A trainer focuses on developing skills through hands-on practice and real-world application, often tailoring sessions to individual or group needs. An instructor primarily delivers structured knowledge and theoretical information, emphasizing comprehension of concepts and principles. While both roles aim to educate, trainers engage more actively in skill-building, whereas instructors prioritize information transfer.
Table of Comparison
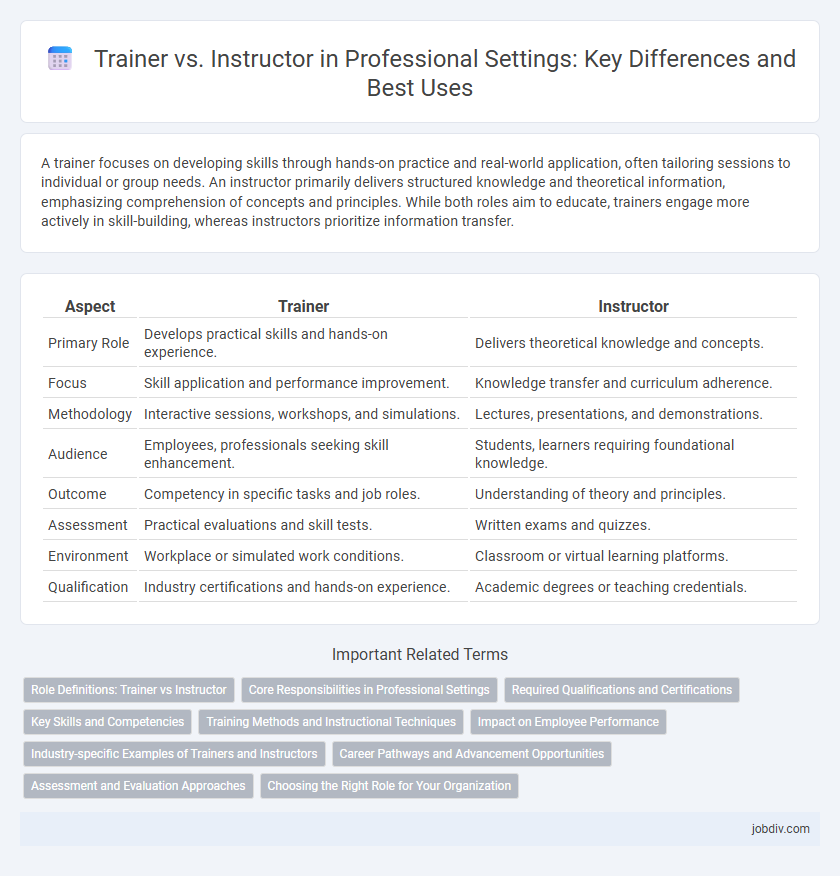
| Aspect | Trainer | Instructor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Develops practical skills and hands-on experience. | Delivers theoretical knowledge and concepts. |
| Focus | Skill application and performance improvement. | Knowledge transfer and curriculum adherence. |
| Methodology | Interactive sessions, workshops, and simulations. | Lectures, presentations, and demonstrations. |
| Audience | Employees, professionals seeking skill enhancement. | Students, learners requiring foundational knowledge. |
| Outcome | Competency in specific tasks and job roles. | Understanding of theory and principles. |
| Assessment | Practical evaluations and skill tests. | Written exams and quizzes. |
| Environment | Workplace or simulated work conditions. | Classroom or virtual learning platforms. |
| Qualification | Industry certifications and hands-on experience. | Academic degrees or teaching credentials. |
Role Definitions: Trainer vs Instructor
Trainers primarily focus on developing specific skills and competencies through hands-on practice and real-world application, often tailored to employee performance improvement in professional settings. Instructors concentrate on delivering structured educational content, emphasizing theoretical knowledge and foundational concepts within formal learning environments. Both roles facilitate learning but differ in approach, with trainers driving practical execution and instructors prioritizing knowledge dissemination.
Core Responsibilities in Professional Settings
Trainers design and deliver tailored programs focused on skill development and performance improvement, emphasizing practical application and ongoing assessment in professional settings. Instructors primarily deliver structured knowledge through formal teaching methods, ensuring comprehension of theoretical concepts aligned with organizational standards. Both roles require domain expertise, but trainers prioritize experiential learning while instructors emphasize foundational knowledge transmission.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Trainers typically require industry-specific certifications such as Certified Professional Trainer (CPT) or Project Management Professional (PMP), emphasizing practical experience and skill application. Instructors often hold advanced academic degrees, like a Master's or Doctorate in Education or their subject area, alongside teaching credentials or certifications such as a state teaching license. Both roles demand continuous professional development, but trainers focus more on hands-on skills certification while instructors prioritize formal educational qualifications.
Key Skills and Competencies
Trainers excel in delivering practical skill development and behavior change through interactive methods, emphasizing communication, adaptability, and motivational skills. Instructors possess strong subject-matter expertise and focus on structured knowledge transfer, with competencies in curriculum design, assessment, and technical proficiency. Both roles require effective interpersonal skills but differ in approach; trainers prioritize engagement and application, while instructors emphasize instructional clarity and content mastery.
Training Methods and Instructional Techniques
Trainers employ interactive training methods such as hands-on activities, simulations, and real-world scenarios to enhance skill acquisition and practical application. Instructors primarily utilize direct instructional techniques like lectures, demonstrations, and structured lesson plans to deliver theoretical knowledge effectively. Both roles integrate assessment tools to evaluate learner progress and adapt their methods for optimal learning outcomes.
Impact on Employee Performance
Trainers enhance employee performance by delivering hands-on skill development tailored to specific job roles, increasing both competency and confidence. Instructors provide foundational knowledge and theoretical understanding that supports long-term employee growth and adaptability. The combined impact of trainers and instructors ensures a comprehensive approach to workforce development, driving higher productivity and improved job performance.
Industry-specific Examples of Trainers and Instructors
Trainers in the hospitality industry conduct hands-on sessions for new waitstaff on customer service protocols and food safety standards, while instructors teach culinary arts theory and techniques in accredited cooking schools. In the IT sector, trainers lead practical workshops on using specific software or cybersecurity measures, whereas instructors deliver structured courses on computer science fundamentals at universities. Manufacturing companies employ trainers to guide employees through equipment operation and safety procedures, in contrast to instructors who provide formal education on industrial engineering principles in technical colleges.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Trainers often focus on skill development and practical application within specific industries, leading to career pathways in corporate training, talent development, and organizational leadership. Instructors typically emphasize academic knowledge and theory, providing advancement opportunities in educational institutions, curriculum design, and advanced certification roles. Both roles offer distinct professional growth, with trainers progressing towards management and consultancy positions, while instructors may advance to academic administration and research specialties.
Assessment and Evaluation Approaches
Trainers emphasize practical assessment methods such as skills demonstrations and on-the-job evaluations to measure learner competence and performance effectiveness. Instructors prioritize formal evaluation approaches including written tests, quizzes, and standardized assessments to gauge theoretical understanding and knowledge retention. Both roles utilize feedback mechanisms, but trainers focus more on real-time corrective guidance while instructors rely on structured grading systems.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Organization
Trainer roles emphasize skill development through hands-on practice and personalized feedback, ideal for organizations aiming to enhance employee performance and technical capabilities. Instructor roles focus on delivering structured knowledge and theory-based content, suitable for organizations that require standardized education and compliance training. Selecting the right role depends on your organization's goals, whether prioritizing practical application or foundational understanding.
Trainer vs Instructor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com