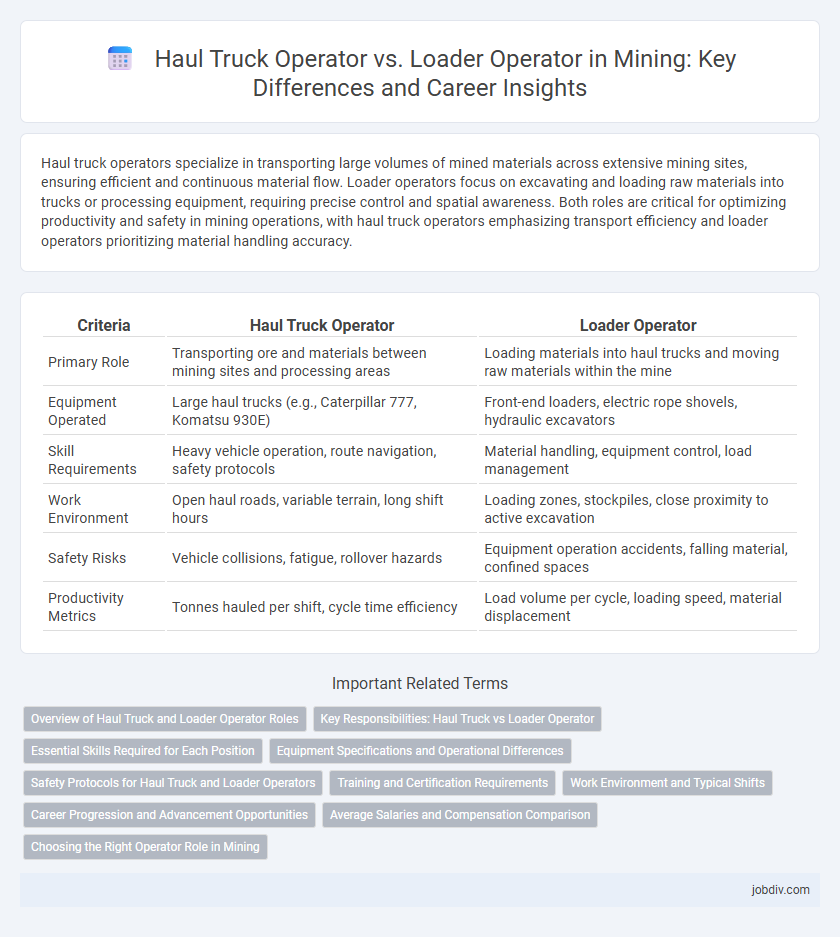
Haul truck operators specialize in transporting large volumes of mined materials across extensive mining sites, ensuring efficient and continuous material flow. Loader operators focus on excavating and loading raw materials into trucks or processing equipment, requiring precise control and spatial awareness. Both roles are critical for optimizing productivity and safety in mining operations, with haul truck operators emphasizing transport efficiency and loader operators prioritizing material handling accuracy.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Haul Truck Operator | Loader Operator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Transporting ore and materials between mining sites and processing areas | Loading materials into haul trucks and moving raw materials within the mine |
| Equipment Operated | Large haul trucks (e.g., Caterpillar 777, Komatsu 930E) | Front-end loaders, electric rope shovels, hydraulic excavators |
| Skill Requirements | Heavy vehicle operation, route navigation, safety protocols | Material handling, equipment control, load management |
| Work Environment | Open haul roads, variable terrain, long shift hours | Loading zones, stockpiles, close proximity to active excavation |
| Safety Risks | Vehicle collisions, fatigue, rollover hazards | Equipment operation accidents, falling material, confined spaces |
| Productivity Metrics | Tonnes hauled per shift, cycle time efficiency | Load volume per cycle, loading speed, material displacement |
Overview of Haul Truck and Loader Operator Roles
Haul Truck Operators manage large off-road trucks to transport mined materials across excavation sites, focusing on safe and efficient haulage. Loader Operators control heavy machinery to excavate, load, and move earth or ore, directly supporting extraction processes. Both roles require expertise in heavy equipment operation, safety protocols, and coordination within mining operations to optimize productivity.
