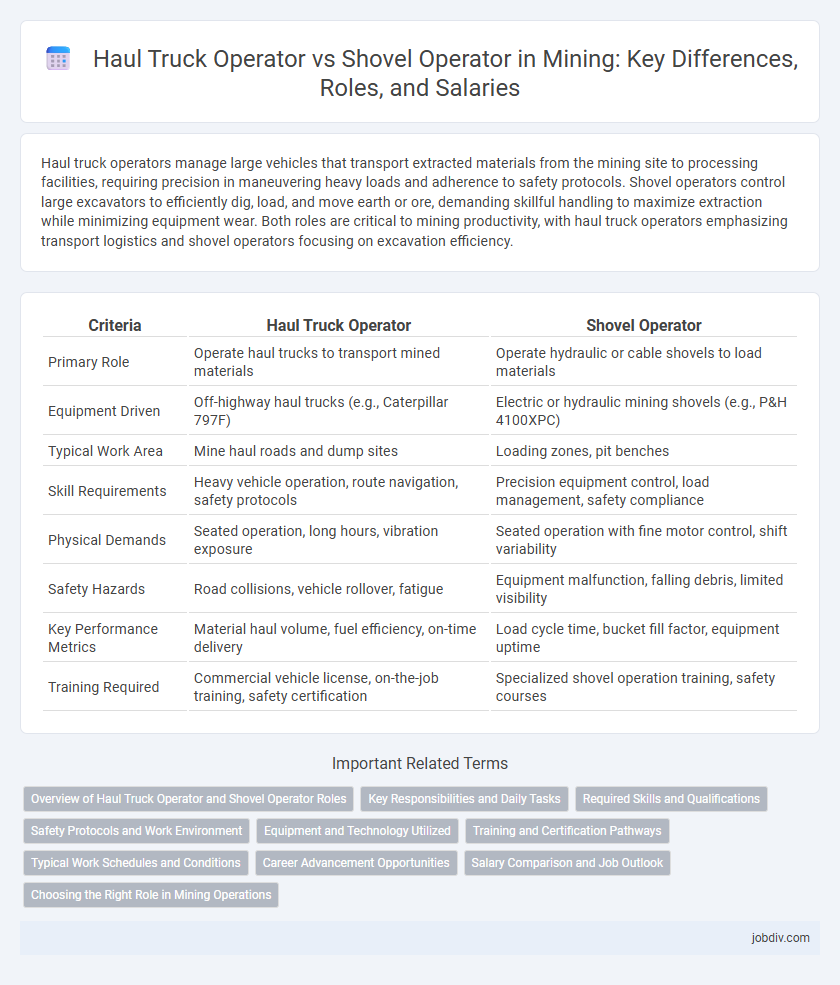
Haul truck operators manage large vehicles that transport extracted materials from the mining site to processing facilities, requiring precision in maneuvering heavy loads and adherence to safety protocols. Shovel operators control large excavators to efficiently dig, load, and move earth or ore, demanding skillful handling to maximize extraction while minimizing equipment wear. Both roles are critical to mining productivity, with haul truck operators emphasizing transport logistics and shovel operators focusing on excavation efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Haul Truck Operator | Shovel Operator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Operate haul trucks to transport mined materials | Operate hydraulic or cable shovels to load materials |
| Equipment Driven | Off-highway haul trucks (e.g., Caterpillar 797F) | Electric or hydraulic mining shovels (e.g., P&H 4100XPC) |
| Typical Work Area | Mine haul roads and dump sites | Loading zones, pit benches |
| Skill Requirements | Heavy vehicle operation, route navigation, safety protocols | Precision equipment control, load management, safety compliance |
| Physical Demands | Seated operation, long hours, vibration exposure | Seated operation with fine motor control, shift variability |
| Safety Hazards | Road collisions, vehicle rollover, fatigue | Equipment malfunction, falling debris, limited visibility |
| Key Performance Metrics | Material haul volume, fuel efficiency, on-time delivery | Load cycle time, bucket fill factor, equipment uptime |
| Training Required | Commercial vehicle license, on-the-job training, safety certification | Specialized shovel operation training, safety courses |
Overview of Haul Truck Operator and Shovel Operator Roles
Haul Truck Operators manage large off-road trucks used to transport ore and waste materials from mining sites to processing areas, requiring skills in heavy machinery operation and safety compliance. Shovel Operators control hydraulic shovels or excavators to load raw materials onto haul trucks, demanding precision in material handling and coordination with truck operators to maximize efficiency. Both roles are critical for streamlined mining operations, with Haul Truck Operators emphasizing transport logistics and Shovel Operators focusing on excavation and loading accuracy.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Haul Truck Operators manage the transportation of ore and waste materials across mining sites, ensuring safe operation of heavy-duty trucks while maintaining haul road conditions. Shovel Operators focus on excavating and loading materials using hydraulic shovels, optimizing digging efficiency and adhering to precise loading protocols. Both roles require adherence to safety standards, equipment inspections, and coordination with site supervisors to maintain workflow continuity.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Haul Truck Operators require strong spatial awareness, mechanical aptitude, and the ability to operate heavy vehicles safely in rugged mine conditions, typically needing a commercial driver's license and experience with large haul trucks. Shovel Operators must possess precise hand-eye coordination, knowledge of hydraulic machinery, and proficiency in operating electric or hydraulic shovels to load material efficiently, often requiring specialized certification and extensive training in excavation equipment. Both roles demand a solid understanding of safety protocols, teamwork, and the ability to interpret site plans to optimize mining productivity.
