A private secretary provides tailored administrative support to high-level executives or individuals, often managing confidential matters and complex schedules with discretion. A personal secretary typically handles routine office tasks such as correspondence, appointments, and basic clerical duties, supporting daily operational needs. Both roles require organizational skills, but private secretaries are trusted with more sensitive information and strategic responsibilities.
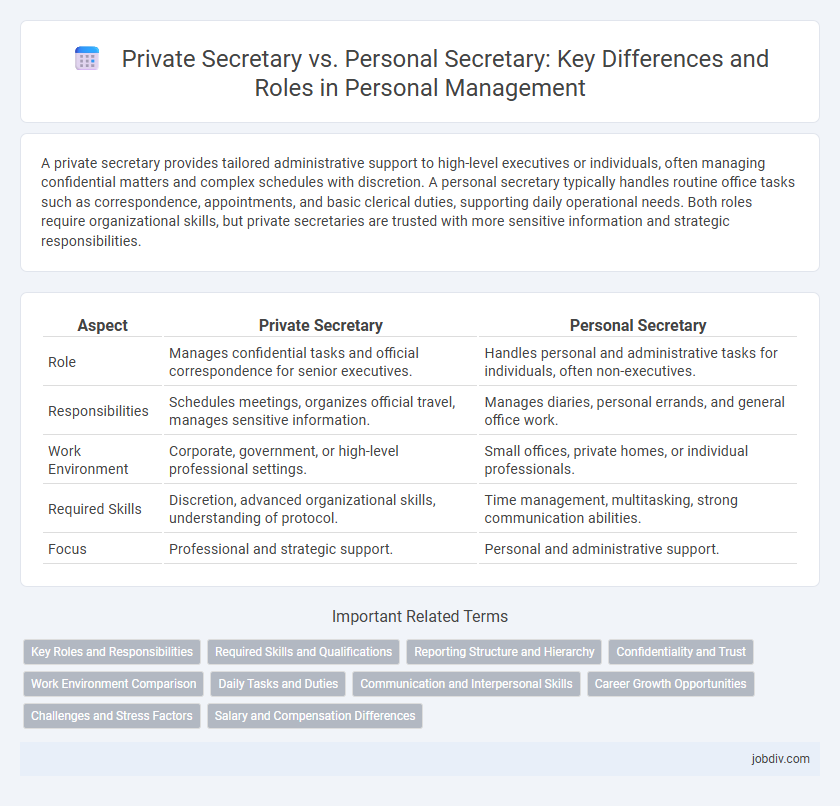
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Private Secretary | Personal Secretary |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Manages confidential tasks and official correspondence for senior executives. | Handles personal and administrative tasks for individuals, often non-executives. |
| Responsibilities | Schedules meetings, organizes official travel, manages sensitive information. | Manages diaries, personal errands, and general office work. |
| Work Environment | Corporate, government, or high-level professional settings. | Small offices, private homes, or individual professionals. |
| Required Skills | Discretion, advanced organizational skills, understanding of protocol. | Time management, multitasking, strong communication abilities. |
| Focus | Professional and strategic support. | Personal and administrative support. |
Key Roles and Responsibilities
A Private Secretary primarily manages confidential communications, schedules, and correspondence for high-level executives, ensuring seamless day-to-day operations. A Personal Secretary handles broader administrative duties such as organizing meetings, preparing documents, and managing personal errands for individuals. Both roles demand excellent organizational skills, discretion, and the ability to prioritize tasks efficiently.
Required Skills and Qualifications
A Private Secretary requires advanced organizational skills, discretion, and proficiency in managing confidential information, often supporting high-level executives or dignitaries. Essential qualifications include strong communication abilities, time management expertise, and familiarity with office software and administrative procedures. Personal Secretaries need similar administrative skills but typically focus more on routine office tasks and personal assistance, requiring proficiency in scheduling, correspondence handling, and multitasking.
Reporting Structure and Hierarchy
A Private Secretary typically reports directly to top executives or high-ranking officials, maintaining a close, confidential working relationship that influences strategic decisions. In contrast, a Personal Secretary usually supports an individual at various organizational levels, with a less formal reporting structure and more administrative focus. The hierarchy places the Private Secretary higher in the organizational chain due to their involvement in critical communications and executive-level responsibilities.
Confidentiality and Trust
A Private Secretary handles sensitive information with the highest level of confidentiality, often working closely with top executives or VIPs where trust is paramount. In contrast, a Personal Secretary may manage a broader range of administrative tasks but does not typically engage with highly confidential matters. The distinction in confidentiality and trust levels makes a Private Secretary indispensable for safeguarding private communications and strategic decisions.
Work Environment Comparison
A Private Secretary typically works in a corporate or executive setting, managing confidential communications and schedules for high-level executives, often requiring discretion and a high degree of professionalism. In contrast, a Personal Secretary usually supports an individual in a more informal or personal context, handling day-to-day tasks such as appointments and correspondence in a less structured environment. Both roles demand strong organizational skills, but Private Secretaries often operate within a formal office atmosphere, whereas Personal Secretaries may have more flexibility in their work environment.
Daily Tasks and Duties
A Private Secretary manages confidential correspondence, schedules high-level meetings, and handles sensitive information for executives or VIPs. A Personal Secretary focuses on organizing daily appointments, managing personal errands, and maintaining communication with internal teams to support individual productivity. Both roles require excellent organizational skills, but a Private Secretary often engages in more strategic and sensitive administrative tasks.
Communication and Interpersonal Skills
A Private Secretary excels in communication by managing confidential information and coordinating high-level interactions, ensuring seamless information flow between executives and stakeholders. Personal Secretaries demonstrate strong interpersonal skills by handling daily correspondence, scheduling, and providing direct support that enhances office efficiency. Both roles require exceptional communication abilities, but Private Secretaries often engage in more strategic dialogue while Personal Secretaries focus on maintaining smooth routine operations.
Career Growth Opportunities
Private secretaries often handle high-level confidential tasks for senior executives, providing exposure to strategic decision-making that can significantly enhance career growth opportunities. Personal secretaries typically focus on administrative support, which may offer steady skill development but more limited advancement potential. Choosing a role depends on career goals, with private secretary positions generally leading to faster progression within corporate or governmental hierarchies.
Challenges and Stress Factors
Private Secretaries often face intense confidentiality demands and high-pressure situations due to their direct support of senior executives, leading to significant stress from maintaining discretion and managing sensitive information. Personal Secretaries encounter challenges in balancing diverse administrative tasks and handling unpredictable scheduling changes, which can cause stress from constant multitasking and time management pressures. Both roles require exceptional organizational skills and emotional resilience to navigate the complexities and demands inherent in their responsibilities.
Salary and Compensation Differences
Private Secretaries typically earn higher salaries than Personal Secretaries due to their strategic roles supporting senior executives, with average annual compensation ranging from $60,000 to $90,000. Personal Secretaries usually receive between $35,000 and $55,000, reflecting their more administrative and routine task focus. Factors influencing salary differences include job responsibilities, required experience, and industry standards.
Private Secretary vs Personal Secretary Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com