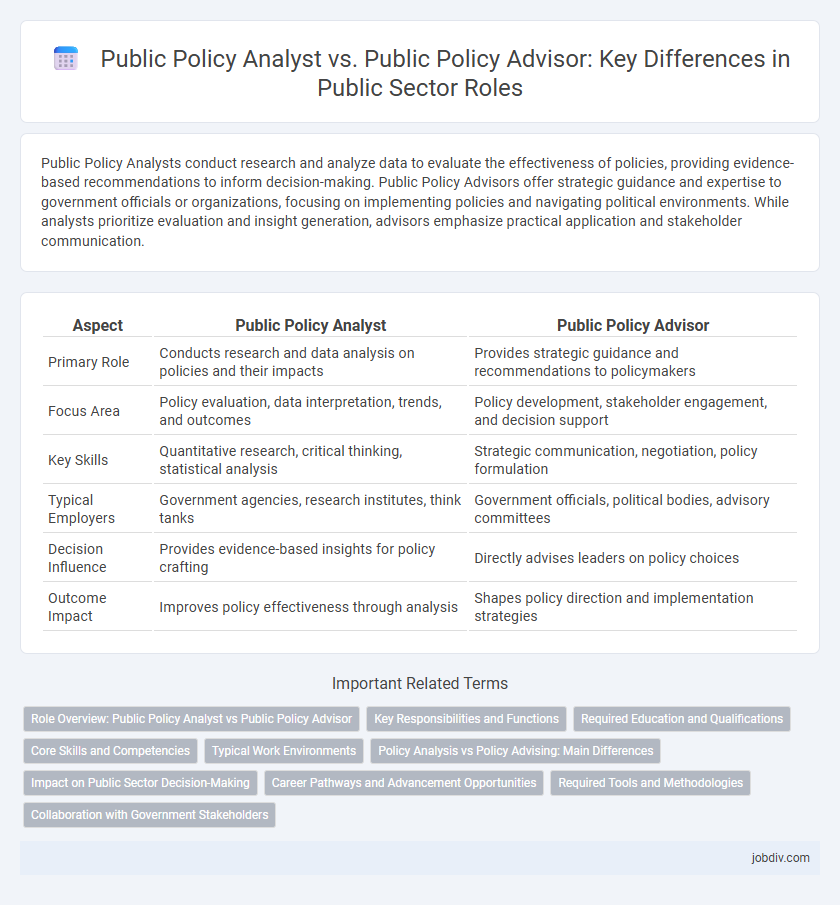
Public Policy Analysts conduct research and analyze data to evaluate the effectiveness of policies, providing evidence-based recommendations to inform decision-making. Public Policy Advisors offer strategic guidance and expertise to government officials or organizations, focusing on implementing policies and navigating political environments. While analysts prioritize evaluation and insight generation, advisors emphasize practical application and stakeholder communication.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Public Policy Analyst | Public Policy Advisor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Conducts research and data analysis on policies and their impacts | Provides strategic guidance and recommendations to policymakers |
| Focus Area | Policy evaluation, data interpretation, trends, and outcomes | Policy development, stakeholder engagement, and decision support |
| Key Skills | Quantitative research, critical thinking, statistical analysis | Strategic communication, negotiation, policy formulation |
| Typical Employers | Government agencies, research institutes, think tanks | Government officials, political bodies, advisory committees |
| Decision Influence | Provides evidence-based insights for policy crafting | Directly advises leaders on policy choices |
| Outcome Impact | Improves policy effectiveness through analysis | Shapes policy direction and implementation strategies |
Role Overview: Public Policy Analyst vs Public Policy Advisor
Public Policy Analysts conduct research, evaluate data, and assess policy impacts to inform decision-making processes, focusing on evidence-based analysis and strategic recommendations. Public Policy Advisors provide expert guidance and strategic advice to government officials or organizations, emphasizing practical solutions and policy implementation. While Analysts prioritize data-driven insights, Advisors focus on applying these insights to shape and influence policy decisions effectively.