Key Responsibilities: Haul Truck vs Loader Operator
Haul Truck Operators are responsible for transporting large volumes of mined materials from the extraction site to processing locations, ensuring efficient load and dump cycles within strict timeframes to optimize production flow. Loader Operators focus on excavating, loading, and transferring materials such as ore or overburden into haul trucks or stockpiles, maintaining precise control for safe and effective material handling. Both roles require adherence to safety protocols, equipment maintenance, and coordination to support continuous mining operations.
Essential Skills Required for Each Position
Haul truck operators must possess advanced spatial awareness, strong multitasking abilities, and proficiency in operating heavy mining vehicles to ensure safe and efficient material transport. Loader operators require exceptional hand-eye coordination, mechanical knowledge for equipment maintenance, and precise control for loading and dumping tasks in confined spaces. Both positions demand situational awareness, adherence to safety protocols, and physical stamina to handle the demanding mining environment.
Equipment Specifications and Operational Differences
Haul truck operators manage large-capacity vehicles designed for transporting mined materials over long distances, with trucks often exceeding payloads of 300 tons and featuring robust horsepower engines for high-speed hauling. Loader operators control front-end loaders or hydraulic shovels, specialized for excavation and material loading, equipped with advanced digging buckets ranging from 10 to 50 cubic yards and precise hydraulic systems for efficient material handling. Operational differences include haul truck operators focusing on route navigation and load distribution, whereas loader operators concentrate on excavation accuracy and effective loading cycles to optimize mining productivity.
Safety Protocols for Haul Truck and Loader Operators
Haul truck operators must strictly adhere to safety protocols including pre-operation inspections, maintaining clear communication with spotters, and following designated haul roads to prevent collisions and rollovers. Loader operators focus on safe equipment handling by performing daily checks, using seat belts, and ensuring visibility when maneuvering in confined areas to avoid striking personnel or equipment. Both roles require rigorous training on emergency procedures and personal protective equipment (PPE) usage to mitigate onsite hazards.
Training and Certification Requirements
Haul truck operators and loader operators in mining both require specialized training and certification to ensure safe and efficient operation of heavy machinery, with haul truck operators often needing additional training in vehicle dynamics and long-haul navigation. Loader operators typically undergo focused instruction on material handling techniques, equipment maintenance, and load safety protocols. Both roles demand adherence to industry regulations such as MSHA certification in the U.S. and equivalent safety standards worldwide to reduce operational risks and maintain productivity.
Work Environment and Typical Shifts
Haul truck operators primarily work outdoors in large open-pit mines, facing varying weather conditions and long distances across rough terrain. Loader operators often operate in confined spaces near excavation sites, managing heavy machinery closely around other equipment and workers. Typical shifts for both roles are commonly 12 hours, with operators working in rotating day and night schedules to maintain continuous mining operations.
Career Progression and Advancement Opportunities
Haul truck operators in mining often have opportunities to advance into supervisory roles or specialized machinery operation due to their experience with large-scale transport logistics. Loader operators, skilled in precise material handling and equipment maintenance, can progress toward equipment technician roles or shift supervisor positions. Both career paths offer pathways to management or training roles, with advancement dependent on technical expertise and leadership skills.
Average Salaries and Compensation Comparison
Haul truck operators in mining typically earn an average salary of $55,000 to $70,000 annually, reflecting their responsibility for transporting large volumes of ore and waste materials across mining sites. Loader operators earn slightly less, with average salaries ranging from $50,000 to $65,000 per year, due to their role in managing material handling and loading onto haul trucks. Compensation packages for both positions often include benefits such as overtime pay, hazard bonuses, and health insurance, with haul truck operators generally receiving higher total compensation due to the extensive operational demands and safety risks associated with vehicle operation.
Choosing the Right Operator Role in Mining
Selecting the right operator role in mining depends on site-specific tasks and equipment efficiency, with haul truck operators specializing in transporting bulk materials over long distances, optimizing cycle times and fuel consumption. Loader operators focus on material excavation and loading, enhancing productivity in fragmented rock or uneven terrain through precise bucket control. Matching operator skills with operational demands maximizes overall mine productivity and safety compliance.
Haul Truck Operator vs Loader Operator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com