Technical consultants specialize in implementing and optimizing technology solutions tailored to specific industry requirements, ensuring system integration and technical efficiency. Business consultants focus on enhancing organizational performance by analyzing business processes, strategy, and management practices to drive growth and operational improvements. Both roles require strong problem-solving skills but differ in their emphasis on technology versus overall business strategy.
Table of Comparison
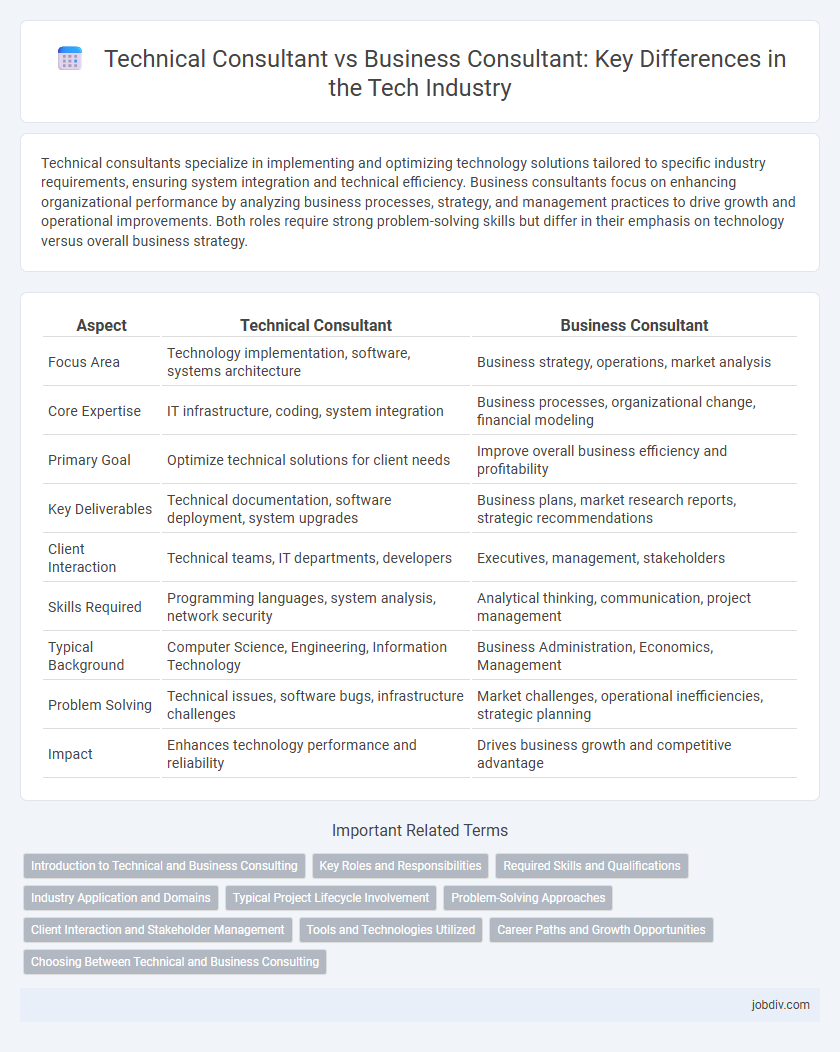
| Aspect | Technical Consultant | Business Consultant |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Area | Technology implementation, software, systems architecture | Business strategy, operations, market analysis |
| Core Expertise | IT infrastructure, coding, system integration | Business processes, organizational change, financial modeling |
| Primary Goal | Optimize technical solutions for client needs | Improve overall business efficiency and profitability |
| Key Deliverables | Technical documentation, software deployment, system upgrades | Business plans, market research reports, strategic recommendations |
| Client Interaction | Technical teams, IT departments, developers | Executives, management, stakeholders |
| Skills Required | Programming languages, system analysis, network security | Analytical thinking, communication, project management |
| Typical Background | Computer Science, Engineering, Information Technology | Business Administration, Economics, Management |
| Problem Solving | Technical issues, software bugs, infrastructure challenges | Market challenges, operational inefficiencies, strategic planning |
| Impact | Enhances technology performance and reliability | Drives business growth and competitive advantage |
Introduction to Technical and Business Consulting
Technical consulting emphasizes expertise in IT systems, software development, and infrastructure optimization to solve complex technological challenges. Business consulting focuses on strategic planning, process improvement, and organizational development to enhance overall business performance. Both roles require analytical skills but differ in their primary objectives and domain knowledge.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Technical Consultants specialize in implementing and optimizing technology solutions, managing system integrations, and providing technical expertise to ensure software and hardware align with business needs. Business Consultants focus on analyzing organizational processes, identifying improvement opportunities, and advising on strategic initiatives to enhance operational efficiency and drive growth. Both roles require strong problem-solving skills, but Technical Consultants emphasize technology deployment while Business Consultants concentrate on business strategy and performance optimization.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Technical consultants must possess strong expertise in IT systems, software development, and data analysis, alongside certifications such as CISSP, PMP, or AWS Certified Solutions Architect. Business consultants require deep knowledge of market analysis, strategic planning, financial modeling, and proficiency in tools like Excel, SAP, or Tableau, often supported by qualifications such as MBA or CBAP. Both roles demand excellent communication and problem-solving skills, but technical consultants emphasize technical proficiency while business consultants prioritize business acumen and industry-specific insights.
