Underground mining involves extracting minerals from beneath the earth's surface through tunnels and shafts, offering access to deep ore deposits while minimizing surface disruption. Surface mining removes minerals near the surface by stripping away soil and rock layers, enabling large-scale extraction but causing significant landscape alteration. Both methods require careful evaluation of geological conditions, environmental impact, and economic feasibility to determine the most effective mining approach.
Table of Comparison
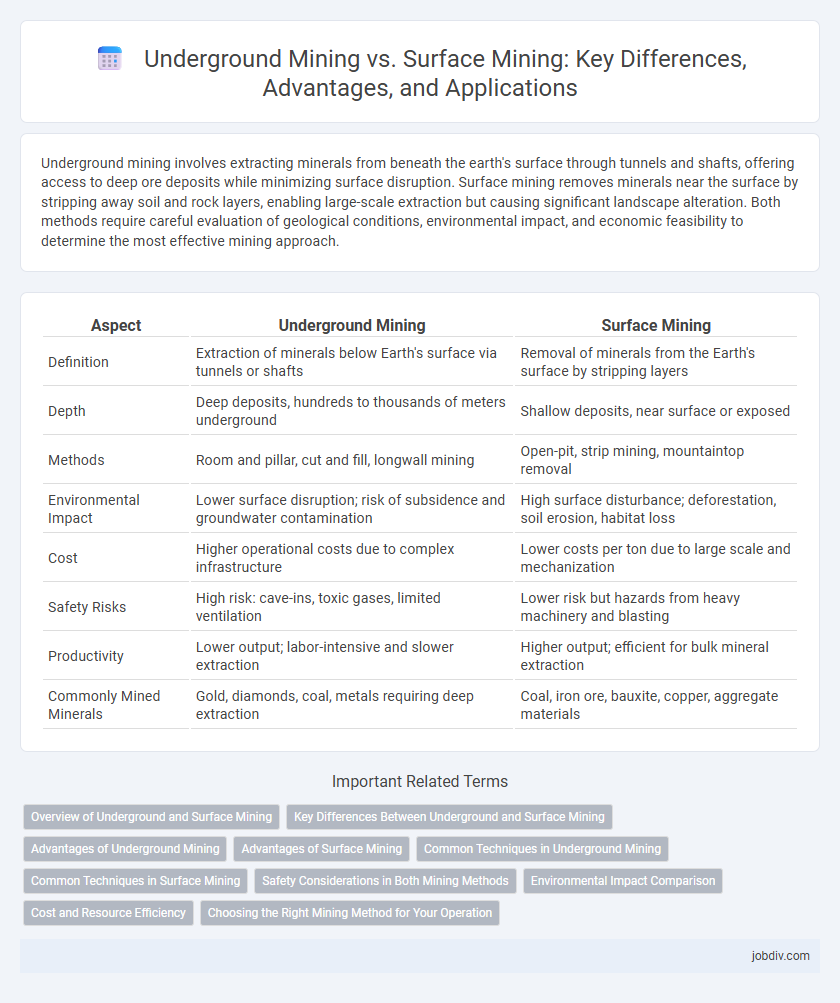
| Aspect | Underground Mining | Surface Mining |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Extraction of minerals below Earth's surface via tunnels or shafts | Removal of minerals from the Earth's surface by stripping layers |
| Depth | Deep deposits, hundreds to thousands of meters underground | Shallow deposits, near surface or exposed |
| Methods | Room and pillar, cut and fill, longwall mining | Open-pit, strip mining, mountaintop removal |
| Environmental Impact | Lower surface disruption; risk of subsidence and groundwater contamination | High surface disturbance; deforestation, soil erosion, habitat loss |
| Cost | Higher operational costs due to complex infrastructure | Lower costs per ton due to large scale and mechanization |
| Safety Risks | High risk: cave-ins, toxic gases, limited ventilation | Lower risk but hazards from heavy machinery and blasting |
| Productivity | Lower output; labor-intensive and slower extraction | Higher output; efficient for bulk mineral extraction |
| Commonly Mined Minerals | Gold, diamonds, coal, metals requiring deep extraction | Coal, iron ore, bauxite, copper, aggregate materials |
Overview of Underground and Surface Mining
Underground mining involves extracting minerals and ores from beneath the earth's surface through tunnels and shafts, enabling access to deep mineral deposits while minimizing surface disturbance. Surface mining, also known as open-pit or strip mining, removes large layers of soil and rock to expose mineral seams near the surface, allowing efficient extraction of shallow deposits with extensive land alteration. Both methods require specialized equipment and safety protocols, with underground mining emphasizing ventilation and structural support, while surface mining prioritizes earth-moving machinery and environmental reclamation.
