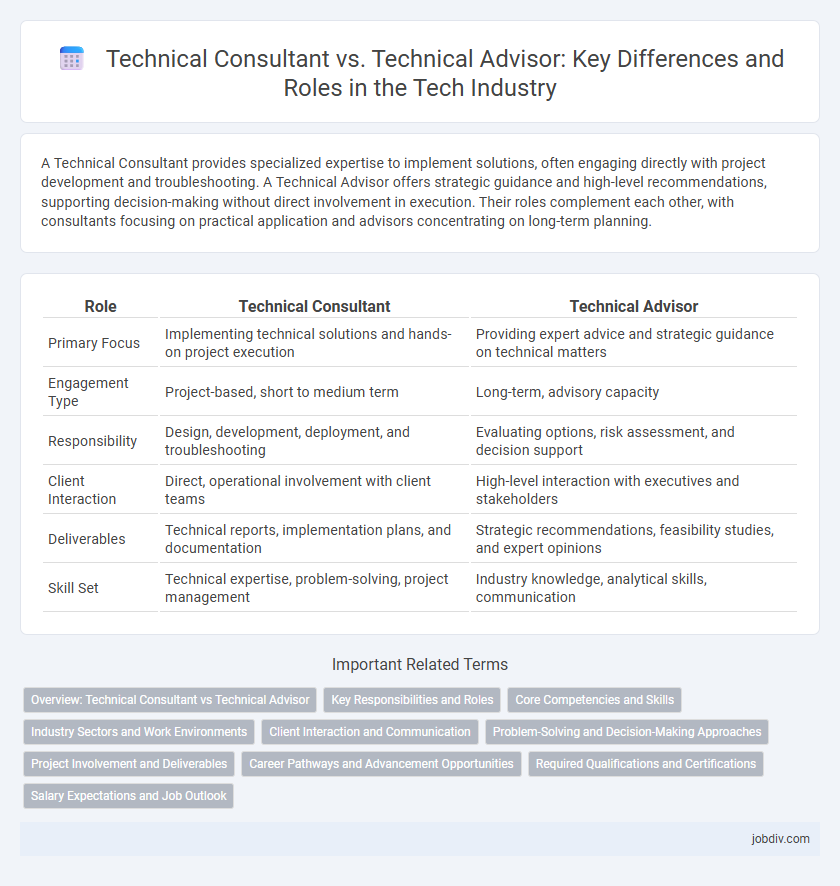
A Technical Consultant provides specialized expertise to implement solutions, often engaging directly with project development and troubleshooting. A Technical Advisor offers strategic guidance and high-level recommendations, supporting decision-making without direct involvement in execution. Their roles complement each other, with consultants focusing on practical application and advisors concentrating on long-term planning.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Technical Consultant | Technical Advisor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Implementing technical solutions and hands-on project execution | Providing expert advice and strategic guidance on technical matters |
| Engagement Type | Project-based, short to medium term | Long-term, advisory capacity |
| Responsibility | Design, development, deployment, and troubleshooting | Evaluating options, risk assessment, and decision support |
| Client Interaction | Direct, operational involvement with client teams | High-level interaction with executives and stakeholders |
| Deliverables | Technical reports, implementation plans, and documentation | Strategic recommendations, feasibility studies, and expert opinions |
| Skill Set | Technical expertise, problem-solving, project management | Industry knowledge, analytical skills, communication |
Overview: Technical Consultant vs Technical Advisor
Technical Consultants provide specialized expertise to implement and optimize technology solutions tailored to client needs, often engaging in project execution and technical problem-solving. Technical Advisors focus on strategic guidance and high-level technical direction, influencing decision-making processes without direct involvement in day-to-day implementation. Both roles require deep technical knowledge, but Consultants emphasize hands-on application while Advisors prioritize advisory and consultative functions.