Key Responsibilities and Functions
Public Policy Analysts conduct in-depth research, data analysis, and evaluation of policy impacts to provide evidence-based recommendations for decision-making. Public Policy Advisors focus on strategic guidance, stakeholder engagement, and translating complex policy information into actionable advice for government officials or organizations. Both roles require strong communication skills, but analysts prioritize analytical rigor while advisors emphasize practical implementation and influence.
Required Education and Qualifications
Public Policy Analysts typically require a bachelor's degree in public administration, political science, economics, or related fields, often complemented by advanced degrees such as a master's in public policy for specialized roles. Public Policy Advisors usually need similar educational backgrounds but place a stronger emphasis on extensive professional experience and advanced certifications in policy analysis, negotiation, or management. Both roles value strong analytical skills, knowledge of governmental processes, and the ability to interpret complex data for policy development and recommendations.
Core Skills and Competencies
Public Policy Analysts excel in research, data evaluation, and policy impact assessment, utilizing quantitative analysis and critical thinking to develop evidence-based recommendations. Public Policy Advisors concentrate on strategic communication, stakeholder engagement, and practical policy implementation, leveraging negotiation skills and political acumen to influence decision-making. Both roles demand proficiency in policy analysis, but Analysts prioritize analytical rigor while Advisors emphasize advisory expertise and interpersonal interaction.
Typical Work Environments
Public Policy Analysts typically work in government agencies, research institutions, and think tanks where they conduct data-driven research and evaluate policy impacts. Public Policy Advisors often operate within political offices, legislative bodies, and advocacy organizations, providing strategic recommendations and guidance to decision-makers. Both roles require collaboration with stakeholders, but Analysts focus more on empirical analysis, while Advisors emphasize policy implementation and stakeholder engagement.
Policy Analysis vs Policy Advising: Main Differences
Public Policy Analysts specialize in researching, evaluating, and interpreting data to develop evidence-based policy recommendations, focusing on quantitative and qualitative analysis. Public Policy Advisors use this analysis to guide decision-makers by offering strategic advice, practical solutions, and communication tailored to political and public contexts. The main difference lies in Analysts' emphasis on data-driven research and Advisors' role in applying insights to influence policy implementation and stakeholder engagement.
Impact on Public Sector Decision-Making
Public Policy Analysts rigorously evaluate data and policy proposals to provide evidence-based recommendations that enhance government effectiveness. Public Policy Advisors leverage these analyses to guide elected officials in strategic decision-making, ensuring alignment with political goals and public interests. Both roles critically shape public sector decisions by blending analytical precision with strategic counsel, directly influencing policy outcomes and governance quality.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Public Policy Analysts primarily conduct research, analyze data, and evaluate policies to provide evidence-based recommendations, often starting in entry-level government or nonprofit roles with opportunities to advance into senior analyst or management positions. Public Policy Advisors typically leverage extensive experience to offer strategic guidance to policymakers and senior officials, with career pathways often leading to influential roles within government agencies, think tanks, or consultancy firms. Advancement in both careers depends on expertise development, networking, and demonstrated impact on policy formulation and implementation.
Required Tools and Methodologies
Public Policy Analysts rely on quantitative tools such as statistical software (e.g., SPSS, Stata), data visualization platforms (e.g., Tableau), and cost-benefit analysis methodologies to evaluate policy effectiveness and predict outcomes. Public Policy Advisors utilize qualitative research methods, stakeholder consultation frameworks, and scenario planning techniques to provide strategic recommendations and guide decision-making processes. Both roles demand proficiency in policy analysis frameworks and advanced data interpretation skills to influence public sector strategies effectively.
Collaboration with Government Stakeholders
Public Policy Analysts conduct in-depth research and data analysis to inform evidence-based recommendations, collaborating closely with government departments to ensure policies are grounded in empirical insights. Public Policy Advisors leverage their expertise and strategic communication skills to engage with policymakers and stakeholders, facilitating alignment and consensus on policy objectives. Both roles prioritize continuous interaction with government officials to advance effective, coherent public policy outcomes.
Public Policy Analyst vs Public Policy Advisor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com