A Public Works Engineer specializes in designing, constructing, and maintaining public infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and water systems to ensure community safety and functionality. In contrast, a Public Utilities Manager oversees the operation, maintenance, and regulation of essential services like water supply, sewage treatment, and electricity distribution to guarantee consistent and reliable service delivery. Both roles require strong technical expertise and leadership skills but differ in scope, with engineers focusing on project execution and managers concentrating on utility operations and administration.
Table of Comparison
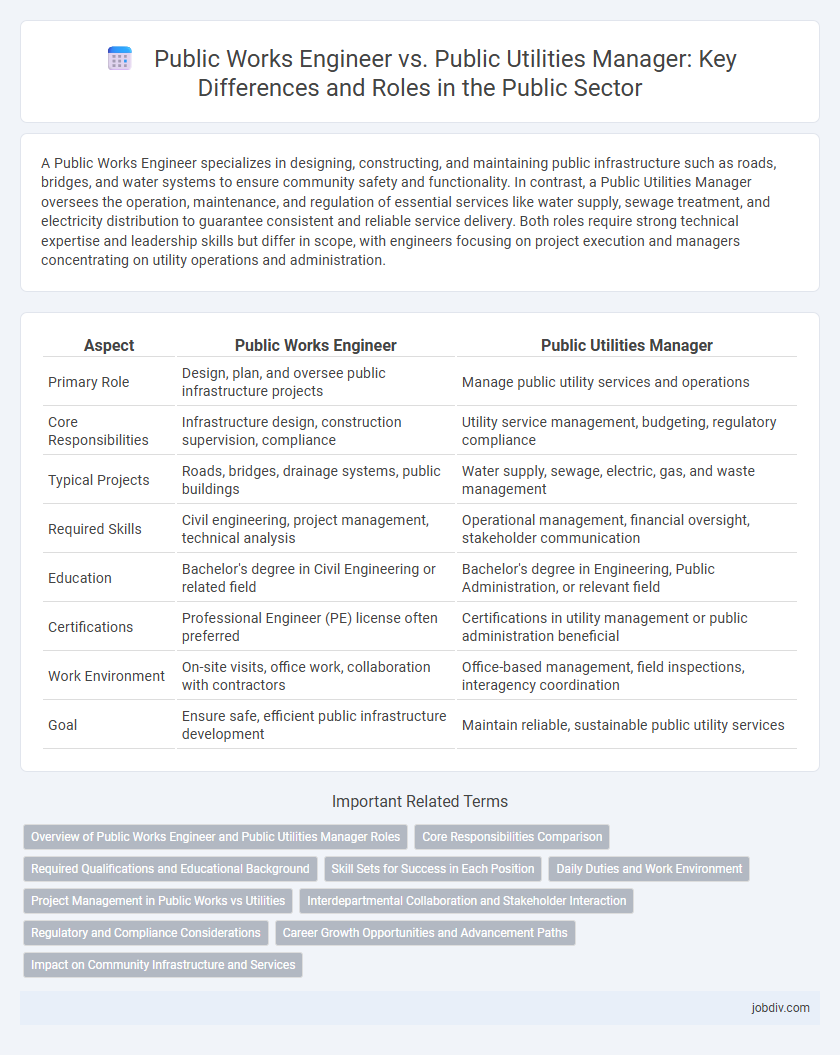
| Aspect | Public Works Engineer | Public Utilities Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Design, plan, and oversee public infrastructure projects | Manage public utility services and operations |
| Core Responsibilities | Infrastructure design, construction supervision, compliance | Utility service management, budgeting, regulatory compliance |
| Typical Projects | Roads, bridges, drainage systems, public buildings | Water supply, sewage, electric, gas, and waste management |
| Required Skills | Civil engineering, project management, technical analysis | Operational management, financial oversight, stakeholder communication |
| Education | Bachelor's degree in Civil Engineering or related field | Bachelor's degree in Engineering, Public Administration, or relevant field |
| Certifications | Professional Engineer (PE) license often preferred | Certifications in utility management or public administration beneficial |
| Work Environment | On-site visits, office work, collaboration with contractors | Office-based management, field inspections, interagency coordination |
| Goal | Ensure safe, efficient public infrastructure development | Maintain reliable, sustainable public utility services |
Overview of Public Works Engineer and Public Utilities Manager Roles
Public Works Engineers design, develop, and maintain infrastructure projects such as roads, bridges, and public buildings to ensure community safety and functionality. Public Utilities Managers oversee the operation and maintenance of public utility services including water supply, sewage treatment, and electrical distribution, focusing on regulatory compliance and resource management. Both roles require collaboration with government agencies and stakeholders to optimize public service delivery and infrastructure sustainability.
