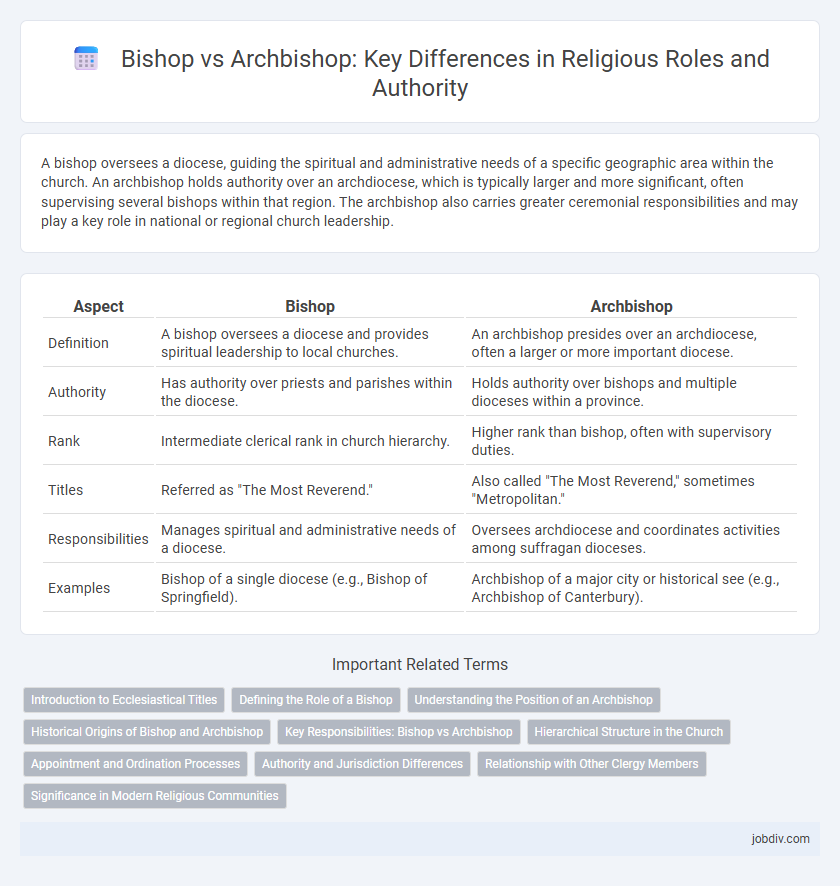
A bishop oversees a diocese, guiding the spiritual and administrative needs of a specific geographic area within the church. An archbishop holds authority over an archdiocese, which is typically larger and more significant, often supervising several bishops within that region. The archbishop also carries greater ceremonial responsibilities and may play a key role in national or regional church leadership.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Bishop | Archbishop |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A bishop oversees a diocese and provides spiritual leadership to local churches. | An archbishop presides over an archdiocese, often a larger or more important diocese. |
| Authority | Has authority over priests and parishes within the diocese. | Holds authority over bishops and multiple dioceses within a province. |
| Rank | Intermediate clerical rank in church hierarchy. | Higher rank than bishop, often with supervisory duties. |
| Titles | Referred as "The Most Reverend." | Also called "The Most Reverend," sometimes "Metropolitan." |
| Responsibilities | Manages spiritual and administrative needs of a diocese. | Oversees archdiocese and coordinates activities among suffragan dioceses. |
| Examples | Bishop of a single diocese (e.g., Bishop of Springfield). | Archbishop of a major city or historical see (e.g., Archbishop of Canterbury). |
Introduction to Ecclesiastical Titles
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who oversees a diocese, providing spiritual leadership and governance within the church hierarchy. An archbishop holds a higher rank, typically presiding over an archdiocese, which is a larger or more significant ecclesiastical territory. These titles reflect the organizational structure and authority within Christian denominations, emphasizing their distinct roles in church administration and pastoral care.
Defining the Role of a Bishop
A bishop serves as a spiritual leader overseeing a diocese, responsible for pastoral care, administering sacraments, and guiding clergy within their jurisdiction. Their primary duties include ordaining priests, confirming church members, and maintaining doctrinal integrity. Bishops function under the authority of archbishops but hold significant authority in governing local church affairs and fostering community faith development.
Understanding the Position of an Archbishop
An archbishop is a senior bishop who presides over an archdiocese, which is a more prominent or important diocese within the church hierarchy. Unlike a bishop who governs a single diocese, an archbishop holds authority over multiple dioceses and often has a supervisory role over other bishops within their ecclesiastical province. This position grants the archbishop greater administrative responsibilities and a higher rank in the Catholic or Orthodox Church structure.
Historical Origins of Bishop and Archbishop
Bishops originated in early Christianity as regional overseers responsible for spiritual guidance and church governance, evolving from the apostles' leadership roles in the first century. Archbishops emerged later in the medieval period as senior bishops overseeing multiple dioceses within larger ecclesiastical provinces, symbolizing an expanded hierarchical authority. This distinction highlights the historical development of church structures aimed at maintaining doctrinal unity and administrative control across growing Christian communities.
Key Responsibilities: Bishop vs Archbishop
A bishop oversees a diocese, managing parish priests, administering sacraments, and guiding the spiritual and administrative needs of the community. An archbishop presides over an archdiocese, which is typically larger or more significant, and holds a supervisory role over several bishops within a province. The archbishop also represents the church in higher ecclesiastical councils and often has greater influence in regional religious matters.
Hierarchical Structure in the Church
A bishop oversees a diocese, managing multiple parishes and serving as the spiritual leader for local clergy and laypersons. An archbishop holds authority over an archdiocese, which is typically a larger or more significant diocese, and often has supervisory responsibilities over several neighboring dioceses led by bishops. This hierarchical structure maintains order and doctrinal unity within the Church, with archbishops playing a key role in regional church governance.
Appointment and Ordination Processes
A bishop is appointed by the pope after a selection process involving recommendations from local clergy and consultation with the apostolic nuncio, followed by episcopal ordination through the laying on of hands by at least three bishops. An archbishop, who usually oversees an archdiocese with greater historical or administrative significance, undergoes the same appointment and ordination processes but may receive a pallium from the pope as a symbol of his metropolitan authority. Both roles require ordination as bishops, but the distinction lies in the jurisdictional responsibilities and ceremonial honors conferred during and after the appointment phase.
Authority and Jurisdiction Differences
A bishop governs a diocese, overseeing local parishes and clergy within a specific geographic area, while an archbishop holds authority over an archdiocese and often exercises metropolitan jurisdiction over several neighboring dioceses. The archbishop's role includes presiding over provincial synods and serving as a symbolic leader with broader administrative responsibilities within the ecclesiastical province. This hierarchical distinction reflects the scope and scale of their jurisdictional and authoritative capacities within the church structure.
Relationship with Other Clergy Members
A bishop oversees a diocese and provides spiritual and administrative guidance to priests and deacons within that region. An archbishop holds authority over an archdiocese and often supervises multiple bishops, coordinating their activities and ensuring doctrinal consistency. The archbishop's role emphasizes leadership among clergy members, fostering collaboration and unity across a broader ecclesiastical territory.
Significance in Modern Religious Communities
Bishops oversee dioceses, ensuring spiritual guidance and administrative leadership within localized communities, while archbishops hold higher ecclesiastical authority, often supervising multiple dioceses or provinces. The archbishop's role carries greater influence in shaping doctrine, mediating church policies, and representing the church in broader religious or societal matters. Their significance in modern religious communities lies in balancing traditional spiritual leadership with contemporary organizational demands, fostering unity across diverse congregations.
Bishop vs Archbishop Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com