Line editing sharpens sentence structure, word choice, and flow to enhance readability and style, while content editing addresses the overall narrative, organization, and clarity of ideas to ensure the story or message is coherent and engaging. Both types of editing are crucial in publishing pets to create a polished, captivating book that resonates with readers. Choosing the right editing process depends on the manuscript's needs, whether refining language details or reshaping the core content.
Table of Comparison
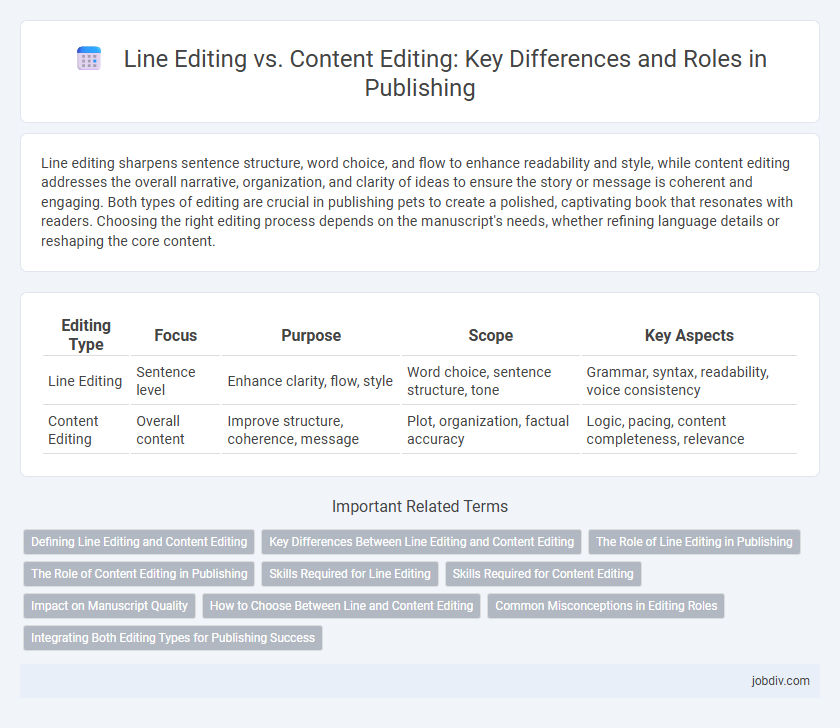
| Editing Type | Focus | Purpose | Scope | Key Aspects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line Editing | Sentence level | Enhance clarity, flow, style | Word choice, sentence structure, tone | Grammar, syntax, readability, voice consistency |
| Content Editing | Overall content | Improve structure, coherence, message | Plot, organization, factual accuracy | Logic, pacing, content completeness, relevance |
Defining Line Editing and Content Editing
Line editing involves refining sentence structure, word choice, and flow to enhance clarity and readability at the sentence and paragraph level. Content editing focuses on evaluating the overall structure, organization, and coherence of the manuscript, ensuring consistency and logical progression of ideas. Both editing types are essential for producing polished, publication-ready texts that effectively convey the author's message.
Key Differences Between Line Editing and Content Editing
Line editing concentrates on enhancing sentence structure, word choice, and flow to improve readability and style, focusing on the micro-level details of the text. Content editing addresses macro-level elements such as plot consistency, character development, and overall narrative coherence, ensuring the story or message is clear and engaging. The key difference lies in line editing refining language mechanics, while content editing shapes the substance and organization of the manuscript.
The Role of Line Editing in Publishing
Line editing plays a critical role in publishing by refining sentence structure, word choice, and flow to enhance readability and maintain the author's voice. This process ensures clarity and consistency throughout the manuscript, targeting grammar, pacing, and tone at a detailed level. Effective line editing bridges the gap between raw content and polished text, preparing the work for successful publication.
The Role of Content Editing in Publishing
Content editing plays a crucial role in publishing by ensuring the manuscript's overall structure, coherence, and clarity meet the target audience's expectations. It involves assessing plot development, character consistency, and thematic elements to enhance the narrative's effectiveness and engagement. Unlike line editing, which focuses on grammar and syntax, content editing shapes the foundational elements that determine a work's market readiness and editorial quality.
Skills Required for Line Editing
Line editing demands a keen eye for grammar, syntax, and style to enhance sentence structure and readability while maintaining the author's voice. Expertise in identifying repetitive phrasing, awkward transitions, and inconsistencies in tone is essential for refining prose at the sentence and paragraph levels. Proficiency with detailed language mechanics and the ability to enhance clarity and flow distinguish skilled line editors from broader content editors.
Skills Required for Content Editing
Content editing demands a deep understanding of narrative structure, character development, and thematic consistency to ensure the manuscript's overall coherence and engagement. Critical skills include the ability to evaluate pacing, plot progression, and audience targeting while providing actionable feedback to enhance clarity and impact. Proficiency in language mechanics complements these skills but is secondary to the broader analytical and creative competencies essential for effective content editing.
Impact on Manuscript Quality
Line editing enhances manuscript quality by refining sentence structure, grammar, and style, ensuring clarity and readability at the sentence level. Content editing improves overall coherence and flow by addressing plot development, character consistency, and thematic elements, resulting in a more compelling narrative. Both editing types are essential for producing polished, professional-quality manuscripts that engage readers effectively.
How to Choose Between Line and Content Editing
Choosing between line editing and content editing depends on the manuscript's current state and author goals; content editing addresses overall structure, plot, pacing, and character development, while line editing hones sentence flow, clarity, grammar, and style. Manuscripts with major narrative or logical issues benefit from content editing to ensure coherence and engagement before refining prose through line editing. Evaluating specific weaknesses and desired outcomes guides authors to select the editing level that maximizes manuscript quality and reader impact.
Common Misconceptions in Editing Roles
Line editing and content editing are often confused, but they serve distinct purposes in the publishing process. Line editing emphasizes sentence structure, word choice, and flow, targeting clarity and style, while content editing focuses on the overall organization, plot consistency, and thematic development of a manuscript. Misunderstandings arise when authors expect content edits from line editors or stylistic fine-tuning from content editors, leading to misaligned expectations in editing roles.
Integrating Both Editing Types for Publishing Success
Integrating line editing and content editing enhances the overall quality of a manuscript by addressing both clarity and structural coherence. Line editing refines language precision, sentence flow, and tone, while content editing ensures plot consistency, character development, and thematic depth. Combining these editing types creates a polished, compelling narrative essential for publishing success.
Line Editing vs Content Editing Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com