A cryptographer designs secure encryption algorithms to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. A cryptanalyst, on the other hand, specializes in analyzing and breaking these encryption methods to find vulnerabilities. Both roles are crucial in the field of cybersecurity, balancing the development and testing of cryptographic defenses.
Table of Comparison
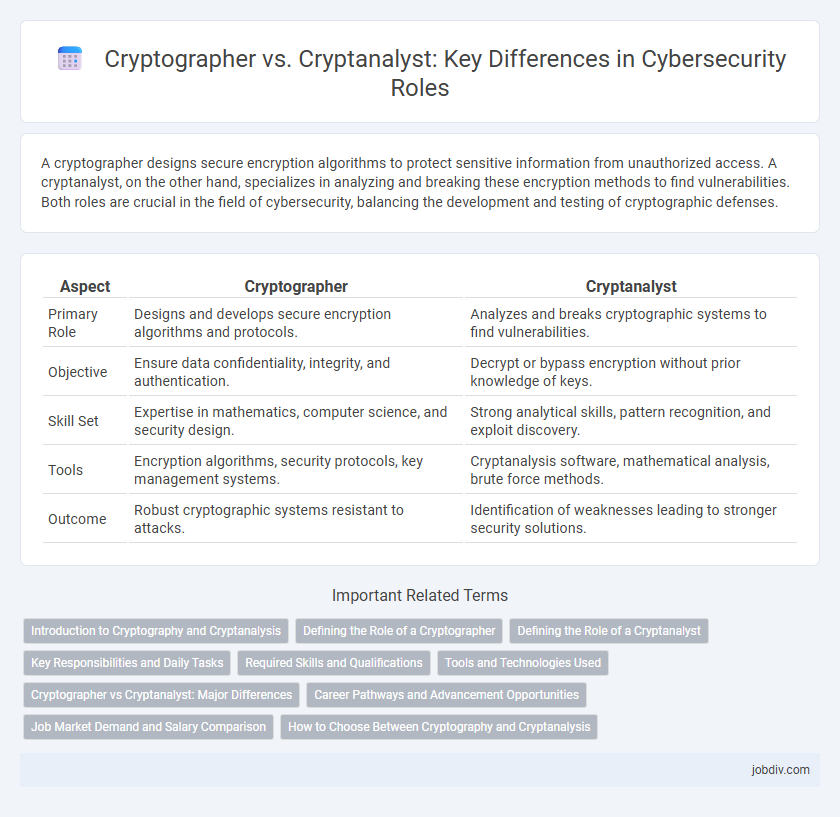
| Aspect | Cryptographer | Cryptanalyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Designs and develops secure encryption algorithms and protocols. | Analyzes and breaks cryptographic systems to find vulnerabilities. |
| Objective | Ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. | Decrypt or bypass encryption without prior knowledge of keys. |
| Skill Set | Expertise in mathematics, computer science, and security design. | Strong analytical skills, pattern recognition, and exploit discovery. |
| Tools | Encryption algorithms, security protocols, key management systems. | Cryptanalysis software, mathematical analysis, brute force methods. |
| Outcome | Robust cryptographic systems resistant to attacks. | Identification of weaknesses leading to stronger security solutions. |
Introduction to Cryptography and Cryptanalysis
Cryptographers design secure encryption algorithms to protect sensitive data by creating complex mathematical models and ciphers. Cryptanalysts specialize in analyzing and breaking these encryption schemes by identifying vulnerabilities and exploiting weaknesses in cryptographic protocols. Understanding the differences between cryptography, which focuses on creating secure systems, and cryptanalysis, which aims to evaluate and compromise those systems, is essential in the field of cybersecurity.
Defining the Role of a Cryptographer
A cryptographer designs encryption algorithms and security protocols to safeguard sensitive data. Their role centers on developing mathematical techniques that ensure confidentiality, integrity, and authentication in digital communication. By creating robust cryptographic systems, they prevent unauthorized access and protect information against evolving cyber threats.
Defining the Role of a Cryptanalyst
A cryptanalyst specializes in deciphering encrypted messages without prior knowledge of the key, aiming to expose vulnerabilities within cryptographic systems. Unlike a cryptographer who designs secure algorithms, the cryptanalyst employs techniques such as frequency analysis, brute force attacks, and pattern recognition to break encryption. Their role is crucial for testing and strengthening the security of communication protocols and data protection mechanisms.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Cryptographers design and develop secure encryption algorithms, protocols, and cryptographic systems to protect sensitive information and ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. They focus on creating new cryptographic techniques and implementing security measures that prevent unauthorized access and cyber threats. Cryptanalysts analyze and attempt to break cryptographic codes and systems, performing vulnerability assessments and cryptographic attacks to identify weaknesses and improve security resilience.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Cryptographers require deep expertise in mathematics, computer science, and algorithm design to develop secure encryption protocols and cryptographic systems. Cryptanalysts specialize in analytical thinking, pattern recognition, and advanced knowledge of cryptographic algorithms to identify vulnerabilities and break codes. Both roles demand proficiency in programming languages, such as Python or C++, and a strong understanding of security principles and network architecture.
Tools and Technologies Used
Cryptographers employ advanced algorithms, such as AES and RSA, along with quantum-resistant protocols to develop secure encryption systems. Cryptanalysts utilize tools like differential cryptanalysis, linear cryptanalysis, and automated software frameworks to identify vulnerabilities in cryptographic schemes. Both professionals heavily rely on high-performance computing and specialized software to test and enhance cryptographic security.
Cryptographer vs Cryptanalyst: Major Differences
Cryptographers develop algorithms and protocols to secure data through encryption, focusing on creating robust cryptographic systems that protect information confidentiality and integrity. Cryptanalysts analyze and attempt to break these cryptographic codes by identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses within encryption methods, aiming to uncover hidden or sensitive data. The major differences lie in their roles: cryptographers build secure systems, while cryptanalysts test and exploit those systems to improve security or reveal flaws.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Cryptographers design advanced encryption algorithms to protect sensitive data, often requiring expertise in mathematics, computer science, and cybersecurity, with career advancement leading to senior cryptographic engineer or security architect roles. Cryptanalysts specialize in analyzing and breaking encryption systems to identify vulnerabilities, and their career progression can lead to positions such as chief security analyst or cryptanalysis researcher in government agencies or cybersecurity firms. Both career paths demand continuous learning of evolving cryptographic techniques and offer opportunities in defense, intelligence, and private sector cybersecurity domains.
Job Market Demand and Salary Comparison
Cryptographers, specializing in developing secure encryption algorithms, typically command higher salaries due to their critical role in cybersecurity innovation, with average earnings ranging from $110,000 to $150,000 annually. Cryptanalysts focus on breaking and analyzing cryptographic systems, a role essential for vulnerability assessment, often earning between $90,000 and $130,000, reflecting strong but slightly lower market demand. Job opportunities for cryptographers are expanding rapidly in sectors like defense, finance, and technology, while cryptanalysts find steady demand primarily in government intelligence and cybersecurity firms.
How to Choose Between Cryptography and Cryptanalysis
Choosing between cryptography and cryptanalysis depends on your interest in either creating secure communication systems or breaking them to identify vulnerabilities. Cryptographers design encryption algorithms and protocols to protect data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity, while cryptanalysts analyze and exploit weaknesses in these systems to improve security or uncover hidden flaws. Career paths in cryptography often require strong backgrounds in mathematics, computer science, and algorithm development, whereas cryptanalysis demands deep analytical skills and proficiency in pattern recognition and cryptographic attack techniques.
Cryptographer vs Cryptanalyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com