Public Health Educators design and implement programs to improve community health through direct education and outreach, focusing on behavior change and health promotion. Health Communication Specialists craft strategic messages tailored for diverse audiences using media channels to effectively disseminate health information and influence public perceptions. Both roles are essential in advancing public health but differ in methods, with educators engaging face-to-face and specialists utilizing communication technologies.
Table of Comparison
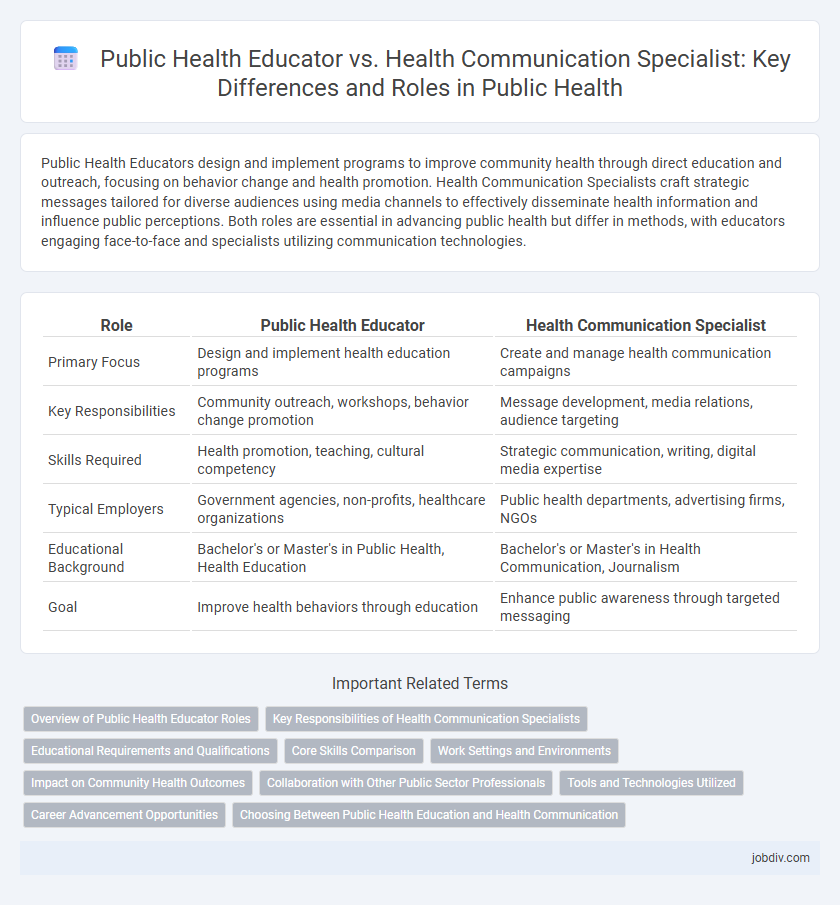
| Role | Public Health Educator | Health Communication Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Design and implement health education programs | Create and manage health communication campaigns |
| Key Responsibilities | Community outreach, workshops, behavior change promotion | Message development, media relations, audience targeting |
| Skills Required | Health promotion, teaching, cultural competency | Strategic communication, writing, digital media expertise |
| Typical Employers | Government agencies, non-profits, healthcare organizations | Public health departments, advertising firms, NGOs |
| Educational Background | Bachelor's or Master's in Public Health, Health Education | Bachelor's or Master's in Health Communication, Journalism |
| Goal | Improve health behaviors through education | Enhance public awareness through targeted messaging |
Overview of Public Health Educator Roles
Public Health Educators design and implement programs aimed at promoting healthy behaviors and preventing disease within communities. They analyze community needs, develop educational materials, and collaborate with healthcare providers to improve public health outcomes. Their role emphasizes direct interaction and advocacy to empower individuals with knowledge and resources for better health decisions.
Key Responsibilities of Health Communication Specialists
Health Communication Specialists design and implement targeted communication strategies that promote public health awareness and behavior change through multimedia campaigns, social media, and community outreach. They analyze audience data and health trends to craft clear, culturally sensitive messages that enhance public understanding of health issues. Their key responsibilities include developing educational materials, managing public relations efforts, and collaborating with healthcare providers to ensure consistent and effective health messaging.
Educational Requirements and Qualifications
Public Health Educators typically require a bachelor's degree in public health, health education, or a related field, with many positions preferring a Certified Health Education Specialist (CHES) credential for professional recognition. Health Communication Specialists often hold degrees in communication, public health, or journalism, emphasizing skills in crafting targeted health messages and media strategies. Both roles benefit from experience in community outreach and knowledge of behavior change theories, but Health Communication Specialists may require advanced training in digital media and health informatics.
Core Skills Comparison
Public Health Educators excel in community outreach, program development, and behavior change strategies, emphasizing health promotion and disease prevention at the population level. Health Communication Specialists specialize in crafting targeted messages, media relations, and strategic communication campaigns to influence public health policies and awareness. Both roles require expertise in cultural competency, data analysis, and health literacy, but Public Health Educators focus more on direct education, while Health Communication Specialists prioritize message design and dissemination.
Work Settings and Environments
Public Health Educators typically work in community health centers, schools, government agencies, and nonprofit organizations where they design and implement educational programs to improve population health. Health Communication Specialists are often employed by healthcare organizations, marketing firms, media outlets, and public relations agencies, focusing on crafting targeted health messages for diverse audiences across multiple platforms. Both roles require adapting communication strategies to specific work environments, with Public Health Educators emphasizing direct community engagement and Health Communication Specialists specializing in strategic media outreach.
Impact on Community Health Outcomes
Public Health Educators design and implement community-based programs to improve health knowledge and behaviors, directly influencing disease prevention and health promotion. Health Communication Specialists craft targeted messaging campaigns that effectively disseminate vital health information, enhancing public awareness and motivating behavior change. Both roles are critical in improving community health outcomes by addressing different facets of education and communication strategies.
Collaboration with Other Public Sector Professionals
Public Health Educators collaborate closely with community health workers, policymakers, and healthcare providers to design and implement effective health programs targeting specific populations. Health Communication Specialists work alongside media professionals, public relations officers, and government agencies to craft persuasive messages that promote healthy behaviors and inform public health campaigns. Both roles require strong interdisciplinary teamwork within the public sector to maximize the impact of health initiatives and improve population outcomes.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
Public Health Educators primarily utilize community outreach platforms, educational software, and health data analysis tools to design and implement health promotion programs. Health Communication Specialists rely on digital content creation tools, social media management software, and analytics platforms to craft and disseminate targeted health messages. Both roles leverage health informatics systems and mobile health applications to enhance public engagement and measure communication effectiveness.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Public Health Educators often advance by developing community programs and securing leadership roles in health promotion, leveraging skills in direct outreach and program management. Health Communication Specialists progress through strategic roles that emphasize media campaigns, digital content creation, and analytics to influence public behavior at a larger scale. Both careers offer pathways to senior positions in government agencies, non-profits, and healthcare organizations, with emphasis on specialized expertise in education or communication strategies driving upward mobility.
Choosing Between Public Health Education and Health Communication
Public Health Educators design and implement programs to promote community health awareness, focusing on behavior change and preventive measures. Health Communication Specialists craft targeted messages and utilize media channels to influence public perception and encourage health-positive actions. Selecting between the two roles depends on whether the objective centers more on direct community engagement and education or strategic message development and media dissemination.
Public Health Educator vs Health Communication Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com