A personal pet often serves as both a companion and a caregiver, providing emotional support and comfort during difficult times. While companions offer friendship and joy, caregiver pets can detect health changes and alert owners to potential issues. Understanding the dual role enhances the bond between humans and their pets, promoting well-being for both.
Table of Comparison
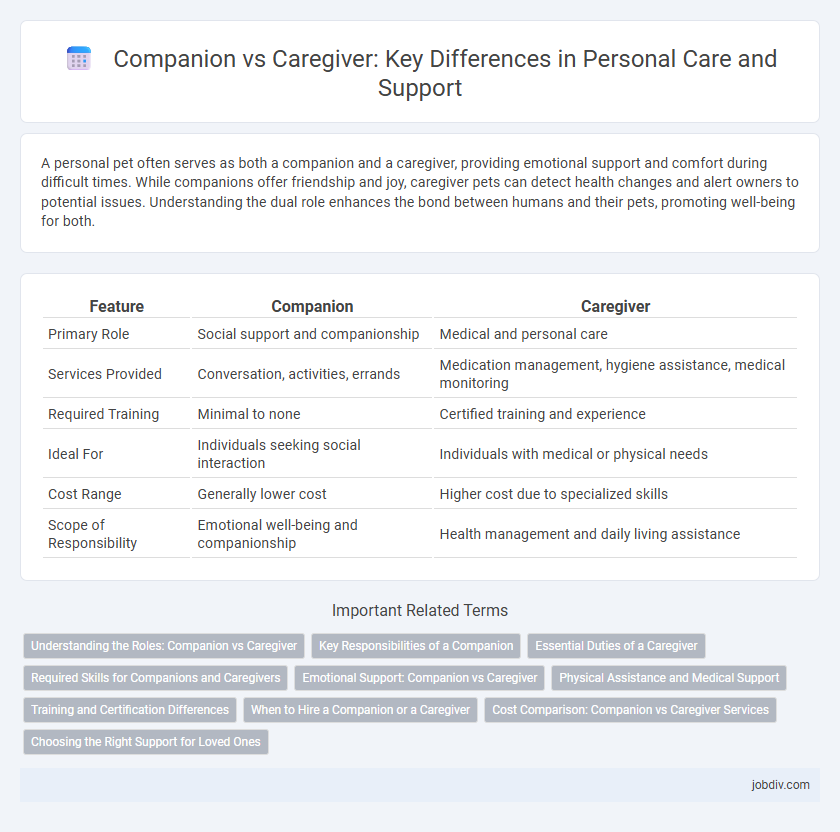
| Feature | Companion | Caregiver |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Social support and companionship | Medical and personal care |
| Services Provided | Conversation, activities, errands | Medication management, hygiene assistance, medical monitoring |
| Required Training | Minimal to none | Certified training and experience |
| Ideal For | Individuals seeking social interaction | Individuals with medical or physical needs |
| Cost Range | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to specialized skills |
| Scope of Responsibility | Emotional well-being and companionship | Health management and daily living assistance |
Understanding the Roles: Companion vs Caregiver
A companion provides social interaction, emotional support, and companionship, enhancing quality of life by reducing loneliness, while a caregiver offers medical assistance and helps with daily living activities like bathing, medication management, and mobility. Understanding these roles clarifies expectations and ensures appropriate support for individuals requiring different levels of care. Distinguishing between companionship and caregiving helps families choose the right type of assistance based on health needs and personal preferences.
Key Responsibilities of a Companion
A companion primarily provides emotional support, engaging in conversations, participating in social activities, and offering companionship to reduce loneliness. They assist with light tasks such as running errands or accompanying clients to appointments but do not perform medical or personal care. Their key responsibility centers on enhancing the client's quality of life through consistent presence and social interaction.
Essential Duties of a Caregiver
Caregivers provide essential duties such as administering medications, assisting with personal hygiene, and managing medical appointments to ensure the well-being of those they care for. They offer physical support for mobility and daily activities, closely monitoring health changes to prevent emergencies. Unlike companions, caregivers are trained professionals equipped to handle complex health-related tasks and provide comprehensive care.
Required Skills for Companions and Caregivers
Companions require strong social and communication skills to provide emotional support and engage clients in meaningful activities. Caregivers need specialized medical knowledge, such as medication management and basic nursing skills, to address physical health needs. Both roles demand patience, empathy, and reliability to ensure the well-being and comfort of those they assist.
Emotional Support: Companion vs Caregiver
Companions provide emotional support through social interaction, companionship, and active listening, which helps reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation. Caregivers offer emotional support that complements medical care by monitoring mental health, recognizing signs of depression or anxiety, and providing reassurance and encouragement during health challenges. Both roles play a critical part in enhancing emotional well-being, but companions focus more on social connection while caregivers address emotional needs linked to physical health.
Physical Assistance and Medical Support
A companion primarily provides social interaction and emotional support without medical responsibilities, focusing on companionship activities rather than physical assistance. Caregivers offer hands-on physical assistance, such as mobility help, bathing, and medication management, ensuring the person's safety and health needs are met. Medical support from caregivers includes administering medications, monitoring vital signs, and coordinating with healthcare professionals for comprehensive care.
Training and Certification Differences
Companions typically provide non-medical support such as companionship and light assistance without requiring formal training or certification. Caregivers often undergo specialized training programs and obtain certifications like CNA (Certified Nursing Assistant) to perform medical and personal care tasks safely. Certification ensures caregivers meet regulatory standards, while companions focus primarily on social and emotional support.
When to Hire a Companion or a Caregiver
Hire a companion when the primary need is social interaction, emotional support, or assistance with light daily activities such as meal preparation and errands. Opt for a caregiver when medical supervision, assistance with personal hygiene, medication management, or help with mobility is required. Choosing between the two depends on the individual's health condition, level of independence, and specific care needs.
Cost Comparison: Companion vs Caregiver Services
Companion services typically cost between $15 to $25 per hour, making them a more affordable option for social interaction and basic assistance. Caregiver services, which include medical support and personal care, generally range from $20 to $40 per hour due to their specialized skills and responsibilities. Choosing between a companion and a caregiver depends on the specific care needs and budget constraints of the individual.
Choosing the Right Support for Loved Ones
Choosing the right support for loved ones involves understanding the distinction between companions and caregivers. Companions provide social interaction, emotional support, and assistance with non-medical tasks, enhancing quality of life and reducing feelings of loneliness. Caregivers offer specialized medical and personal care, including medication management and physical assistance, ensuring safety and health needs are met effectively.
Companion vs Caregiver Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com