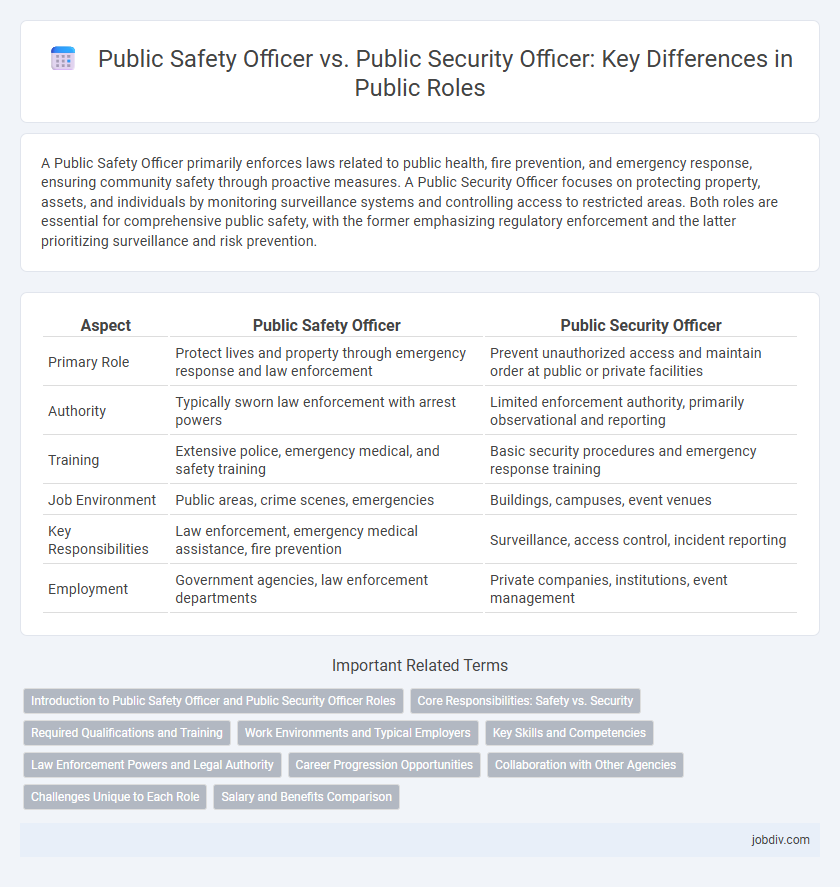
A Public Safety Officer primarily enforces laws related to public health, fire prevention, and emergency response, ensuring community safety through proactive measures. A Public Security Officer focuses on protecting property, assets, and individuals by monitoring surveillance systems and controlling access to restricted areas. Both roles are essential for comprehensive public safety, with the former emphasizing regulatory enforcement and the latter prioritizing surveillance and risk prevention.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Public Safety Officer | Public Security Officer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Protect lives and property through emergency response and law enforcement | Prevent unauthorized access and maintain order at public or private facilities |
| Authority | Typically sworn law enforcement with arrest powers | Limited enforcement authority, primarily observational and reporting |
| Training | Extensive police, emergency medical, and safety training | Basic security procedures and emergency response training |
| Job Environment | Public areas, crime scenes, emergencies | Buildings, campuses, event venues |
| Key Responsibilities | Law enforcement, emergency medical assistance, fire prevention | Surveillance, access control, incident reporting |
| Employment | Government agencies, law enforcement departments | Private companies, institutions, event management |
Introduction to Public Safety Officer and Public Security Officer Roles
Public Safety Officers are trained professionals responsible for maintaining community safety through emergency response, law enforcement, and public education. Public Security Officers primarily focus on protecting private property, controlling access, and monitoring surveillance to prevent unauthorized activities. Both roles require vigilance and effective communication to ensure secure environments in diverse settings.
