Astrobiologists study the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe, encompassing a broad range of scientific disciplines including biology, chemistry, and planetary science. Exobiologists focus specifically on the search for life beyond Earth, investigating extraterrestrial environments to understand the potential for life. Both fields overlap but differ in scope, with astrobiology addressing life's broader cosmic context and exobiology concentrating on the existence and detection of life on other planets.
Table of Comparison
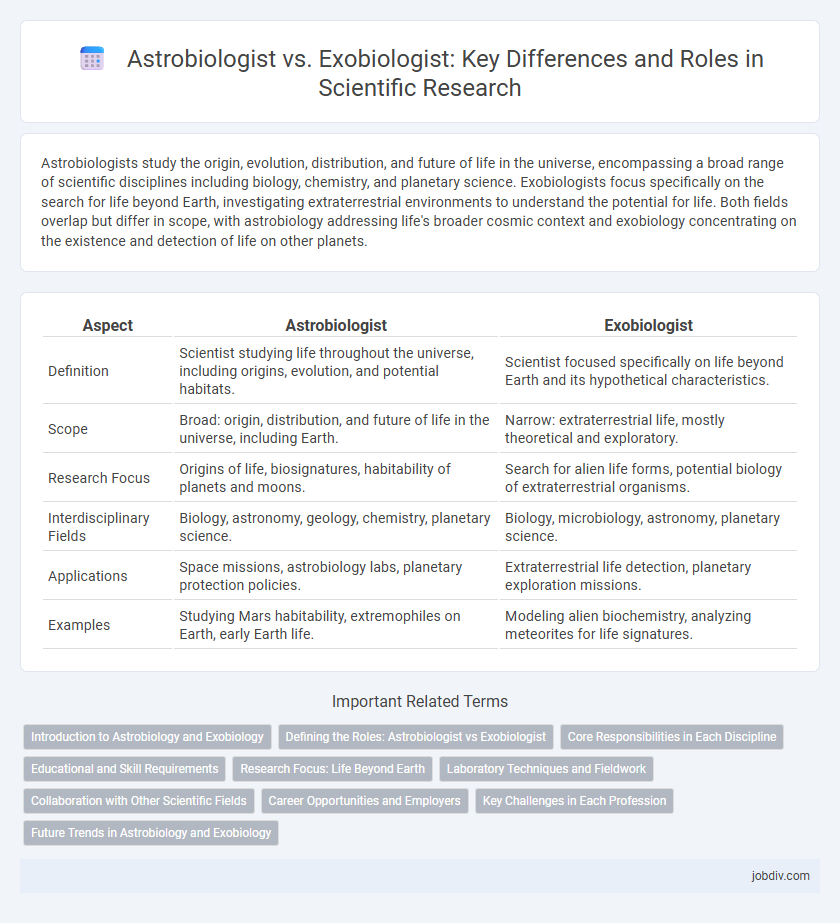
| Aspect | Astrobiologist | Exobiologist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scientist studying life throughout the universe, including origins, evolution, and potential habitats. | Scientist focused specifically on life beyond Earth and its hypothetical characteristics. |
| Scope | Broad: origin, distribution, and future of life in the universe, including Earth. | Narrow: extraterrestrial life, mostly theoretical and exploratory. |
| Research Focus | Origins of life, biosignatures, habitability of planets and moons. | Search for alien life forms, potential biology of extraterrestrial organisms. |
| Interdisciplinary Fields | Biology, astronomy, geology, chemistry, planetary science. | Biology, microbiology, astronomy, planetary science. |
| Applications | Space missions, astrobiology labs, planetary protection policies. | Extraterrestrial life detection, planetary exploration missions. |
| Examples | Studying Mars habitability, extremophiles on Earth, early Earth life. | Modeling alien biochemistry, analyzing meteorites for life signatures. |
Introduction to Astrobiology and Exobiology
Astrobiologists study the origin, evolution, and distribution of life in the universe, integrating biology, chemistry, and planetary science to explore life's potential beyond Earth. Exobiologists specifically investigate the existence of extraterrestrial life forms and their possible biochemical signatures, often focusing on extremophiles and habitable environments on other planets. Both fields overlap significantly but differ in scope, with astrobiology encompassing broader cosmic processes while exobiology zeroes in on life beyond Earth.