Safety Protocols and Work Environment
Haul Truck Operators and Shovel Operators follow stringent safety protocols tailored to their specific roles, such as maintaining clear communication and adhering to blind spot awareness to prevent accidents. The haul truck operator's work environment involves navigating large trucks across uneven terrain, requiring constant vigilance and adherence to load limits to mitigate rollover risks. Shovel operators work in a confined cabin with limited visibility, necessitating the use of safety locks and regular equipment inspections to avoid mechanical hazards and ensure operator protection.
Equipment and Technology Utilized
Haul truck operators utilize large capacity off-road trucks equipped with advanced GPS and payload management systems to optimize material transport and reduce fuel consumption. Shovel operators work with electric or hydraulic shovels featuring precise automation controls, high-torque engines, and real-time monitoring technologies for efficient material excavation. Both roles rely on integrated communication networks and data analytics platforms to enhance operational safety and productivity in mining environments.
Training and Certification Pathways
Haul truck operators require training that emphasizes vehicle controls, load management, and safety protocols, often culminating in certification through organizations like the National Mining Association or Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA). Shovel operators undergo specialized training focused on equipment maneuvering, excavation techniques, and hazard identification, typically certified through industry-specific programs or manufacturer training courses. Both operator roles demand continuous education to comply with evolving safety standards and technological advancements in mining operations.
Typical Work Schedules and Conditions
Haul truck operators typically work 12-hour shifts, often on a rotating schedule that includes nights and weekends, to ensure continuous material transport in surface mining operations. Shovel operators also follow similar shift patterns, maintaining consistent excavation cycles and working in varying weather conditions to load haul trucks efficiently. Both roles demand adaptability to long hours in outdoor environments with exposure to noise, dust, and vibration, requiring strict adherence to safety protocols.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Haul Truck Operators often access career advancement through roles in fleet management, logistics coordination, and safety supervision, leveraging their expertise in vehicle operation and transport efficiency. Shovel Operators typically advance by moving into equipment maintenance supervision, site operations management, and mining engineering support, capitalizing on their technical skills in heavy machinery and excavation processes. Both positions provide pathways to leadership roles in mine site operations, with progression influenced by experience, certifications, and specialized training within the mining industry.
Salary Comparison and Job Outlook
Haul truck operators in mining typically earn between $60,000 and $90,000 annually, with demand strong due to increasing mine production and automation advancements. Shovel operators have a similar salary range, often between $55,000 and $85,000, but their job outlook is slightly more stable as they are essential for material loading and handling in diverse mining operations. Both roles experience steady growth driven by expanding mineral extraction projects and the need for skilled heavy equipment operators.
Choosing the Right Role in Mining Operations
Choosing the right role in mining operations depends on your skills and career goals. Haul truck operators manage massive loads, requiring precision and focus on safety during transportation of ore and materials across the site. Shovel operators control heavy excavation equipment, demanding expertise in digging, loading, and maintaining optimal production cycles to maximize efficiency.
Haul Truck Operator vs Shovel Operator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com