Core Responsibilities: Safety vs. Security
Public Safety Officers focus on emergency response, risk prevention, and ensuring community health by managing hazards such as fires, accidents, and medical emergencies. Public Security Officers concentrate on protecting property, enforcing access control, and monitoring surveillance to deter theft, vandalism, and unauthorized entry. Both roles prioritize safeguarding individuals and assets, but Safety Officers emphasize life preservation, while Security Officers focus on crime prevention.
Required Qualifications and Training
Public Safety Officers typically require certifications in emergency medical response and law enforcement training, emphasizing skills in first aid, CPR, and basic police procedures. Public Security Officers often need specialized training in surveillance, conflict resolution, and property protection, with qualifications varying based on private security regulations. Both roles demand background checks and adherence to local licensing requirements, but Public Safety Officers usually undergo more rigorous state-mandated training programs.
Work Environments and Typical Employers
Public Safety Officers typically work in government agencies, emergency response teams, and community service organizations, operating in dynamic environments such as urban areas, schools, and public events to ensure citizen safety. Public Security Officers are often employed by private security firms, corporate facilities, and residential complexes, focusing on protecting property and monitoring surveillance systems within controlled environments like office buildings and gated communities. Both roles require collaboration with law enforcement but differ in their primary work settings and employer types, reflecting variations in operational scope and responsibilities.
Key Skills and Competencies
Public Safety Officers demonstrate expertise in emergency response, crowd control, and first aid, ensuring the well-being of communities during crises. Public Security Officers specialize in surveillance, access control, and threat detection to maintain secure environments in public and private spaces. Both roles require strong communication, situational awareness, and the ability to enforce laws and regulations effectively.
Law Enforcement Powers and Legal Authority
Public Safety Officers typically possess broader law enforcement powers, including the authority to arrest, detain, and enforce criminal laws within their jurisdiction. Public Security Officers generally have limited legal authority, focusing on protecting property, monitoring premises, and reporting incidents rather than performing arrests or engaging in criminal investigations. The distinction in legal authority is critical, as Public Safety Officers often hold sworn positions with state or local law enforcement agencies, whereas Public Security Officers operate primarily in a private or specialized security capacity.
Career Progression Opportunities
Public Safety Officers often have broader career progression opportunities due to their involvement in emergency response, law enforcement, and community services, which can lead to specialized roles such as fire investigation or emergency management. Public Security Officers typically focus on protecting property and enforcing access control, with career growth commonly advancing toward supervisory roles or corporate security management. Both career paths benefit from certifications and continued training, but Public Safety Officers generally have a wider scope for upward mobility within public sector agencies.
Collaboration with Other Agencies
Public Safety Officers collaborate closely with law enforcement, fire departments, and emergency medical services to coordinate responses during crises, ensuring comprehensive community protection. Public Security Officers primarily interface with private organizations and local businesses to prevent security breaches and support law enforcement efforts through information sharing. Effective interagency communication enhances situational awareness and resource allocation, fostering a unified approach to public safety challenges.
Challenges Unique to Each Role
Public Safety Officers face challenges related to emergency response, crisis management, and community policing that require extensive training in medical aid, conflict resolution, and public interaction. Public Security Officers primarily confront security risks such as unauthorized access, surveillance threats, and asset protection, emphasizing prevention and rapid incident reporting within private or corporate environments. Both roles demand vigilance and adaptability but differ in focus, with Public Safety Officers prioritizing life-saving interventions and Public Security Officers concentrating on safeguarding property and information integrity.
Salary and Benefits Comparison
Public Safety Officers typically earn an average salary ranging from $45,000 to $65,000 annually, often accompanied by comprehensive benefits including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave. Public Security Officers usually receive a slightly lower average salary, between $35,000 and $50,000 per year, with benefits commonly covering basic healthcare and limited pension options. Salary differences are influenced by job responsibilities, required training, and jurisdiction, making Public Safety Officers generally better compensated and supported in terms of benefits.
Public Safety Officer vs Public Security Officer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com