Key Responsibilities and Roles
Technical Consultants specialize in providing expert solutions by analyzing client requirements, designing tailored technologies, and ensuring implementation aligns with business objectives. Technical Advisors focus on offering strategic guidance, reviewing project frameworks, and advising on best practices to optimize technical performance and risk management. Both roles demand deep technical expertise, but Consultants drive execution while Advisors influence decision-making at a strategic level.
Core Competencies and Skills
Technical Consultants excel in project management, system integration, and client-specific technology solutions, leveraging expertise in software development, cybersecurity, and data analytics to drive business outcomes. Technical Advisors specialize in strategic guidance, risk assessment, and compliance, with deep knowledge in industry standards, regulatory frameworks, and emerging technologies to inform decision-making processes. Both roles require strong communication, problem-solving abilities, and proficiency in IT infrastructure, but Consultants focus more on implementation, while Advisors emphasize advisory and governance functions.
Industry Sectors and Work Environments
Technical Consultants typically engage with diverse industry sectors such as IT, manufacturing, and finance, offering specialized solutions tailored to complex project requirements. They often operate within client environments, providing hands-on implementation and strategic guidance to optimize technology use. Technical Advisors focus more on long-term strategic planning and high-level decision support, commonly embedded in corporate or organizational settings where they influence policy and technology roadmaps.
Client Interaction and Communication
Technical Consultants engage directly with clients to analyze needs, provide tailored solutions, and ensure project alignment through detailed discussions and clarifications. Technical Advisors offer expert guidance and strategic recommendations, often communicating at a higher level to influence decision-making and long-term planning. Both roles require strong interpersonal skills, but Consultants prioritize hands-on interaction while Advisors focus on advisory communication.
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making Approaches
Technical Consultants leverage in-depth industry expertise to diagnose complex problems and develop tailored solutions that align with business objectives. They employ structured methodologies and data-driven analysis to guide decision-making, ensuring practical implementation and measurable impact. In contrast, Technical Advisors prioritize strategic insight and experience-based recommendations, facilitating high-level decision-making by evaluating risks, opportunities, and technological trends without direct involvement in execution.
Project Involvement and Deliverables
Technical Consultants engage deeply in project execution, offering specialized expertise to design, implement, and optimize technical solutions, directly influencing deliverables such as system architecture, software deployment, and technical documentation. Technical Advisors primarily provide strategic guidance and high-level recommendations, focusing on aligning technical approaches with business objectives and ensuring compliance with industry standards, which shapes project direction rather than producing tangible deliverables. The distinction lies in active hands-on project participation by consultants versus consultative oversight and advisory insights from advisors.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Technical Consultants typically follow a career pathway that advances through roles such as Senior Consultant, Solutions Architect, and eventually Program Manager, leveraging project-based expertise and client-facing experience. Technical Advisors often progress toward specialized advisory positions, including Chief Technical Advisor or strategic roles like CTO, focusing on deep industry knowledge and long-term organizational impact. Both roles offer distinct advancement opportunities: Consultants excel in client engagement and solution delivery, while Advisors emphasize thought leadership and strategic influence.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Technical Consultants typically require advanced degrees in computer science, engineering, or related fields, alongside certifications such as PMP, Six Sigma, or AWS Certified Solutions Architect to demonstrate project management and technical expertise. Technical Advisors often hold specialized certifications relevant to their industry, like CISSP for cybersecurity or ITIL for IT service management, highlighting their advisory role in risk assessment and compliance. Both roles demand strong analytical skills and continuous professional development to stay current with evolving technologies and industry standards.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Technical Consultants typically earn higher salaries, with average annual pay ranging from $85,000 to $120,000, reflecting their role in delivering specialized project solutions and hands-on implementation. Technical Advisors often command salaries between $70,000 and $100,000, emphasizing their strategic guidance and expertise in technology direction rather than direct execution. The job outlook for Technical Consultants is strong due to increasing demand for technical project management, while Technical Advisors see steady growth as organizations seek expert advice to navigate evolving technology landscapes.
Technical Consultant vs Technical Advisor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com