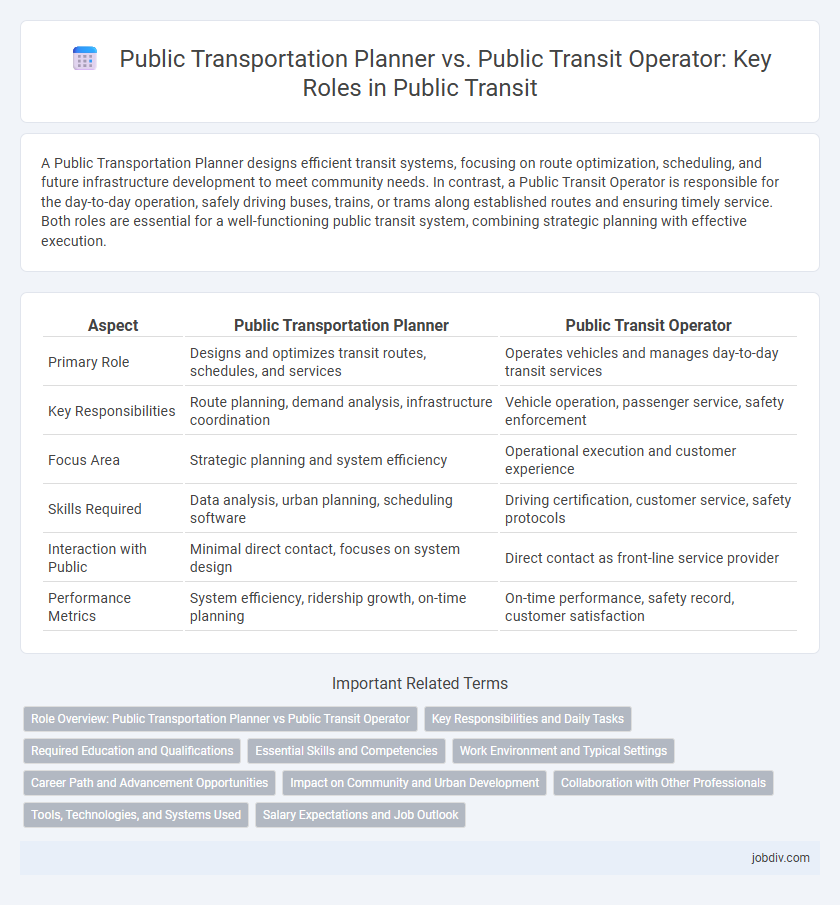
A Public Transportation Planner designs efficient transit systems, focusing on route optimization, scheduling, and future infrastructure development to meet community needs. In contrast, a Public Transit Operator is responsible for the day-to-day operation, safely driving buses, trains, or trams along established routes and ensuring timely service. Both roles are essential for a well-functioning public transit system, combining strategic planning with effective execution.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Public Transportation Planner | Public Transit Operator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Designs and optimizes transit routes, schedules, and services | Operates vehicles and manages day-to-day transit services |
| Key Responsibilities | Route planning, demand analysis, infrastructure coordination | Vehicle operation, passenger service, safety enforcement |
| Focus Area | Strategic planning and system efficiency | Operational execution and customer experience |
| Skills Required | Data analysis, urban planning, scheduling software | Driving certification, customer service, safety protocols |
| Interaction with Public | Minimal direct contact, focuses on system design | Direct contact as front-line service provider |
| Performance Metrics | System efficiency, ridership growth, on-time planning | On-time performance, safety record, customer satisfaction |
Role Overview: Public Transportation Planner vs Public Transit Operator
Public Transportation Planners analyze transit patterns, design routes, and develop strategies to improve efficiency and accessibility in urban mobility systems. Public Transit Operators are responsible for safely driving buses, trains, or other vehicles according to established schedules, ensuring timely passenger transport. While planners focus on system-wide optimization and policy development, operators execute daily operations and interact directly with commuters.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Public Transportation Planners analyze transit data, design efficient routes, and develop long-term transportation strategies to improve public mobility and reduce congestion. Public Transit Operators are responsible for safely driving buses, trains, or trams on established routes, managing passenger interactions, and adhering to schedules. While planners focus on system-wide optimization and policy development, operators ensure daily service reliability and passenger safety.
