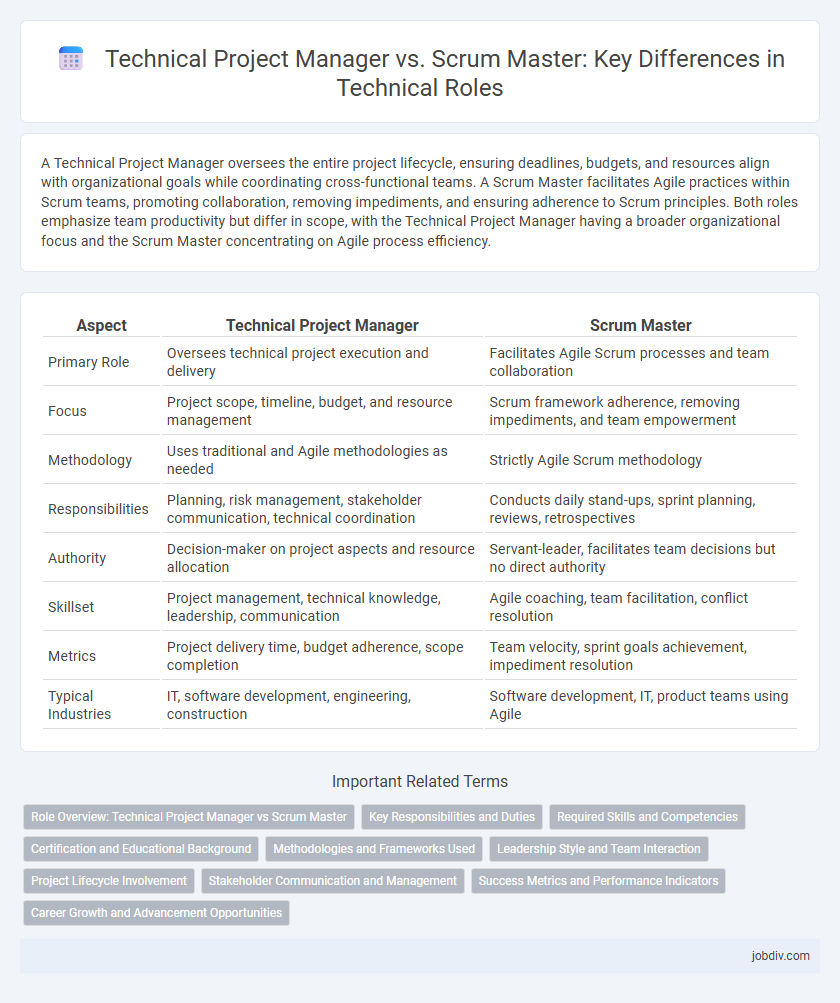
A Technical Project Manager oversees the entire project lifecycle, ensuring deadlines, budgets, and resources align with organizational goals while coordinating cross-functional teams. A Scrum Master facilitates Agile practices within Scrum teams, promoting collaboration, removing impediments, and ensuring adherence to Scrum principles. Both roles emphasize team productivity but differ in scope, with the Technical Project Manager having a broader organizational focus and the Scrum Master concentrating on Agile process efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Technical Project Manager | Scrum Master |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Oversees technical project execution and delivery | Facilitates Agile Scrum processes and team collaboration |
| Focus | Project scope, timeline, budget, and resource management | Scrum framework adherence, removing impediments, and team empowerment |
| Methodology | Uses traditional and Agile methodologies as needed | Strictly Agile Scrum methodology |
| Responsibilities | Planning, risk management, stakeholder communication, technical coordination | Conducts daily stand-ups, sprint planning, reviews, retrospectives |
| Authority | Decision-maker on project aspects and resource allocation | Servant-leader, facilitates team decisions but no direct authority |
| Skillset | Project management, technical knowledge, leadership, communication | Agile coaching, team facilitation, conflict resolution |
| Metrics | Project delivery time, budget adherence, scope completion | Team velocity, sprint goals achievement, impediment resolution |
| Typical Industries | IT, software development, engineering, construction | Software development, IT, product teams using Agile |
Role Overview: Technical Project Manager vs Scrum Master
A Technical Project Manager oversees project planning, resource allocation, and timeline management, ensuring technical deliverables align with business goals and stakeholder expectations. The Scrum Master facilitates Agile ceremonies, removes impediments, and supports the development team in adhering to Scrum principles and continuous improvement. While the Technical Project Manager focuses on project execution and cross-functional coordination, the Scrum Master emphasizes team dynamics and Agile process optimization.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
A Technical Project Manager oversees project planning, resource allocation, risk management, and timeline tracking to ensure successful delivery of technical projects. A Scrum Master facilitates agile ceremonies, removes impediments, and coaches the development team on Agile principles to optimize productivity within Scrum frameworks. Both roles require strong communication skills but differ in scope, with the Technical Project Manager focusing on overall project execution while the Scrum Master concentrates on team collaboration and Agile process adherence.
