A Public Health Officer enforces policies and regulations to protect community health, often responding to outbreaks and ensuring compliance with health standards. A Public Health Educator focuses on creating and delivering educational programs to promote healthy behaviors and prevent diseases. Both roles are essential in public health, with the officer emphasizing regulation and the educator prioritizing awareness and prevention.
Table of Comparison
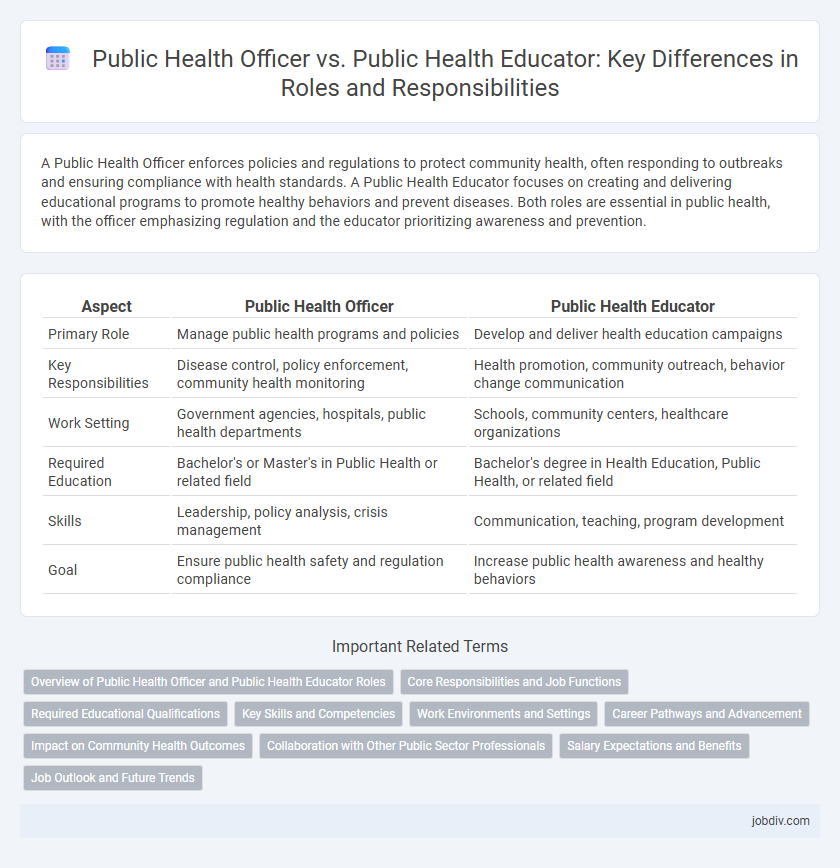
| Aspect | Public Health Officer | Public Health Educator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage public health programs and policies | Develop and deliver health education campaigns |
| Key Responsibilities | Disease control, policy enforcement, community health monitoring | Health promotion, community outreach, behavior change communication |
| Work Setting | Government agencies, hospitals, public health departments | Schools, community centers, healthcare organizations |
| Required Education | Bachelor's or Master's in Public Health or related field | Bachelor's degree in Health Education, Public Health, or related field |
| Skills | Leadership, policy analysis, crisis management | Communication, teaching, program development |
| Goal | Ensure public health safety and regulation compliance | Increase public health awareness and healthy behaviors |
Overview of Public Health Officer and Public Health Educator Roles
Public Health Officers focus on enforcing health regulations, managing disease prevention programs, and responding to public health emergencies to protect community health. Public Health Educators develop and implement educational campaigns, promote healthy behaviors, and work to improve health literacy among diverse populations. Both roles collaborate with government agencies and community organizations to enhance public health outcomes through prevention and education.
Core Responsibilities and Job Functions
Public Health Officers primarily focus on monitoring and controlling disease outbreaks, enforcing health regulations, and developing policies to protect community health. Public Health Educators design and implement programs aimed at promoting wellness and preventing illness through education and outreach activities. Both roles collaborate with healthcare providers and communities but differ in the balance between regulatory enforcement and educational initiatives.
Required Educational Qualifications
Public Health Officers typically require a bachelor's degree in public health, health administration, or a related field, with many positions favoring a master's degree such as an MPH (Master of Public Health). Public Health Educators generally need at least a bachelor's degree in health education, community health, or health promotion, while advanced roles may require a master's degree and certification like CHES (Certified Health Education Specialist). Both career paths benefit from specialized training in epidemiology, biostatistics, and health policy to effectively design and implement public health strategies.
Key Skills and Competencies
Public Health Officers excel in epidemiology, policy implementation, and emergency response coordination, emphasizing skills in data analysis, regulatory compliance, and community health assessment. Public Health Educators specialize in communication strategies, health promotion, and behavior change theories, demonstrating competencies in curriculum development, outreach program management, and cultural competence. Both roles require strong interpersonal abilities, but Officers prioritize strategic planning and enforcement, while Educators focus on educational outreach and advocacy.
Work Environments and Settings
Public Health Officers typically work in government agencies, hospitals, and emergency response units where they oversee health regulations and manage disease prevention programs. Public Health Educators are often found in community organizations, schools, and non-profits, focusing on developing educational campaigns and promoting healthy lifestyles. Both roles collaborate in clinics and public health departments but differ in their primary work environments and interaction levels with the community.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Public Health Officers typically follow career pathways that emphasize regulatory compliance, epidemiology, and emergency preparedness, advancing into roles such as Health Program Managers or Epidemiologists. Public Health Educators focus on designing and implementing community health education programs, progressing into positions like Health Promotion Specialists or Community Outreach Coordinators. Both careers offer opportunities for specialization and leadership, with advancement often supported by certifications such as Certified Health Education Specialist (CHES) or Public Health credentials.
Impact on Community Health Outcomes
Public Health Officers oversee policy implementation and emergency response strategies, directly influencing community health outcomes through regulatory enforcement and resource allocation. Public Health Educators enhance these outcomes by designing targeted health promotion programs that increase awareness and encourage preventive behaviors among diverse populations. Both roles are essential in reducing disease incidence and improving population health metrics by combining strategic oversight with education-driven behavioral change.
Collaboration with Other Public Sector Professionals
Public Health Officers collaborate closely with epidemiologists, policy makers, and emergency responders to design and implement health interventions. Public Health Educators work alongside community leaders, schools, and healthcare providers to promote health literacy and preventive behaviors. Both roles emphasize teamwork with public sector professionals to enhance community health outcomes and ensure coordinated public health strategies.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Public Health Officers typically earn higher salaries, with median annual incomes around $70,000, reflecting their broader responsibilities in policy enforcement and emergency response. Public Health Educators usually have median salaries near $55,000 but benefit from specialized training stipends and community outreach bonuses. Both roles offer comprehensive benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and opportunities for professional development.
Job Outlook and Future Trends
The job outlook for Public Health Officers remains strong, with a projected growth rate of 11% from 2022 to 2032, driven by increasing public health challenges and governmental health initiatives. Public Health Educators are expected to experience a similar growth rate, around 13%, fueled by rising demand for community health promotion and disease prevention programs. Future trends emphasize the integration of digital health technologies and data analytics in both roles, enhancing disease surveillance, health education, and policy implementation.
Public Health Officer vs Public Health Educator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com