Core Responsibilities Comparison
Public Works Engineers focus on designing, constructing, and maintaining infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and public buildings, ensuring compliance with safety and engineering standards. Public Utilities Managers oversee the operation and maintenance of essential services like water supply, sewage, and electricity distribution, managing budgets and coordinating service delivery. Both roles require strong project management skills, but Public Works Engineers emphasize technical engineering tasks, while Public Utilities Managers prioritize utility service operations and regulatory compliance.
Required Qualifications and Educational Background
Public Works Engineers typically require a Bachelor's degree in Civil Engineering or a related field, along with professional engineer (PE) licensure and experience in infrastructure design and project management. Public Utilities Managers often hold a degree in Environmental Science, Engineering, or Business Administration, complemented by certifications in utility management and extensive knowledge of regulatory compliance. Both roles demand strong analytical skills and experience with public sector standards, but Public Works Engineers focus more on technical engineering qualifications while Utilities Managers prioritize operational oversight and regulatory expertise.
Skill Sets for Success in Each Position
A Public Works Engineer excels in technical skills such as civil engineering, project design, and infrastructure management, ensuring efficient construction and maintenance of public facilities. A Public Utilities Manager requires strong leadership, regulatory knowledge, and budget management capabilities to oversee utility services like water, gas, and electricity effectively. Both positions demand problem-solving abilities and communication skills, but engineers emphasize technical proficiency while managers focus on operational and administrative expertise.
Daily Duties and Work Environment
Public Works Engineers primarily focus on designing, maintaining, and overseeing infrastructure projects such as roads, bridges, and water systems, often working onsite to ensure compliance with engineering standards and safety regulations. Public Utilities Managers supervise the operation and maintenance of essential services like water, gas, and electricity, coordinating teams, managing budgets, and ensuring regulatory compliance within office and field environments. Both roles require collaboration with government agencies and contractors, but Public Works Engineers emphasize technical design and project execution, whereas Public Utilities Managers concentrate on operational management and service delivery.
Project Management in Public Works vs Utilities
Public Works Engineers specialize in the planning, design, and execution of infrastructure projects such as roads, bridges, and public buildings, ensuring adherence to engineering standards and municipal regulations. Public Utilities Managers oversee the operation, maintenance, and improvement of essential services like water, gas, and electricity, focusing on resource management and regulatory compliance. Project management in public works emphasizes construction timelines, civil engineering requirements, and public safety, while utilities project management centers on system reliability, service continuity, and utility-specific regulatory frameworks.
Interdepartmental Collaboration and Stakeholder Interaction
Public Works Engineers coordinate closely with municipal departments to design and oversee infrastructure projects, ensuring technical specifications align with community needs. Public Utilities Managers engage with a broader range of stakeholders, including regulatory agencies, service providers, and the public, to maintain and improve utility services. Both roles require strong interdepartmental collaboration to facilitate efficient resource allocation and address complex urban challenges.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Public Works Engineers focus on designing and managing infrastructure projects while ensuring adherence to construction codes, environmental regulations, and safety standards. Public Utilities Managers oversee utility services such as water and electricity, emphasizing compliance with federal, state, and local regulations including EPA guidelines and utility commission mandates. Both roles require thorough knowledge of regulatory frameworks to maintain public safety and operational efficiency in municipal services.
Career Growth Opportunities and Advancement Paths
Public Works Engineers typically advance by gaining specialized expertise in infrastructure design, project management, and civil engineering, often moving into senior engineering roles or departmental leadership within municipal agencies. Public Utilities Managers focus on overseeing essential services like water, electricity, and waste management, progressing toward higher executive positions such as Utility Director or Regional Manager, emphasizing operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. Both career paths offer growth through advanced certifications, leadership experience, and increased responsibility managing public infrastructure and services.
Impact on Community Infrastructure and Services
Public Works Engineers design and oversee the construction and maintenance of critical infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and public buildings, directly enhancing community safety and accessibility. Public Utilities Managers focus on the operation and management of essential services including water supply, wastewater treatment, and electricity distribution, ensuring reliable and efficient utility delivery. Both roles are vital in sustaining and improving community infrastructure, with engineers emphasizing structural development and managers prioritizing utility service continuity and quality.
Public Works Engineer vs Public Utilities Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com