Typesetters focus on arranging text with precision, ensuring fonts, spacing, and alignment meet publishing standards for readability. Layout designers integrate text and images, creating visually appealing pages that enhance the reader's experience by balancing content structure and aesthetic elements. Both roles are critical in producing polished publications, with typesetters emphasizing textual accuracy and layout designers prioritizing overall design harmony.
Table of Comparison
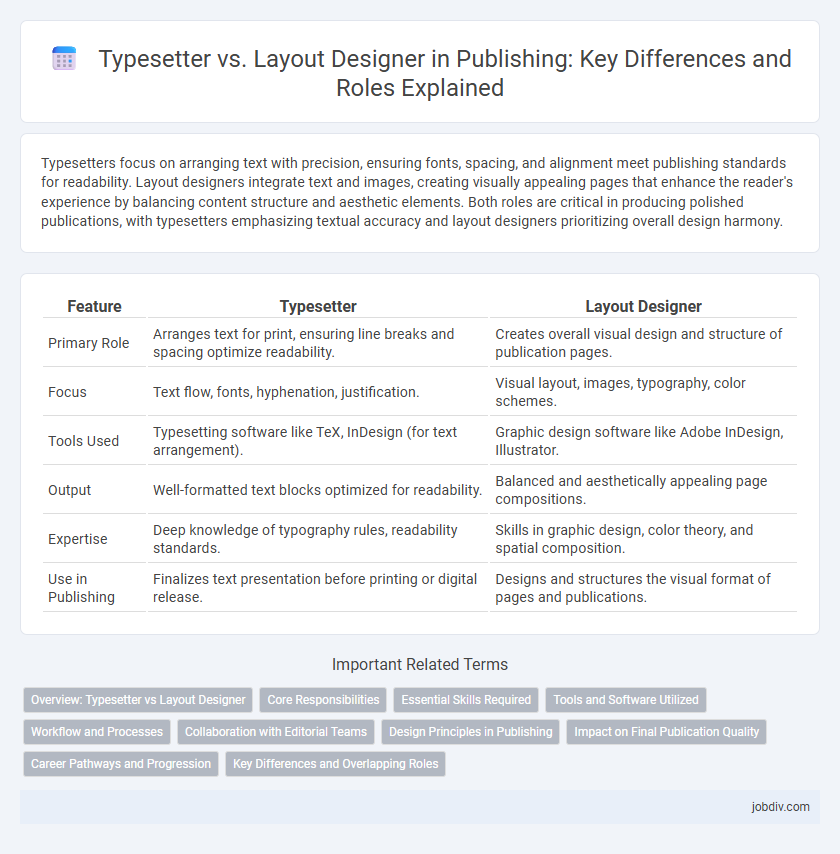
| Feature | Typesetter | Layout Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Arranges text for print, ensuring line breaks and spacing optimize readability. | Creates overall visual design and structure of publication pages. |
| Focus | Text flow, fonts, hyphenation, justification. | Visual layout, images, typography, color schemes. |
| Tools Used | Typesetting software like TeX, InDesign (for text arrangement). | Graphic design software like Adobe InDesign, Illustrator. |
| Output | Well-formatted text blocks optimized for readability. | Balanced and aesthetically appealing page compositions. |
| Expertise | Deep knowledge of typography rules, readability standards. | Skills in graphic design, color theory, and spatial composition. |
| Use in Publishing | Finalizes text presentation before printing or digital release. | Designs and structures the visual format of pages and publications. |
Overview: Typesetter vs Layout Designer
A typesetter specializes in arranging text for print, ensuring the accuracy of fonts, spacing, and alignment to create readable content. A layout designer focuses on the overall visual composition of a page, balancing text, images, and white space to achieve aesthetic appeal and effective communication. Both roles are essential in publishing, with typesetting emphasizing text detail and layout design prioritizing the holistic presentation.
Core Responsibilities
Typesetters specialize in arranging text accurately and ensuring consistent font styles, sizes, and spacing to enhance readability and prepare manuscripts for printing or digital publication. Layout designers focus on the visual organization of text, images, and graphic elements to create aesthetically appealing and functional page designs that align with a publication's branding and target audience. Both roles collaborate closely to maintain balance between content clarity and visual presentation in publishing projects.
Essential Skills Required
Typesetters require precision in typography, font management, and attention to detail to ensure textual content is readable and error-free. Layout designers must master graphic design principles, spatial arrangement, and the use of design software such as Adobe InDesign or QuarkXPress to create visually compelling page compositions. Both roles demand strong collaboration skills and an understanding of the publishing workflow to produce cohesive printed or digital materials.
Tools and Software Utilized
Typesetters primarily utilize software such as Adobe InDesign, QuarkXPress, and LaTeX to arrange text and ensure accurate font, spacing, and alignment in preparing manuscripts for printing. Layout designers leverage advanced tools like Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, and InDesign to create visually compelling page arrangements incorporating images, graphics, and typography for aesthetic appeal. Both roles require proficiency in digital publishing software, but typesetters emphasize text accuracy and consistency while layout designers focus on creative visual composition.
Workflow and Processes
Typesetters specialize in arranging text for readability and typographic accuracy, ensuring manuscripts meet publication standards through precise font selection, spacing, and alignment. Layout designers focus on integrating visual elements like images, graphics, and typographic hierarchy to create visually engaging pages that enhance user experience and brand identity. Workflow processes for typesetters emphasize content formatting and error correction, whereas layout designers prioritize creative composition and spatial organization within publication templates.
Collaboration with Editorial Teams
Typesetters meticulously format manuscripts to ensure text consistency and readability, while layout designers create visually engaging page compositions that enhance user experience. Collaboration between these roles and editorial teams streamlines revisions, aligning textual accuracy with aesthetic presentation. Effective communication ensures that editorial changes are seamlessly integrated into both the content and design, optimizing publication quality.
Design Principles in Publishing
Typesetters focus on arranging text for readability and typographic consistency, ensuring proper font selection, line spacing, and alignment to optimize the flow of content. Layout designers prioritize the overall visual structure, integrating images, white space, and graphic elements to create an engaging and balanced page composition. Both roles apply core design principles such as hierarchy, contrast, and alignment to enhance user experience and maintain publication standards.
Impact on Final Publication Quality
Typesetters ensure precise text formatting, correct line spacing, and font consistency, directly influencing the readability and professional appearance of the publication. Layout designers create visual hierarchies, arrange images and text blocks, and balance white space, which enhances user engagement and aesthetic appeal. The collaboration between typesetters and layout designers results in a polished final product that meets both functional and artistic standards in publishing quality.
Career Pathways and Progression
Typesetters specialize in preparing text for print or digital formats, focusing on font selection, spacing, and alignment to ensure readability and aesthetic appeal, often starting as apprentices or assistants before advancing to lead typesetting roles. Layout designers integrate typography, images, and graphics to create visually compelling pages for magazines, books, or digital media, commonly progressing from junior designer positions to senior or art director roles. Career pathways in publishing highlight typesetters transitioning into digital production or prepress management, while layout designers may evolve into creative directors or multimedia design specialists, reflecting the industry's increasing demand for technical proficiency and creative expertise.
Key Differences and Overlapping Roles
Typesetters specialize in arranging text for print or digital formats, ensuring optimal readability and typography accuracy, while layout designers integrate text, images, and graphic elements to create cohesive visual compositions. Both roles require strong attention to detail and familiarity with design software, yet typesetters concentrate more on the technical aspects of text formatting and font selection. Overlapping responsibilities include collaborating on page setup, adjusting spacing, and maintaining consistency in style across publishing projects.
Typesetter vs Layout Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com