A Public Finance Manager oversees the strategic allocation and management of government funds, ensuring fiscal policies align with public goals and compliance standards. In contrast, a Public Budget Analyst focuses on detailed budget preparation, analysis, and monitoring to optimize resource distribution and track financial performance. Both roles require expertise in public sector finance but differ in scope, with managers handling broader financial strategy and analysts concentrating on budget specifics.
Table of Comparison
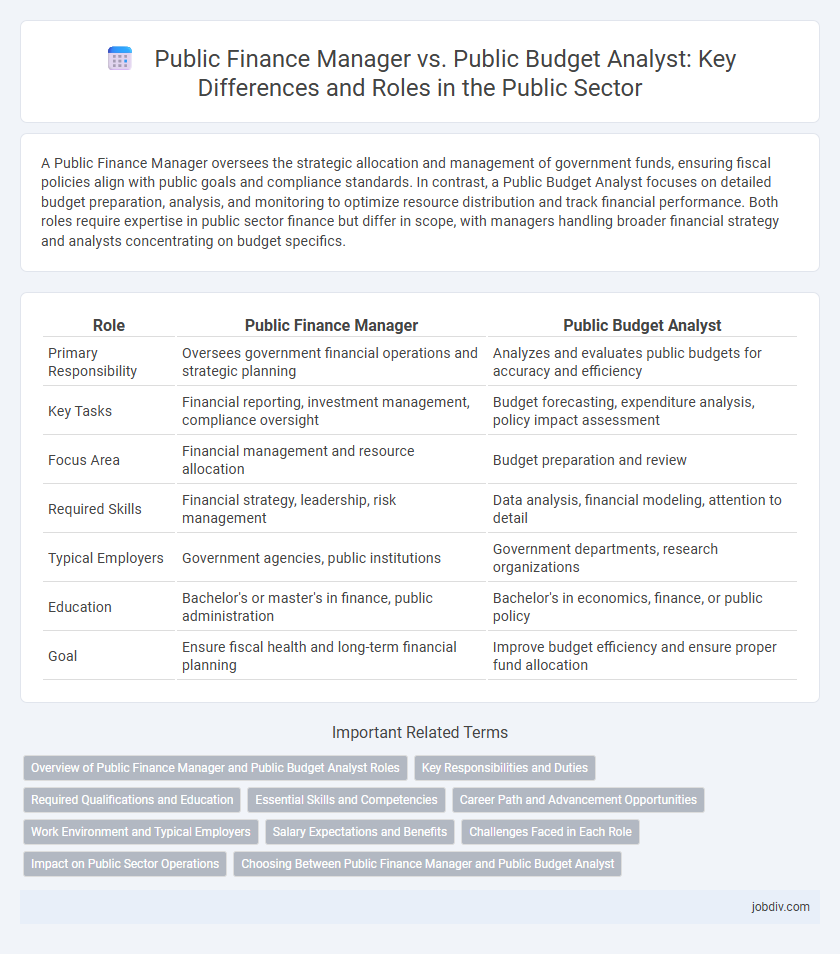
| Role | Public Finance Manager | Public Budget Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Oversees government financial operations and strategic planning | Analyzes and evaluates public budgets for accuracy and efficiency |
| Key Tasks | Financial reporting, investment management, compliance oversight | Budget forecasting, expenditure analysis, policy impact assessment |
| Focus Area | Financial management and resource allocation | Budget preparation and review |
| Required Skills | Financial strategy, leadership, risk management | Data analysis, financial modeling, attention to detail |
| Typical Employers | Government agencies, public institutions | Government departments, research organizations |
| Education | Bachelor's or master's in finance, public administration | Bachelor's in economics, finance, or public policy |
| Goal | Ensure fiscal health and long-term financial planning | Improve budget efficiency and ensure proper fund allocation |
Overview of Public Finance Manager and Public Budget Analyst Roles
Public Finance Managers oversee the management of government funds, ensuring efficient allocation and compliance with financial regulations. Public Budget Analysts evaluate budget proposals, analyze financial data, and provide recommendations to optimize resource distribution. Both roles involve critical analysis and strategic planning to support public sector fiscal responsibility.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
A Public Finance Manager oversees the strategic planning, management, and allocation of government funds to ensure fiscal responsibility and compliance with regulations. In contrast, a Public Budget Analyst focuses on evaluating budget proposals, analyzing financial data, and preparing detailed reports to guide decision-making processes. Both roles require expertise in financial analysis, but the manager emphasizes broader financial management and policy implementation, while the analyst prioritizes budgetary review and cost-benefit analysis.
