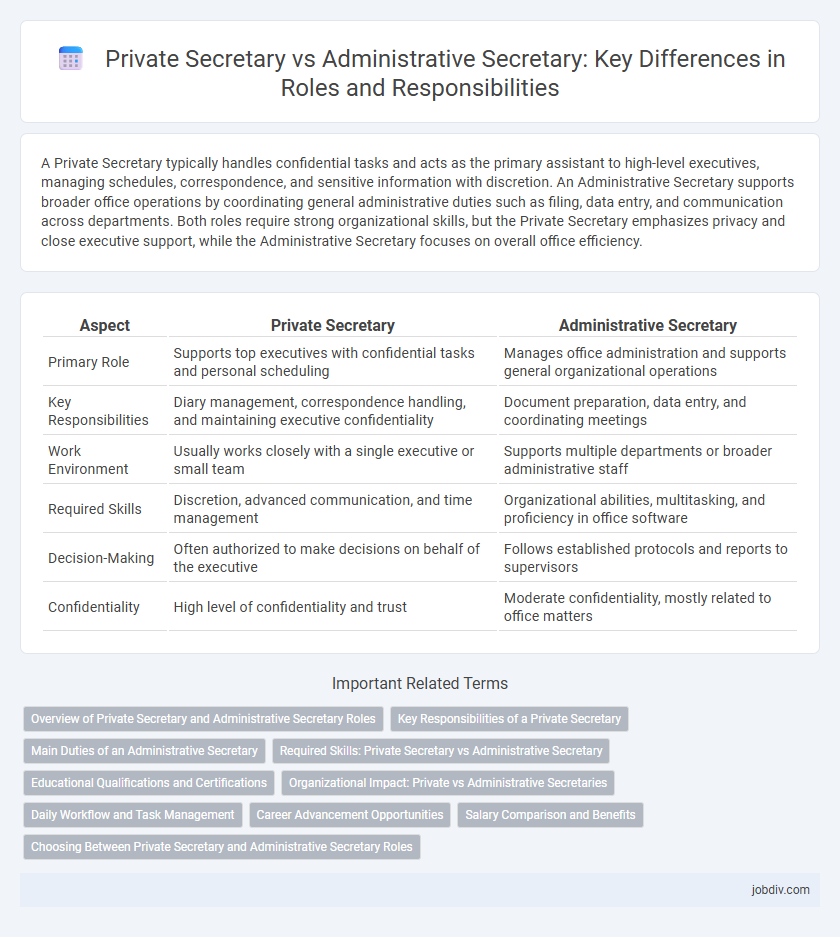
A Private Secretary typically handles confidential tasks and acts as the primary assistant to high-level executives, managing schedules, correspondence, and sensitive information with discretion. An Administrative Secretary supports broader office operations by coordinating general administrative duties such as filing, data entry, and communication across departments. Both roles require strong organizational skills, but the Private Secretary emphasizes privacy and close executive support, while the Administrative Secretary focuses on overall office efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Private Secretary | Administrative Secretary |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Supports top executives with confidential tasks and personal scheduling | Manages office administration and supports general organizational operations |
| Key Responsibilities | Diary management, correspondence handling, and maintaining executive confidentiality | Document preparation, data entry, and coordinating meetings |
| Work Environment | Usually works closely with a single executive or small team | Supports multiple departments or broader administrative staff |
| Required Skills | Discretion, advanced communication, and time management | Organizational abilities, multitasking, and proficiency in office software |
| Decision-Making | Often authorized to make decisions on behalf of the executive | Follows established protocols and reports to supervisors |
| Confidentiality | High level of confidentiality and trust | Moderate confidentiality, mostly related to office matters |
Overview of Private Secretary and Administrative Secretary Roles
A Private Secretary manages confidential correspondence, schedules, and communications for executives, ensuring smooth personal and professional organization. An Administrative Secretary handles general office duties such as managing records, coordinating meetings, and supporting team operations across departments. Both roles require strong organizational skills but differ in focus, with the Private Secretary emphasizing personalized executive support and the Administrative Secretary concentrating on broader office administration.