Required Skills and Competencies
Technical Project Managers require strong expertise in project planning, risk management, and stakeholder communication to ensure successful delivery of complex technical initiatives. Scrum Masters must excel in agile coaching, team facilitation, and conflict resolution to foster a collaborative and adaptive environment aligned with Scrum principles. Both roles demand proficiency in collaboration tools, leadership abilities, and a deep understanding of software development lifecycles.
Certification and Educational Background
Technical Project Managers often hold certifications such as PMP (Project Management Professional) or PRINCE2, emphasizing formal project management methodologies and comprehensive planning skills. Scrum Masters typically pursue Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) or Professional Scrum Master (PSM) credentials, focusing on agile frameworks and team facilitation expertise. Educational backgrounds for Technical Project Managers usually include degrees in engineering, computer science, or business administration, while Scrum Masters often have diverse qualifications supplemented by specialized agile training.
Methodologies and Frameworks Used
Technical Project Managers oversee diverse methodologies such as Waterfall, Agile, and Lean, tailoring frameworks to project needs and stakeholder demands. Scrum Masters specialize exclusively in the Scrum framework, facilitating sprint planning, daily stand-ups, and retrospectives to enhance team collaboration and iterative delivery. Both roles require deep understanding of Agile principles, but Technical Project Managers manage broader project scopes beyond Scrum's team-focused processes.
Leadership Style and Team Interaction
A Technical Project Manager emphasizes directive leadership, coordinating cross-functional teams through structured planning and defined deliverables while maintaining accountability for project outcomes. In contrast, a Scrum Master adopts a servant-leadership style, facilitating team collaboration, removing impediments, and fostering an Agile mindset to promote self-organization and continuous improvement. The Technical Project Manager directs project execution with top-down communication, whereas the Scrum Master encourages bottom-up feedback and empowers team autonomy.
Project Lifecycle Involvement
Technical Project Managers oversee the entire project lifecycle from initiation to closure, ensuring alignment with business goals, resource allocation, and risk management. Scrum Masters focus primarily on the sprint cycles within the Agile framework, facilitating team collaboration and removing impediments during development iterations. The Technical Project Manager's role encompasses broader project scope and cross-functional coordination, while the Scrum Master's involvement centers on iterative delivery and Agile process adherence.
Stakeholder Communication and Management
Technical Project Managers excel in stakeholder communication by providing comprehensive project updates, managing expectations, and aligning technical deliverables with business goals through clear, structured reporting. Scrum Masters facilitate stakeholder engagement by fostering collaboration between development teams and stakeholders, ensuring transparency during sprint reviews and retrospectives to address feedback promptly. Both roles prioritize effective stakeholder management but differ in approach: Technical Project Managers maintain top-down communication channels, while Scrum Masters emphasize continuous, iterative dialogue within Agile frameworks.
Success Metrics and Performance Indicators
Success metrics for a Technical Project Manager typically include on-time delivery, budget adherence, and resource allocation efficiency, ensuring technical milestones align with business objectives. Scrum Masters are measured by team velocity, sprint goal achievement, and removal of impediments, emphasizing facilitation of Agile practices and continuous improvement. Both roles rely on performance indicators like stakeholder satisfaction and quality of deliverables, but the Project Manager focuses on overall project scope while the Scrum Master prioritizes team collaboration and process optimization.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Technical Project Managers often have broader career growth opportunities due to their involvement in cross-functional leadership, budget management, and strategic planning across various methodologies. Scrum Masters, while highly specialized in Agile frameworks and team facilitation, typically advance into roles such as Agile Coach or Product Owner that focus on process optimization and team dynamics. Both paths offer strong advancement potential, but Technical Project Managers may experience faster progression into executive project leadership roles due to their wider organizational scope.
Technical Project Manager vs Scrum Master Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com