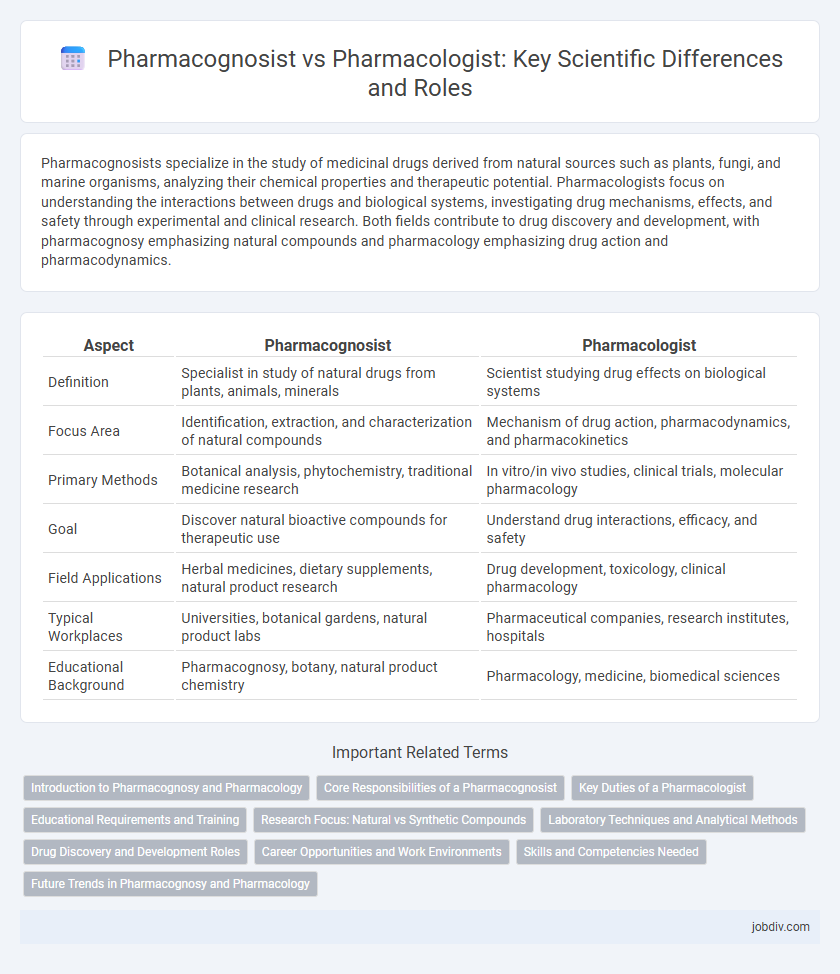
Pharmacognosists specialize in the study of medicinal drugs derived from natural sources such as plants, fungi, and marine organisms, analyzing their chemical properties and therapeutic potential. Pharmacologists focus on understanding the interactions between drugs and biological systems, investigating drug mechanisms, effects, and safety through experimental and clinical research. Both fields contribute to drug discovery and development, with pharmacognosy emphasizing natural compounds and pharmacology emphasizing drug action and pharmacodynamics.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pharmacognosist | Pharmacologist |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specialist in study of natural drugs from plants, animals, minerals | Scientist studying drug effects on biological systems |
| Focus Area | Identification, extraction, and characterization of natural compounds | Mechanism of drug action, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics |
| Primary Methods | Botanical analysis, phytochemistry, traditional medicine research | In vitro/in vivo studies, clinical trials, molecular pharmacology |
| Goal | Discover natural bioactive compounds for therapeutic use | Understand drug interactions, efficacy, and safety |
| Field Applications | Herbal medicines, dietary supplements, natural product research | Drug development, toxicology, clinical pharmacology |
| Typical Workplaces | Universities, botanical gardens, natural product labs | Pharmaceutical companies, research institutes, hospitals |
| Educational Background | Pharmacognosy, botany, natural product chemistry | Pharmacology, medicine, biomedical sciences |
Introduction to Pharmacognosy and Pharmacology
Pharmacognosy explores the study of medicinal drugs derived from natural sources, including plants, minerals, and microorganisms, emphasizing the identification, extraction, and analysis of bioactive compounds. Pharmacologists focus on understanding drug interactions, mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics in biological systems to develop and optimize therapeutic agents. Both fields play a critical role in drug discovery and development, with pharmacognosy providing natural product leads and pharmacology evaluating their efficacy and safety.
