A QA Engineer focuses on the overall quality assurance processes, including defining standards, creating quality plans, and ensuring compliance throughout the development lifecycle. Test Engineers primarily concentrate on designing, executing, and automating test cases to identify defects and validate software functionality. While both roles aim to improve product quality, QA Engineers take a broader view of process improvement, whereas Test Engineers focus more on practical testing activities.
Table of Comparison
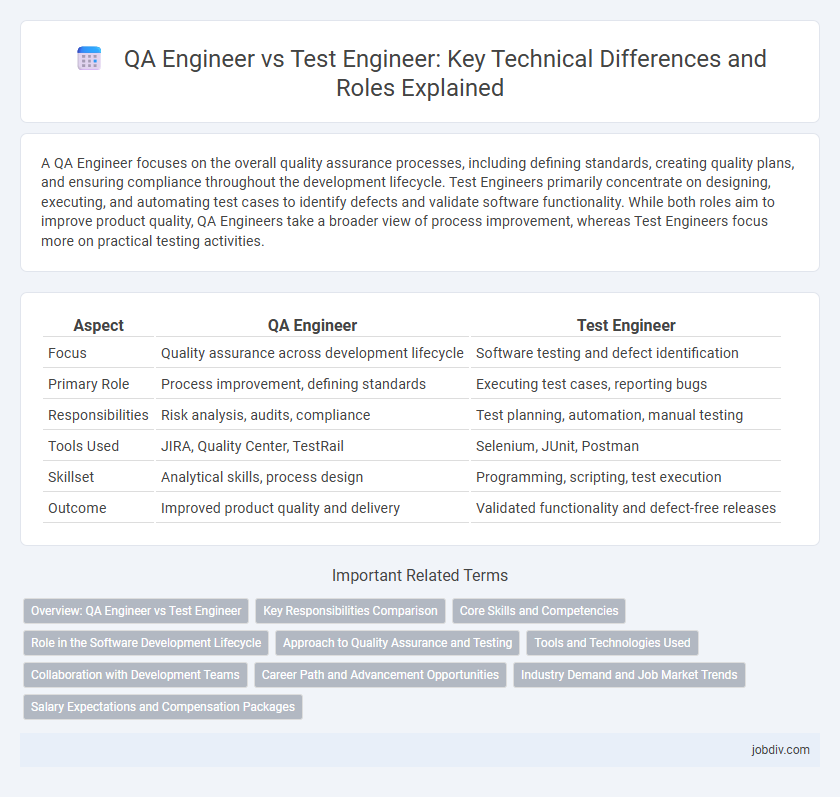
| Aspect | QA Engineer | Test Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Quality assurance across development lifecycle | Software testing and defect identification |
| Primary Role | Process improvement, defining standards | Executing test cases, reporting bugs |
| Responsibilities | Risk analysis, audits, compliance | Test planning, automation, manual testing |
| Tools Used | JIRA, Quality Center, TestRail | Selenium, JUnit, Postman |
| Skillset | Analytical skills, process design | Programming, scripting, test execution |
| Outcome | Improved product quality and delivery | Validated functionality and defect-free releases |
Overview: QA Engineer vs Test Engineer
QA Engineers focus on designing and implementing quality assurance processes to ensure product standards, while Test Engineers concentrate on executing test cases and identifying defects in software applications. QA Engineers develop comprehensive strategies for quality improvement across the development lifecycle, whereas Test Engineers specialize in hands-on testing activities and automation. Both roles collaborate closely to deliver reliable, high-quality software products.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
A QA Engineer primarily focuses on designing and implementing quality assurance processes, developing test plans, and ensuring compliance with industry standards to improve product quality. A Test Engineer emphasizes creating, executing, and automating test cases to identify software defects and validate functionality against requirements. Both roles collaborate closely but differ in scope, with QA Engineers overseeing overall quality strategies and Test Engineers concentrating on systematic testing activities.
Core Skills and Competencies
QA Engineers excel in process improvement, risk analysis, and quality management methodologies, ensuring software development aligns with industry standards. Test Engineers possess deep technical skills in test case design, automation frameworks, and defect tracking tools, directly validating software functionality and performance. Both roles require strong analytical abilities and proficiency in programming languages such as Python, Java, or C#, but QA Engineers emphasize strategic quality assurance, whereas Test Engineers focus on tactical execution of test activities.
Role in the Software Development Lifecycle
QA Engineers focus on overseeing the entire software development lifecycle by establishing quality standards, designing test strategies, and ensuring compliance with industry best practices. Test Engineers primarily concentrate on the execution of test cases, identifying defects, and validating software functionality during various development phases. Both roles collaborate closely with development and product teams to improve software reliability and performance.
Approach to Quality Assurance and Testing
QA Engineers focus on designing comprehensive quality assurance processes that include defining standards, overseeing test strategies, and ensuring product adherence to requirements throughout the development lifecycle. Test Engineers primarily concentrate on executing detailed test cases, identifying defects, and validating functionality through manual or automated testing techniques. The QA Engineer's approach encompasses process improvement and risk management, while the Test Engineer emphasizes practical test execution and bug detection.
Tools and Technologies Used
QA Engineers primarily utilize tools like Selenium, JIRA, and TestRail to manage test cases, track defects, and automate functional testing across various platforms. Test Engineers often focus on using specialized automation frameworks such as Appium, LoadRunner, and Postman to conduct performance, API, and mobile testing with precision. Both roles require proficiency in continuous integration tools like Jenkins and version control systems such as Git to ensure seamless collaboration and deployment workflows.
Collaboration with Development Teams
QA Engineers collaborate closely with development teams to integrate quality assurance processes early in the software development lifecycle, ensuring continuous feedback and early defect detection. Test Engineers primarily focus on executing test cases and reporting defects but increasingly engage with developers to clarify requirements and improve test coverage. Effective collaboration between QA and Test Engineers with developers enhances product reliability, accelerates release cycles, and minimizes rework.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
QA Engineers often transition into roles such as Automation Engineer or QA Manager by developing skills in coding, test automation, and process optimization, which enhances career advancement opportunities. Test Engineers typically advance by specializing in performance, security, or usability testing, gaining deep domain expertise that leads to roles like Test Architect or Product Quality Lead. Both career paths offer growth through continuous learning in tools like Selenium, JIRA, and Jenkins, with leadership roles requiring strong project management and communication skills.
Industry Demand and Job Market Trends
QA Engineers are increasingly sought after for their expertise in automated testing and quality assurance frameworks, reflecting industry trends toward continuous integration and deployment. Test Engineers remain vital for their specialized skills in exploratory and manual testing, particularly in sectors requiring rigorous compliance and safety standards. Market demand favors professionals who blend technical proficiency in test automation tools with a comprehensive understanding of software development life cycles.
Salary Expectations and Compensation Packages
QA Engineers typically earn higher salaries than Test Engineers due to broader responsibilities in quality assurance processes, including automation and strategy development, with average compensation ranging from $70,000 to $110,000 annually in the US. Test Engineers often receive compensation packages between $60,000 and $95,000, focusing primarily on executing and designing test cases, but may have fewer opportunities for performance-based bonuses or stock options. Comprehensive salary packages for QA Engineers often include benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and professional development stipends, reflecting their critical role in software lifecycle management.
QA Engineer vs Test Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com