A personal loan officer specializes in providing unsecured loans tailored to individual financial needs, offering flexibility for various personal expenses. In contrast, a mortgage broker focuses exclusively on home loans, connecting borrowers with multiple lenders to secure the best mortgage rates and terms. Understanding the distinct roles helps borrowers choose the right expert for personal loans or home financing.
Table of Comparison
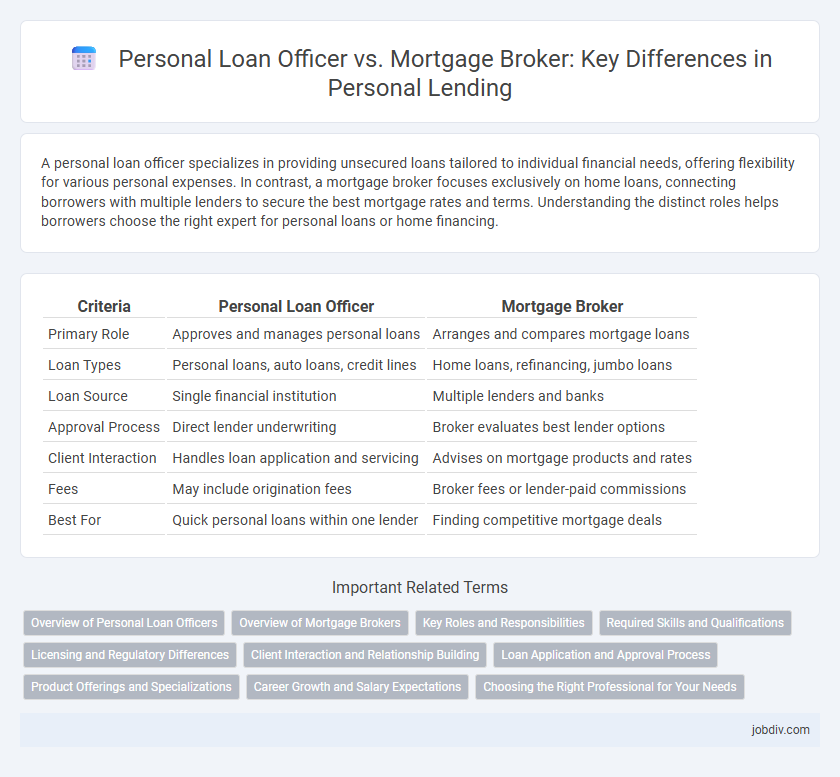
| Criteria | Personal Loan Officer | Mortgage Broker |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Approves and manages personal loans | Arranges and compares mortgage loans |
| Loan Types | Personal loans, auto loans, credit lines | Home loans, refinancing, jumbo loans |
| Loan Source | Single financial institution | Multiple lenders and banks |
| Approval Process | Direct lender underwriting | Broker evaluates best lender options |
| Client Interaction | Handles loan application and servicing | Advises on mortgage products and rates |
| Fees | May include origination fees | Broker fees or lender-paid commissions |
| Best For | Quick personal loans within one lender | Finding competitive mortgage deals |
Overview of Personal Loan Officers
Personal loan officers specialize in evaluating, authorizing, or recommending approval of personal loan applications, focusing on unsecured loans such as debt consolidation, medical expenses, or major purchases. They typically work directly for banks, credit unions, or financial institutions, guiding clients through the application process and assessing creditworthiness. Their role centers on personal lending products rather than home financing, distinguishing them from mortgage brokers who deal exclusively with property loans.
Overview of Mortgage Brokers
Mortgage brokers act as intermediaries between borrowers and multiple mortgage lenders, helping clients find the best loan options tailored to their financial situations. They offer access to a wide range of mortgage products, including fixed-rate, adjustable-rate, and government-backed loans, increasing the likelihood of securing favorable terms. Mortgage brokers evaluate credit scores, income, and debt-to-income ratios to match borrowers with lenders that meet their specific needs efficiently.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
A Personal Loan Officer primarily assesses individual creditworthiness, processes loan applications, and approves personal loans based on borrowers' income, credit history, and repayment capacity. A Mortgage Broker specializes in navigating various mortgage products, advising clients on competitive rates, and facilitating loan approval for home purchases or refinancing. Both roles require strong financial knowledge and client relationship skills but differ in loan types and regulatory frameworks they operate within.
Required Skills and Qualifications
A Personal Loan Officer requires strong skills in credit analysis, customer service, and knowledge of personal finance products, typically holding a bachelor's degree in finance or business and obtaining relevant licensing such as the NMLS certification. In contrast, a Mortgage Broker must excel in understanding real estate markets, loan products, and regulatory compliance, often possessing licenses specific to mortgage brokerage and expertise in mortgage underwriting. Both roles demand excellent communication, attention to detail, and proficiency in financial software to assess client eligibility and tailor loan solutions effectively.
Licensing and Regulatory Differences
Personal loan officers typically require state-specific licenses regulated by the Nationwide Multistate Licensing System (NMLS), focusing on consumer loans and credit products. Mortgage brokers must obtain specialized mortgage broker licenses, adhering to regulations under the Secure and Fair Enforcement for Mortgage Licensing Act (SAFE Act), with stringent compliance on mortgage origination and lending practices. Both roles are subject to federal laws like the Truth in Lending Act (TILA), but mortgage brokers face additional scrutiny due to the larger financial risks and regulatory complexity in home financing.
Client Interaction and Relationship Building
A Personal Loan Officer typically maintains frequent, direct communication with clients, offering tailored financial advice and fostering trust through personalized service. Mortgage Brokers often act as intermediaries between clients and multiple lenders, managing interactions to find the best loan products, but may have less continuous contact. Building strong client relationships is essential for both roles, with loan officers emphasizing ongoing engagement and brokers focusing on efficient brokerage and client satisfaction.
Loan Application and Approval Process
Personal Loan Officers streamline the loan application by directly assessing creditworthiness and income to approve unsecured loans quickly. Mortgage Brokers act as intermediaries who connect borrowers with multiple lenders, gathering extensive documentation and navigating complex underwriting criteria for home loans. The approval process with Mortgage Brokers often takes longer but can yield more competitive mortgage rates compared to the typically faster and more straightforward personal loan approval by Loan Officers.
Product Offerings and Specializations
Personal Loan Officers primarily focus on unsecured loan products such as personal loans, auto loans, and credit lines tailored for individual credit needs. Mortgage Brokers specialize in home financing solutions including fixed-rate mortgages, adjustable-rate mortgages, and refinancing options, leveraging a network of lenders to find competitive rates. The distinction lies in product offerings: personal loan officers manage consumer credit products, while mortgage brokers navigate complex real estate financing options.
Career Growth and Salary Expectations
Personal Loan Officers can experience steady career growth with opportunities to advance into senior loan management roles, often earning median salaries ranging from $50,000 to $80,000 annually. Mortgage Brokers typically have higher earning potential, with commissions and bonuses elevating total compensation to $60,000-$120,000 or more, depending on sales performance. Both careers demand strong financial knowledge and client service skills, but Mortgage Brokers may benefit from larger networks and market volatility affecting commission income.
Choosing the Right Professional for Your Needs
Choosing between a personal loan officer and a mortgage broker depends on your specific financial needs and loan goals. A personal loan officer typically works for a single bank or lender and offers products from that institution, ensuring streamlined approvals and consistent service. Mortgage brokers, on the other hand, access multiple lenders, providing a wider range of loan options and competitive rates tailored to home financing requirements.
Personal Loan Officer vs Mortgage Broker Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com