Required Education and Qualifications
Public Transportation Planners typically require a bachelor's degree in urban planning, transportation engineering, or a related field, with many positions favoring a master's degree and experience in GIS and data analysis. Public Transit Operators generally need a high school diploma or equivalent, along with completion of a formal training program, obtaining a commercial driver's license (CDL), and passing background checks and drug screenings. Planners focus on strategic development and policy-making, whereas operators emphasize safety, vehicle operation, and customer service.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Public Transportation Planners excel in data analysis, route optimization, and strategic planning to improve transit efficiency and accessibility. Public Transit Operators demonstrate strong vehicle operation skills, safety compliance, and customer service expertise to ensure reliable and secure passenger transport. Both roles require effective communication, problem-solving abilities, and knowledge of transportation regulations to support smooth public transit operations.
Work Environment and Typical Settings
Public Transportation Planners typically work in office environments using advanced software to design routes, schedules, and infrastructure improvements for urban transit systems. Public Transit Operators spend their work shifts on the road or tracks, operating buses, trains, or trams in dynamic, often outdoor settings with direct interaction with passengers. Planners coordinate with city officials and engineers, while operators focus on adhering to schedules and safety protocols within real-time transit environments.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Public Transportation Planners specialize in designing efficient transit systems, using data analysis and urban planning skills to develop long-term transportation strategies, often advancing to roles like senior planner or transit agency manager. Public Transit Operators focus on the day-to-day operation of buses, trains, or other transit vehicles, with career growth opportunities including positions such as lead operator, dispatcher, or supervisor. Both career paths offer opportunities for advancement by gaining certifications, experience, and leadership skills within the public transportation sector.
Impact on Community and Urban Development
Public Transportation Planners design comprehensive transit systems that enhance urban mobility, reduce traffic congestion, and promote sustainable development, directly influencing community growth and land use patterns. Public Transit Operators ensure the daily execution of these plans by managing vehicles and schedules, providing reliable services that connect neighborhoods and support economic activity. Together, their coordinated efforts improve accessibility, reduce carbon emissions, and foster inclusive urban environments.
Collaboration with Other Professionals
Public transportation planners work closely with urban planners, engineers, and data analysts to design efficient transit routes and improve system infrastructure. Public transit operators collaborate primarily with dispatchers, maintenance crews, and safety inspectors to ensure timely and safe vehicle operations. Effective collaboration between planners and operators enhances service reliability and meets community mobility needs.
Tools, Technologies, and Systems Used
Public Transportation Planners utilize advanced Geographic Information Systems (GIS), data analytics platforms, and simulation software to design efficient transit routes and schedules. Public Transit Operators rely on real-time vehicle tracking systems, automated fare collection technologies, and communication tools like radio dispatch and mobile apps for effective passenger service management. Both professionals leverage integrated transit management systems to enhance coordination and operational efficiency across urban transit networks.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Public Transportation Planners typically earn an average salary ranging from $60,000 to $90,000 annually, reflecting their role in designing and improving transit systems, while Public Transit Operators usually have lower average salaries between $30,000 and $50,000 due to their focus on operating transit vehicles such as buses and trains. The job outlook for Public Transportation Planners is projected to grow by about 6% over the next decade, driven by urban development and the need for sustainable transportation solutions, whereas Public Transit Operator positions are expected to grow slower, around 4%, influenced by automation and changing ridership patterns. Both careers offer stable employment opportunities with regional variations depending on transit infrastructure investment and population density.
Public Transportation Planner vs Public Transit Operator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com