Required Qualifications and Education
Public Finance Managers generally require a bachelor's degree in finance, economics, or public administration, with many positions favoring candidates who hold a master's degree or relevant certifications such as Certified Public Finance Officer (CPFO). Public Budget Analysts typically need a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, or public administration, with some roles valuing experience in budget management or advanced degrees for higher-level analysis positions. Both roles benefit from strong analytical skills, proficiency in financial software, and knowledge of government regulations and fiscal policies.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Public Finance Managers excel in strategic financial planning, fiscal policy analysis, and team leadership, ensuring effective allocation of public resources. Public Budget Analysts demonstrate strong analytical skills, proficiency in budget forecasting, and expertise in financial reporting to evaluate budget proposals and monitor expenditures. Both roles require a deep understanding of government regulations, quantitative analysis, and effective communication to support transparent and accountable public financial management.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Public Finance Managers often progress to senior leadership roles such as Director of Finance or Chief Financial Officer in government agencies, leveraging their expertise in managing public funds and strategic financial planning. Public Budget Analysts typically advance by specializing in budget forecasting, policy analysis, or by moving into advisory positions that influence fiscal decision-making at municipal, state, or federal levels. Both career paths offer opportunities for growth through advanced certifications like Certified Government Financial Manager (CGFM) and continued education in public administration or finance.
Work Environment and Typical Employers
Public Finance Managers typically work in government agencies, municipalities, and public sector organizations, overseeing financial strategy and compliance in office settings. Public Budget Analysts often operate within federal, state, or local government departments, analyzing budget proposals and expenditures in collaborative, data-driven environments. Both roles commonly require interaction with policymakers and financial teams, but Budget Analysts focus more on detailed budget preparation, while Finance Managers emphasize broader financial management and reporting.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Public Finance Managers typically earn higher salaries, with average annual pay ranging from $80,000 to $120,000, reflecting their broader responsibilities in managing government funds and financial strategies. Public Budget Analysts generally have salary expectations between $60,000 and $90,000, focusing on budget preparation and analysis. Benefits for both roles often include health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, but Public Finance Managers may receive additional executive perks and enhanced pension options due to their senior positions.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Public Finance Managers grapple with challenges such as ensuring accurate financial reporting, managing complex public funds, and aligning expenditures with policy goals amidst evolving regulations. Public Budget Analysts face difficulties in forecasting budget needs, analyzing allocation impacts, and advising on fiscal constraints while balancing diverse stakeholder interests. Both roles demand strong analytical skills and adaptability to shifting economic conditions and government priorities.
Impact on Public Sector Operations
Public Finance Managers oversee the strategic allocation of resources, ensuring efficient fund distribution that directly supports government programs and public services, thereby enhancing fiscal stability and operational effectiveness. Public Budget Analysts conduct detailed financial assessments and budget reviews, providing data-driven recommendations that optimize expenditure and improve accountability within public sector projects. Both roles are critical in shaping sustainable financial policies that impact the delivery and quality of public sector operations.
Choosing Between Public Finance Manager and Public Budget Analyst
Choosing between a Public Finance Manager and a Public Budget Analyst depends on career goals and expertise; a Public Finance Manager oversees the strategic management of public funds and financial operations, ensuring compliance with regulations and optimizing resource allocation. In contrast, a Public Budget Analyst focuses on preparing, analyzing, and monitoring budgets, providing detailed financial reports and forecasts to support decision-making. Professionals seeking leadership roles in financial policy and resource management may prefer the Public Finance Manager path, while those interested in data analysis and budget evaluation often find the Public Budget Analyst role more suitable.
Public Finance Manager vs Public Budget Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com