Defining the Roles: Astrobiologist vs Exobiologist
Astrobiologists study the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe, integrating biology, chemistry, and planetary science to understand life's potential beyond Earth. Exobiologists specifically focus on searching for and analyzing extraterrestrial life forms and the environmental conditions that support such life on other planets and moons. Both disciplines overlap in exploring life's existence outside Earth but differ in scope, with astrobiology encompassing broader theoretical and practical aspects of life's cosmic context.
Core Responsibilities in Each Discipline
Astrobiologists study the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe, integrating biology, chemistry, and astronomy to understand life's potential beyond Earth. Exobiologists specifically focus on detecting and analyzing extraterrestrial life, emphasizing the search for microbial life forms on other planets and moons through planetary missions and sample analysis. Both disciplines require expertise in molecular biology and planetary science, but astrobiology has a broader scope encompassing life's universal principles, while exobiology zeroes in on life detection techniques and extraterrestrial environments.
Educational and Skill Requirements
Astrobiologists typically require a strong foundation in biology, chemistry, and planetary science, often holding advanced degrees in these disciplines to analyze life's potential in the universe. Exobiologists, a subset within astrobiology, emphasize molecular biology, microbiology, and bioinformatics, requiring specialized training to study extraterrestrial life forms and their environments. Both fields demand proficiency in data analysis, laboratory techniques, and interdisciplinary research to explore life's origin, evolution, and distribution beyond Earth.
Research Focus: Life Beyond Earth
Astrobiologists study the origin, evolution, and potential distribution of life throughout the universe, encompassing a multidisciplinary approach that includes biology, chemistry, and planetary science. Exobiologists specifically focus on the search for extraterrestrial life forms and analyze environments beyond Earth to detect biosignatures and assess habitability. Both fields prioritize understanding life beyond Earth but differ in scope, with astrobiology addressing broader cosmic contexts and exobiology concentrating on detecting actual alien organisms.
Laboratory Techniques and Fieldwork
Astrobiologists employ advanced laboratory techniques such as spectroscopy and molecular analysis to study the potential for life beyond Earth, often simulating extraterrestrial environments. Exobiologists focus extensively on fieldwork, collecting and analyzing samples from extreme terrestrial environments like hydrothermal vents and Antarctic ice to understand life's adaptability. Both disciplines integrate microbial culturing and genetic sequencing, enhancing insights into life's origins and possibilities on other planets.
Collaboration with Other Scientific Fields
Astrobiologists and exobiologists often collaborate with fields such as planetary science, geology, and chemistry to analyze extraterrestrial environments and potential biosignatures. Their interdisciplinary approach integrates data from telescopic observations, spacecraft missions, and laboratory experiments to understand life's origins and existence beyond Earth. This synergy enhances the development of advanced detection technologies and theoretical models crucial for space exploration missions.
Career Opportunities and Employers
Astrobiologists and exobiologists explore life beyond Earth, with astrobiologists often engaging in interdisciplinary research across biology, chemistry, and planetary science, while exobiologists focus specifically on investigating the potential for extraterrestrial life. Career opportunities for both fields include positions at space agencies like NASA and ESA, research institutions, universities, and private aerospace companies such as SpaceX and Blue Origin. Employers prioritize candidates with expertise in molecular biology, bioinformatics, planetary geology, and astrobiological instrumentation to advance missions related to the search for life on Mars, icy moons, and exoplanets.
Key Challenges in Each Profession
Astrobiologists face the key challenge of understanding life's origin, evolution, and potential distribution in the universe using interdisciplinary approaches from biology, chemistry, and planetary science. Exobiologists primarily confront the difficulty of detecting and analyzing extraterrestrial life forms without direct specimens, relying heavily on remote sensing and robotic exploration technologies. Both professions require advanced knowledge of extremophiles and biosignatures to interpret data from harsh extraterrestrial environments accurately.
Future Trends in Astrobiology and Exobiology
Astrobiologists and exobiologists increasingly leverage advanced space telescopes and AI-driven biosignature detection to explore extraterrestrial life possibilities. Future trends highlight the integration of molecular biology with planetary science to study extremophiles on Mars and icy moons like Europa and Enceladus. Research efforts emphasize in situ experiments and sample-return missions to validate life-detection technologies and refine theoretical models of life's origins beyond Earth.
Astrobiologist vs Exobiologist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com