Core Responsibilities of a Pharmacognosist
Pharmacognosists specialize in the study and analysis of natural products derived from plants, animals, and minerals to discover bioactive compounds with therapeutic potential. Their core responsibilities include identifying, isolating, and characterizing phytochemicals and other natural substances for drug development and quality control of herbal medicines. They conduct pharmacognostic research, phytochemical screening, and botanical authentication to ensure the efficacy and safety of natural remedies in pharmaceutical applications.
Key Duties of a Pharmacologist
Pharmacologists conduct in-depth research on drug interactions, mechanisms, efficacy, and safety through clinical and preclinical studies, aiming to develop new medications and improve existing treatments. Their key duties include designing experiments, analyzing biological data, and collaborating with interdisciplinary teams to translate scientific findings into therapeutic applications. Unlike pharmacognosists who specialize in natural products, pharmacologists focus on synthetic compounds and biochemical pathways influencing drug response.
Educational Requirements and Training
Pharmacognosists typically require a degree in pharmacy, pharmaceutical sciences, or botanical sciences with specialized training in natural products, emphasizing the study of medicinal plants and bioactive compounds. Pharmacologists need a strong foundation in biology, chemistry, and physiology, often holding advanced degrees such as a Master's or Ph.D. in pharmacology or related biomedical sciences with extensive laboratory training in drug action mechanisms. Both fields demand rigorous education but differ in focus; pharmacognosists center on natural sources and extraction techniques, whereas pharmacologists concentrate on drug effects and development through experimental methods.
Research Focus: Natural vs Synthetic Compounds
Pharmacognosists primarily investigate natural compounds derived from plants, fungi, and marine organisms to identify bioactive substances with therapeutic potential. Pharmacologists, on the other hand, focus extensively on synthetic compounds, designing and testing chemically engineered drugs to understand their pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics. Both disciplines contribute to drug discovery, but pharmacognosy emphasizes natural product research while pharmacology centers on synthetic drug development.
Laboratory Techniques and Analytical Methods
Pharmacognosists specialize in identifying and extracting bioactive compounds from natural sources using techniques like chromatography, spectroscopy, and microscopy, emphasizing plant and microbial material analysis. Pharmacologists focus on studying drug actions and mechanisms through in vitro and in vivo assays, employing methods such as receptor binding studies, pharmacokinetic modeling, and biochemical assays. Both disciplines utilize analytical instruments like HPLC and mass spectrometry, but pharmacognosists prioritize natural product characterization while pharmacologists concentrate on drug efficacy and safety evaluations.
Drug Discovery and Development Roles
Pharmacognosists specialize in identifying and isolating bioactive compounds from natural sources, playing a critical role in the initial stages of drug discovery by screening plants, fungi, and marine organisms for therapeutic potential. Pharmacologists focus on understanding drug mechanisms, efficacy, and safety through in vitro and in vivo studies, guiding the optimization and development of novel pharmaceuticals. Together, these disciplines synergize to accelerate the translation of natural compounds into clinically viable drugs, enhancing the pipeline of drug development.
Career Opportunities and Work Environments
Pharmacognosists primarily explore natural products and medicinal plants, finding career opportunities in research institutes, herbal product development companies, and academic settings focused on natural drug discovery. Pharmacologists engage in drug action studies, holding key roles in pharmaceutical companies, clinical trial organizations, and regulatory agencies involved in drug development and safety evaluation. Both fields offer diverse work environments, with pharmacognosists emphasizing botanicals and pharmacologists concentrating on synthetic and biological drug mechanisms.
Skills and Competencies Needed
Pharmacognosists require expertise in botany, natural product chemistry, and analytical techniques to identify and extract bioactive compounds from medicinal plants. Pharmacologists must possess strong knowledge in physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacokinetics to study drug interactions, mechanisms, and effects on biological systems. Both fields demand critical thinking, laboratory skills, and proficiency in research methodologies to advance drug discovery and development.
Future Trends in Pharmacognosy and Pharmacology
Future trends in pharmacognosy emphasize the integration of advanced analytical techniques such as metabolomics and genomics to discover novel bioactive compounds from natural sources. Pharmacology is rapidly advancing through personalized medicine and AI-driven drug design, enhancing targeted therapies and reducing adverse effects. Both fields increasingly converge in biotechnological approaches, enabling accelerated drug development and sustainable sourcing of pharmacological agents.
Pharmacognosist vs Pharmacologist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com