Technical Specialists possess in-depth expertise and handle complex issues involving system design, implementation, and advanced troubleshooting. Technical Support professionals focus on assisting end-users by resolving common problems and maintaining system functionality. Both roles are critical for ensuring optimal performance and addressing technical challenges efficiently.
Table of Comparison
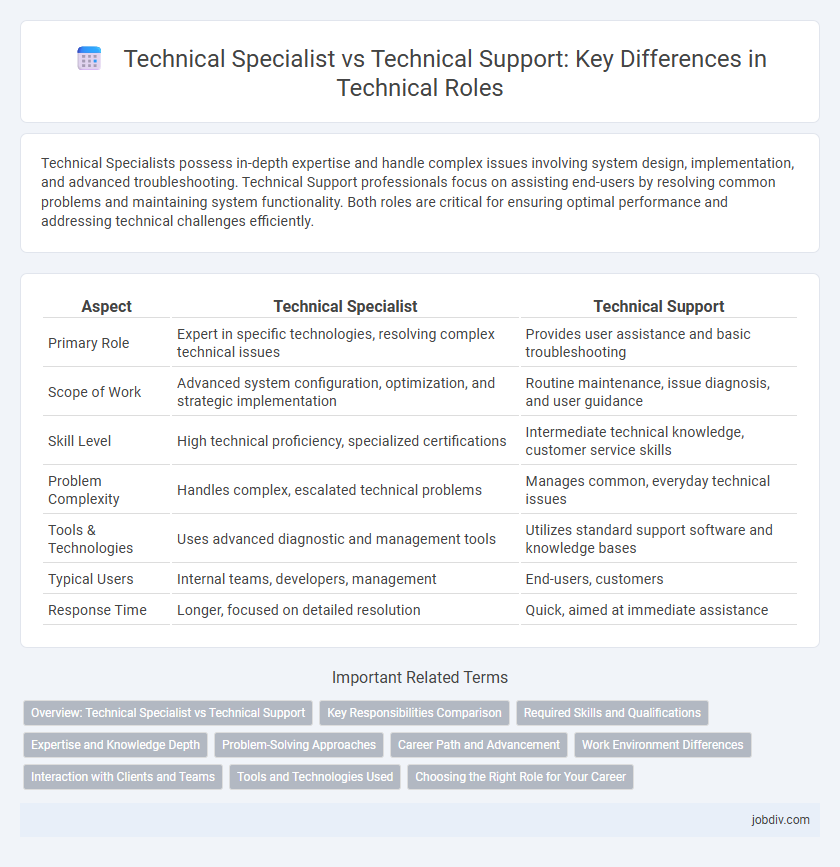
| Aspect | Technical Specialist | Technical Support |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Expert in specific technologies, resolving complex technical issues | Provides user assistance and basic troubleshooting |
| Scope of Work | Advanced system configuration, optimization, and strategic implementation | Routine maintenance, issue diagnosis, and user guidance |
| Skill Level | High technical proficiency, specialized certifications | Intermediate technical knowledge, customer service skills |
| Problem Complexity | Handles complex, escalated technical problems | Manages common, everyday technical issues |
| Tools & Technologies | Uses advanced diagnostic and management tools | Utilizes standard support software and knowledge bases |
| Typical Users | Internal teams, developers, management | End-users, customers |
| Response Time | Longer, focused on detailed resolution | Quick, aimed at immediate assistance |
Overview: Technical Specialist vs Technical Support
Technical Specialists possess in-depth expertise in specific technologies and focus on problem-solving, system design, and implementation, while Technical Support primarily handles troubleshooting, user assistance, and incident resolution. Technical Specialists often engage in advanced configurations and strategic planning, whereas Technical Support provides frontline guidance to end-users and ensures system functionality. Both roles are essential for maintaining IT infrastructure, but their scope and responsibilities differ significantly in complexity and specialization.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
Technical Specialists focus on in-depth system analysis, implementation, and optimization of complex technological solutions, ensuring alignment with organizational goals. Technical Support professionals handle troubleshooting, user assistance, and maintenance of existing infrastructure to resolve operational issues promptly. While Technical Specialists design and enhance systems, Technical Support ensures continuous functionality and user satisfaction through effective problem resolution.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Technical Specialists require advanced expertise in specific technologies, with certifications such as Cisco CCNP, Microsoft MCSE, or specialized programming languages. Technical Support professionals need strong problem-solving skills, customer service experience, and proficiency in troubleshooting common hardware and software issues, often holding ITIL or CompTIA A+ certifications. Both roles demand excellent communication abilities, but Technical Specialists emphasize in-depth technical knowledge, while Technical Support focuses on user assistance and issue resolution.
Expertise and Knowledge Depth
Technical Specialists possess advanced expertise and deep knowledge in specific technologies or systems, enabling them to perform complex problem-solving and system optimization. Technical Support professionals have broader, yet less specialized knowledge aimed at troubleshooting and resolving common user issues quickly. The depth of knowledge in Technical Specialists allows for handling intricate technical challenges beyond the scope of standard support tasks.
Problem-Solving Approaches
Technical Specialists apply in-depth expertise and advanced analytical techniques to diagnose complex system issues, often developing customized solutions tailored to specific technical challenges. Technical Support professionals utilize standardized troubleshooting protocols and knowledge bases to resolve common user problems efficiently, ensuring system stability and user satisfaction. Both roles emphasize problem-solving but differ in scope; Specialists tackle intricate problems requiring specialized knowledge, while Support addresses routine issues through procedural methods.
Career Path and Advancement
Technical Specialists typically advance through deep expertise and certifications in specific technologies, leading to roles such as Solutions Architect or Systems Engineer. Technical Support professionals often progress by developing broad problem-solving skills and customer service experience, moving into positions like Support Manager or IT Service Manager. Understanding these distinct career paths helps professionals align their skills with long-term advancement goals in the technology sector.
Work Environment Differences
Technical Specialists often work in environments that require deep expertise, such as research labs, development teams, or IT infrastructure departments, focusing on complex problem-solving and system optimization. Technical Support personnel typically operate in customer-facing roles within call centers or help desks, addressing end-user issues and providing real-time assistance for software or hardware. The work environment of Technical Specialists is generally more collaborative and strategic, while Technical Support roles emphasize quick response times and direct user interaction.
Interaction with Clients and Teams
Technical Specialists provide expert-level solutions and strategic guidance during client interactions, often addressing complex issues that require in-depth technical knowledge. Technical Support primarily handles routine troubleshooting and assists clients with immediate software or hardware problems, ensuring operational continuity. Collaboration within teams differs as Technical Specialists frequently engage in cross-functional projects, while Technical Support focuses on resolving tickets efficiently within support teams.
Tools and Technologies Used
Technical Specialists utilize advanced diagnostic software, network analyzers, and system configuration tools to develop and implement complex solutions, often requiring deep expertise in specific technologies like cloud platforms or cybersecurity frameworks. Technical Support professionals rely primarily on ticketing systems, remote access tools, and knowledge bases to troubleshoot and resolve end-user issues efficiently, focusing on hardware, software, and peripheral devices. The distinction lies in the specialization and complexity of tools, with Specialists handling high-level configurations and integrations, while Support emphasizes reactive problem-solving and user assistance.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Career
Technical Specialists bring deep expertise in specific technologies, driving innovation and complex problem-solving within specialized domains. Technical Support professionals excel in troubleshooting and customer assistance, ensuring seamless technology usage and user satisfaction. Choosing the right role depends on your career goals: specialize in advanced systems and projects or focus on frontline problem resolution and user support.
Technical Specialist vs Technical Support Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com