Key Differences Between Underground and Surface Mining
Underground mining involves extracting minerals from deep beneath the earth's surface through tunnels or shafts, allowing access to deposits that are not economically viable for surface mining. Surface mining removes minerals located close to the surface by stripping away soil and rock layers, typically using open-pit or strip mining techniques. The key differences between underground and surface mining include depth of excavation, environmental impact, operational cost, and safety risks, with underground mining posing higher safety hazards but lower surface disturbance compared to surface mining.
Advantages of Underground Mining
Underground mining offers significant advantages such as reduced environmental impact and minimized surface land disturbance compared to surface mining. This method allows access to deeper ore bodies that are not feasible with surface techniques, ensuring efficient extraction of valuable minerals. Enhanced safety protocols and advanced ventilation systems improve working conditions, making underground mining a viable option for extracting high-grade resources.
Advantages of Surface Mining
Surface mining offers higher productivity and safety compared to underground mining due to easier access to mineral deposits and reduced risk of cave-ins. Its equipment scale and operational efficiency enable the extraction of large ore volumes, lowering overall costs per ton produced. Environmental impact can be more manageable through land reclamation techniques after surface mining operations conclude.
Common Techniques in Underground Mining
Common techniques in underground mining include room and pillar, cut and fill, sublevel stoping, and block caving. Room and pillar involves excavating ore while leaving pillars to support the roof, commonly used in flat-lying deposits. Block caving is a cost-effective bulk mining method for massive ore bodies, relying on gravity to fragment ore for extraction.
Common Techniques in Surface Mining
Surface mining commonly employs techniques such as open-pit mining, which involves excavating large pits to extract ore near the surface, and strip mining, where layers of soil and rock are removed to expose mineral seams. Mountaintop removal is another technique used to access coal seams by blasting away the summit of a mountain. These methods provide efficient extraction of minerals with minimal tunneling compared to underground mining, often resulting in higher production rates and greater exposure of ore bodies.
Safety Considerations in Both Mining Methods
Underground mining presents increased safety risks such as tunnel collapses, hazardous gas exposure, and limited escape routes, requiring rigorous ventilation systems and structural support. Surface mining, while generally safer due to open-air conditions, poses dangers like slope failures, equipment accidents, and dust inhalation. Effective safety protocols in both methods include continuous monitoring, worker training, and emergency response plans to mitigate potential hazards.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Underground mining reduces surface land disturbance and habitat destruction compared to surface mining, which involves extensive excavation and deforestation. However, underground mining poses risks of groundwater contamination and subsidence that can impact ecosystems. Surface mining generates significant air pollution and erosion, resulting in greater long-term environmental degradation than most underground operations.
Cost and Resource Efficiency
Underground mining generally incurs higher operational costs due to complex ventilation, safety measures, and specialized equipment, but it allows access to deeper mineral deposits with minimal surface disturbance. Surface mining offers lower extraction costs and higher resource recovery rates for shallow deposits, making it more cost-effective for large-scale, near-surface mineral extraction. Choosing between underground and surface mining depends heavily on ore depth, deposit size, and economic feasibility to maximize resource efficiency.
Choosing the Right Mining Method for Your Operation
Selecting between underground mining and surface mining depends on ore depth, deposit size, and environmental impact considerations. Underground mining offers precise extraction with minimal surface disruption, ideal for deep and high-grade ore bodies, while surface mining enables efficient removal of large, near-surface deposits. Optimizing operational costs and complying with environmental regulations are critical factors in determining the most effective mining method.
Underground Mining vs Surface Mining Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com