A personal companion pet provides emotional support, affection, and companionship, fostering a deep bond that enhances overall well-being. In contrast, a caregiver's role revolves around meeting the pet's physical needs, including feeding, grooming, and medical care. Balancing these roles ensures a healthy, happy pet life supported by both emotional and practical care.
Table of Comparison
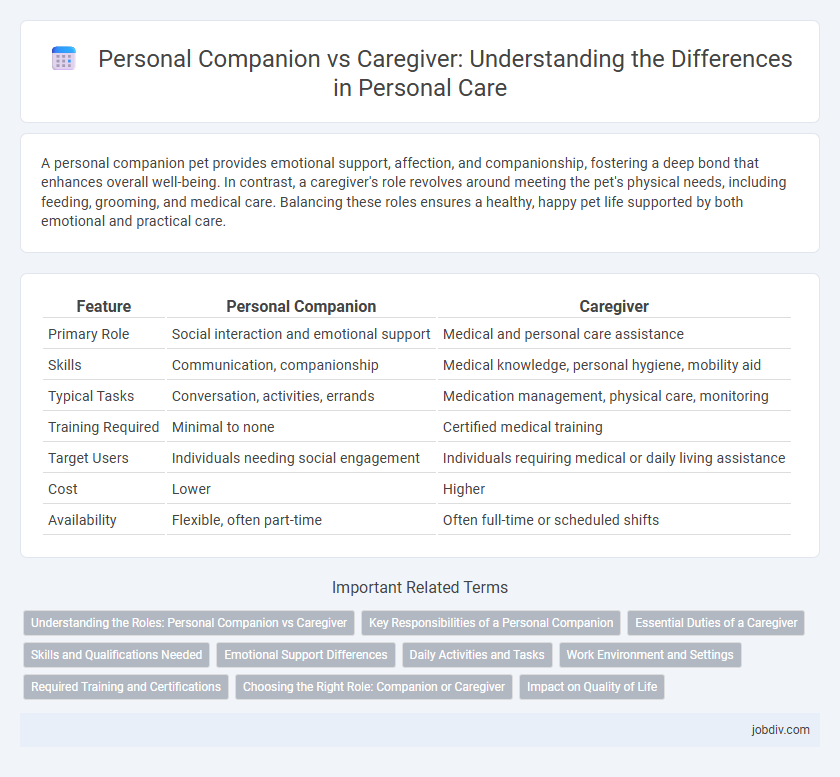
| Feature | Personal Companion | Caregiver |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Social interaction and emotional support | Medical and personal care assistance |
| Skills | Communication, companionship | Medical knowledge, personal hygiene, mobility aid |
| Typical Tasks | Conversation, activities, errands | Medication management, physical care, monitoring |
| Training Required | Minimal to none | Certified medical training |
| Target Users | Individuals needing social engagement | Individuals requiring medical or daily living assistance |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Availability | Flexible, often part-time | Often full-time or scheduled shifts |
Understanding the Roles: Personal Companion vs Caregiver
Personal companions provide social interaction, emotional support, and assistance with daily activities like errands and light housekeeping, enhancing overall well-being. Caregivers offer specialized medical care, such as medication management, wound care, and mobility assistance, tailored to individual health needs. Differentiating these roles helps families choose appropriate support based on physical and emotional requirements.
Key Responsibilities of a Personal Companion
A Personal Companion provides emotional support, engaging in meaningful conversations and participating in social activities to enhance the individual's quality of life. They assist with non-medical tasks such as meal preparation, light housekeeping, and running errands, fostering independence and comfort. Unlike caregivers who focus on medical and physical care, Personal Companions prioritize companionship and mental well-being.
Essential Duties of a Caregiver
A caregiver's essential duties include managing medication schedules, assisting with daily living activities such as bathing and dressing, and monitoring health conditions to ensure safety. They provide emotional support and communicate with healthcare professionals to coordinate care plans effectively. Unlike a personal companion, caregivers deliver medical and physical assistance critical for maintaining a patient's well-being.
Skills and Qualifications Needed
A Personal Companion requires strong interpersonal skills, empathy, and the ability to provide emotional support, often without formal medical training. In contrast, a Caregiver must possess certified healthcare qualifications, such as CPR and first aid, alongside knowledge of medical procedures and patient care. Both roles demand reliability, patience, and effective communication, but Caregivers typically require specialized training to manage health-related tasks safely.
Emotional Support Differences
A personal companion primarily offers emotional support by engaging in meaningful conversations, providing companionship, and reducing feelings of loneliness. Caregivers, while offering some emotional support, focus more on medical tasks and physical assistance, which can limit their availability for deeper emotional connections. Emotional support from a personal companion significantly enhances mental well-being and promotes a sense of comfort and security.
Daily Activities and Tasks
A Personal Companion primarily provides social interaction and assistance with daily activities such as meal preparation, light housekeeping, and running errands, enhancing emotional well-being and independence. A Caregiver offers more comprehensive support, including medical care tasks like medication management, physical assistance with mobility, and monitoring health conditions. Both roles focus on daily tasks, but caregivers handle complex health needs while personal companions emphasize companionship and basic support.
Work Environment and Settings
A Personal Companion often works in less clinical, home-based environments fostering social interaction and emotional support, whereas a Caregiver typically operates in more structured settings like nursing homes or hospitals providing medical and physical assistance. The Personal Companion's role emphasizes companionship and daily activity engagement, while the Caregiver manages health-related tasks including medication administration and mobility support. Work environments for Personal Companions prioritize comfort and socialization, contrasting with the clinical and health-focused atmosphere common for Caregivers.
Required Training and Certifications
Personal companions typically require basic training in interpersonal skills and may complete CPR or first aid certification, focusing on social and emotional support. Caregivers need comprehensive training that includes medical knowledge, patient care techniques, and certifications such as Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA) or Home Health Aide (HHA). Regulatory requirements for caregivers often mandate ongoing education and competency evaluations to ensure high standards of care.
Choosing the Right Role: Companion or Caregiver
Choosing the right role depends on the individual's specific needs; a personal companion offers social interaction, emotional support, and assistance with daily activities, while a caregiver provides more comprehensive medical or physical care. Assessing the level of independence, health conditions, and personal preferences helps determine whether companionship or professional caregiving is most appropriate. Tailoring support to lifestyle requirements ensures optimal well-being and quality of life.
Impact on Quality of Life
Personal companions enhance quality of life by providing emotional support and social interaction, reducing feelings of loneliness and isolation. Caregivers focus on physical assistance and medical needs, ensuring safety and managing health conditions. Both roles significantly improve well-being, but personal companions contribute more to mental and emotional health, while caregivers address functional and medical challenges.
Personal Companion vs Caregiver Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com