Key Responsibilities of a Private Secretary
A Private Secretary manages confidential correspondence, schedules appointments, and coordinates communication on behalf of executives, ensuring seamless daily operations. They specialize in handling sensitive information, organizing meetings with key stakeholders, and preparing briefing materials tailored to the executive's priorities. Unlike Administrative Secretaries, Private Secretaries often act as trusted advisors, facilitating strategic decision-making through efficient information flow and time management.
Main Duties of an Administrative Secretary
An Administrative Secretary manages executive schedules, coordinates meetings, and handles correspondence to ensure smooth office operations. They oversee document preparation, maintain records, and facilitate communication between departments to support organizational efficiency. Their main duties also include managing travel arrangements, preparing reports, and assisting with basic financial tasks such as budget tracking.
Required Skills: Private Secretary vs Administrative Secretary
A Private Secretary requires advanced organizational skills, discretion, and the ability to manage confidential information while coordinating closely with executives. An Administrative Secretary must excel in multitasking, office software proficiency, and effective communication to support broader office operations. Both roles demand strong time management and problem-solving abilities, but the Private Secretary often needs enhanced interpersonal skills for executive interaction.
Educational Qualifications and Certifications
A Private Secretary typically requires a bachelor's degree in business administration or a related field, emphasizing advanced organizational and communication skills, whereas an Administrative Secretary often holds a diploma or associate degree in office administration or secretarial studies. Certifications such as Certified Administrative Professional (CAP) or Microsoft Office Specialist (MOS) enhance qualifications for both roles, but Private Secretaries might also pursue executive assistant certifications for higher-level responsibilities. Educational pathways for Private Secretaries focus more on strategic management and executive support, while Administrative Secretaries emphasize operational efficiency and clerical proficiency.
Organizational Impact: Private vs Administrative Secretaries
Private Secretaries enhance organizational impact by managing confidential communications and facilitating executive decision-making processes, ensuring seamless leadership operations. Administrative Secretaries contribute by coordinating office workflows, scheduling, and supporting team activities, which optimizes overall business efficiency. Both roles are pivotal, but Private Secretaries focus more on high-level strategic support while Administrative Secretaries maintain operational stability.
Daily Workflow and Task Management
A Private Secretary primarily manages confidential communications, schedules high-profile meetings, and handles sensitive correspondence daily, ensuring seamless coordination for executives. An Administrative Secretary focuses on organizing office operations, maintaining records, and supporting multiple departments with routine administrative tasks to enhance overall efficiency. Both roles demand excellent time management skills, but the Private Secretary's workflow centers on personalized executive support while the Administrative Secretary manages broader office logistics.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Private Secretaries often experience faster career advancement due to their close interaction with senior executives and involvement in high-level decision-making, offering valuable exposure to strategic operations. Administrative Secretaries typically have broader office management responsibilities, which build versatile skills applicable across various industries but may lead to a more gradual career progression. Networking opportunities for Private Secretaries tend to be more concentrated within executive leadership circles, enhancing prospects for promotions into specialized administrative or executive roles.
Salary Comparison and Benefits
Private Secretaries typically earn higher salaries than Administrative Secretaries due to specialized responsibilities and close work with senior executives. Benefits for Private Secretaries often include performance bonuses, greater job security, and access to exclusive professional development opportunities. Administrative Secretaries usually receive standard benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans but may have less emphasis on variable compensation.
Choosing Between Private Secretary and Administrative Secretary Roles
Choosing between a Private Secretary and an Administrative Secretary role depends on the level of responsibility and confidentiality required. A Private Secretary typically manages high-level executive communications, confidential matters, and strategic scheduling, while an Administrative Secretary handles general office duties, correspondence, and support tasks across departments. Evaluating the organizational hierarchy and the nature of secretarial duties helps determine the best fit for career goals and skill sets.
Private Secretary vs Administrative Secretary Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com