Industry Application and Domains
Technical Consultants specialize in implementing and optimizing technology solutions across industries such as IT, manufacturing, and telecommunications, leveraging technical expertise in software development, systems integration, and infrastructure management. Business Consultants concentrate on strategic planning, process improvement, and organizational change within sectors like finance, healthcare, and retail, focusing on business models, market analysis, and operational efficiency. Both roles are essential in industry digital transformation initiatives, with Technical Consultants addressing technical feasibility and Business Consultants aligning technology with business goals.
Typical Project Lifecycle Involvement
Technical consultants typically engage early in the project lifecycle during requirements gathering, system design, and implementation phases to ensure technical feasibility and integration. Business consultants are primarily involved in the initial analysis, defining business objectives, and during change management to align project outcomes with organizational strategy. Both roles collaborate during testing and deployment to balance technical solutions with business needs for successful project delivery.
Problem-Solving Approaches
Technical consultants employ data-driven and system-focused problem-solving methodologies, leveraging expertise in IT infrastructure, software development, and technical analytics to design and implement targeted solutions. Business consultants emphasize strategic analysis, organizational behavior, and market trends to address operational inefficiencies and align business processes with corporate goals. Both approaches require critical thinking and stakeholder collaboration, but technical consultants prioritize technological feasibility while business consultants focus on business impact and organizational change management.
Client Interaction and Stakeholder Management
Technical Consultants prioritize in-depth client interaction by analyzing specific technology requirements and delivering tailored solutions that address complex IT challenges. Business Consultants focus on stakeholder management by aligning business objectives with organizational goals, facilitating communication across departments to drive strategic initiatives. Effective collaboration between both consultants enhances project success through comprehensive understanding of technical capabilities and business needs.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
Technical Consultants leverage advanced software applications such as cloud platforms, programming languages, and system integration tools to design and implement technology solutions tailored to client infrastructure. Business Consultants utilize data analytics tools, CRM systems, and project management software to optimize organizational processes and drive strategic decisions. The distinct toolsets reflect their core focus: Technical Consultants prioritize technical architecture and development, while Business Consultants emphasize operational efficiency and business growth.
Career Paths and Growth Opportunities
Technical consultants typically have career paths rooted in IT infrastructure, software development, and system integration, offering growth through specialization in emerging technologies and certifications. Business consultants focus on organizational strategy, process optimization, and change management, with advancement tied to industry expertise and leadership skills. Both career tracks provide opportunities for cross-functional roles, but technical consultants often advance through technical mastery, while business consultants progress via strategic influence and client management.
Choosing Between Technical and Business Consulting
Choosing between technical and business consulting depends on the expertise required to address organizational challenges; technical consultants specialize in IT systems, software implementation, and infrastructure optimization, while business consultants focus on strategy, process improvement, and market analysis. Organizations prioritize technical consulting when deploying technology solutions or integrating new platforms, whereas business consulting is essential for aligning business goals, enhancing operational efficiency, and driving growth. Evaluating project scope, desired outcomes, and industry-specific demands ensures an effective consultant selection tailored to organizational needs.
Technical Consultant vs Business Consultant Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com