, finance, or legal compliance. The core difference lies in the scope of authority and responsibility: line managers drive execution, whereas staff managers facilitate and guide through professional counsel.
Decision-Making Authority Comparison
Line managers possess direct decision-making authority over operational tasks, team workflows, and day-to-day employee management, enabling swift execution aligned with organizational goals. Staff managers primarily serve advisory roles, offering specialized expertise and recommendations without final decision-making power over line functions. This distinction highlights the line manager's pivotal role in tactical decisions versus the staff manager's influence through strategic support and consultancy.
Impact on Organizational Structure
Line managers directly oversee operational teams, shaping the organizational structure by creating clear reporting lines and accountability within departments. Staff managers provide specialized support and advisory functions, influencing the structure through cross-functional collaboration and coordination without direct authority over line personnel. This distinction affects decision-making flow, with line managers driving execution and staff managers enhancing strategy and support frameworks.
Collaboration and Communication Styles
Line managers prioritize direct communication and hands-on collaboration with their teams to ensure operational efficiency and task completion. Staff managers adopt a consultative communication style, providing specialized advice and support to line managers without direct authority. Effective collaboration between line and staff managers relies on clear role definitions and mutual respect to enhance organizational decision-making and problem-solving.
Career Path and Growth Opportunities
Line managers typically advance through operational roles with direct team oversight, gaining skills in leadership, project management, and performance evaluation, which open pathways to senior management positions. Staff managers often develop expertise in specialized functions such as HR, finance, or IT, enabling career growth through subject matter proficiency and advisory roles that can lead to strategic leadership or consultancy careers. The career progression of line managers usually involves broader organizational responsibility, while staff managers focus on deepening functional expertise and influencing corporate policy from a support position.
Challenges Faced by Each Role
Line managers face challenges such as balancing direct team supervision with organizational goals, managing performance and motivation on the front lines, and addressing immediate operational issues. Staff managers encounter difficulties in providing expert advice and support across departments while ensuring alignment with overall strategy, often struggling with influence without direct authority. Both roles require strong communication and conflict resolution skills to navigate the complexities of their distinct responsibilities.
Best Practices for Effective Line and Staff Management
Effective line management involves direct supervision, clear communication of operational goals, and real-time problem-solving to ensure frontline productivity and team alignment. Staff managers excel by providing specialized expertise, strategic support, and policy formulation that empower line managers to execute tasks efficiently. Best practices include fostering collaboration between line and staff managers, leveraging data-driven decision-making, and maintaining transparent feedback loops to optimize organizational performance.
Line Manager vs Staff Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com