Technical Support professionals primarily address user issues by troubleshooting software and hardware problems, ensuring system functionality and user satisfaction. Technical Specialists possess in-depth knowledge of specific technologies, managing complex implementations, system integrations, and providing expert guidance on advanced technical challenges. Both roles are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency but differ in scope, with support focusing on reactive problem-solving and specialists emphasizing proactive technical strategy and innovation.
Table of Comparison
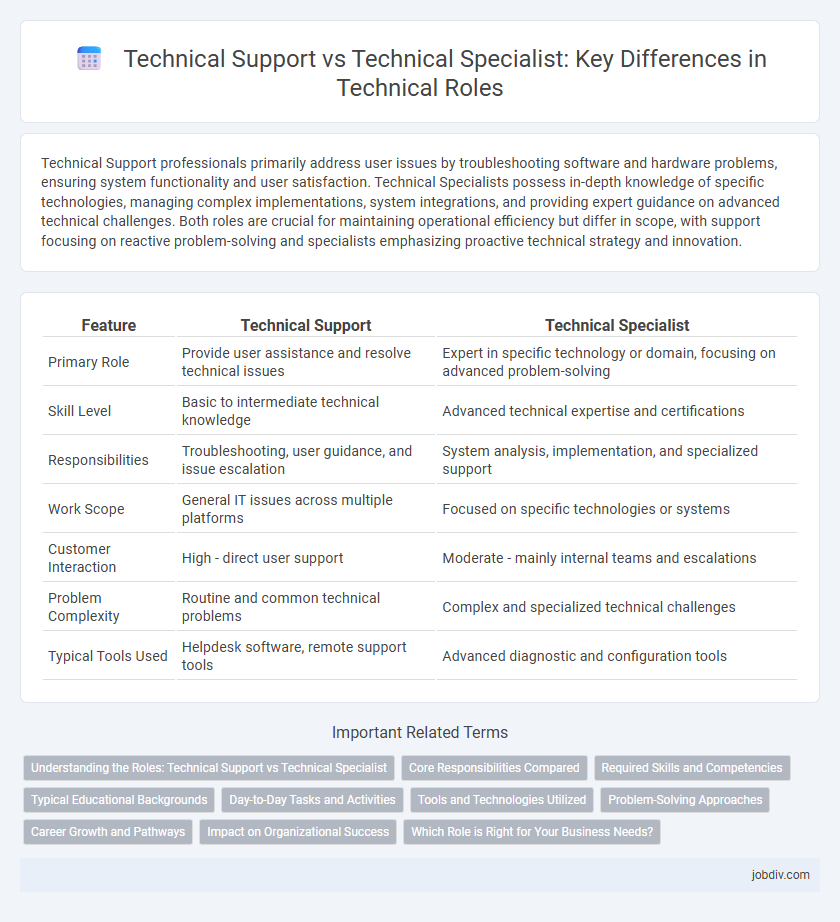
| Feature | Technical Support | Technical Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Provide user assistance and resolve technical issues | Expert in specific technology or domain, focusing on advanced problem-solving |
| Skill Level | Basic to intermediate technical knowledge | Advanced technical expertise and certifications |
| Responsibilities | Troubleshooting, user guidance, and issue escalation | System analysis, implementation, and specialized support |
| Work Scope | General IT issues across multiple platforms | Focused on specific technologies or systems |
| Customer Interaction | High - direct user support | Moderate - mainly internal teams and escalations |
| Problem Complexity | Routine and common technical problems | Complex and specialized technical challenges |
| Typical Tools Used | Helpdesk software, remote support tools | Advanced diagnostic and configuration tools |
Understanding the Roles: Technical Support vs Technical Specialist
Technical Support professionals focus on resolving user issues, troubleshooting hardware and software problems, and providing customer assistance to ensure system functionality. Technical Specialists possess deep expertise in a specific technology or platform, often leading complex projects, optimizing systems, and developing advanced technical solutions. Differentiating these roles highlights the contrast between broad user-facing support and specialized technical proficiency within IT environments.
Core Responsibilities Compared
Technical Support primarily handles troubleshooting, user assistance, and issue resolution, focusing on providing timely solutions to end-users and maintaining system functionality. Technical Specialists possess deeper expertise in specific technologies, responsible for advanced problem analysis, system configuration, and implementation of complex solutions. The core distinction lies in the support role's operational focus versus the specialist's strategic involvement in technical innovation and system optimization.
Required Skills and Competencies
Technical Support professionals excel in troubleshooting, customer communication, and basic system diagnostics, requiring strong interpersonal skills and foundational technical knowledge. Technical Specialists possess advanced expertise in specific technologies or systems, demanding deep analytical abilities, specialized certifications, and proficiency in complex problem-solving. Both roles require adaptability and continuous learning to keep pace with evolving technology landscapes.
Typical Educational Backgrounds
Technical Support professionals often hold an associate degree or certifications in IT, computer science, or related fields, emphasizing foundational knowledge in troubleshooting and customer assistance. Technical Specialists typically possess a bachelor's degree or higher in computer science, engineering, or specific technical disciplines, focusing on advanced system design, problem-solving, and specialized technologies. Certifications such as CompTIA A+, Cisco CCNA, or Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE) enhance credibility for both roles, aligning education with industry standards.
Day-to-Day Tasks and Activities
Technical Support professionals handle daily troubleshooting, respond to user inquiries, and resolve hardware or software issues to maintain system functionality. Technical Specialists perform advanced diagnostics, implement complex solutions, and optimize technical systems based on in-depth expertise in specific technologies. Daily activities of Technical Specialists often involve system configuration, performance monitoring, and providing guidance on specialized technical challenges beyond standard support scope.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
Technical Support professionals primarily utilize remote diagnostic tools, ticketing systems like Jira or Zendesk, and knowledge bases to troubleshoot and resolve user issues efficiently. Technical Specialists often leverage advanced software platforms such as network analyzers, database management systems, and programming environments to implement solutions and optimize system performance. Both roles require proficiency in cybersecurity tools and cloud services like AWS or Azure to maintain and secure IT infrastructure.
Problem-Solving Approaches
Technical Support professionals primarily use standardized troubleshooting protocols and diagnostic tools to resolve common hardware and software issues efficiently. In contrast, Technical Specialists employ in-depth knowledge and advanced analytical techniques to address complex, system-specific problems that require customized solutions. Both roles emphasize problem-solving but differ in scope, with Technical Support focusing on broad issue resolution and Technical Specialists targeting specialized, technical challenges.
Career Growth and Pathways
Technical support roles emphasize foundational troubleshooting and customer interaction skills, providing entry-level experience crucial for upward mobility in IT careers. Technical specialists possess advanced expertise in specific technologies or systems, often leading to higher-level positions in system architecture, project management, or specialized consulting. Career growth for technical specialists typically involves targeted certifications and domain mastery, while technical support professionals benefit from broad skill development and hands-on problem-solving.
Impact on Organizational Success
Technical Support ensures seamless operations by resolving user issues promptly, minimizing downtime, and maintaining productivity across departments. Technical Specialists drive innovation and strategic improvements through deep expertise in specific technologies, directly influencing product development and system optimization. Together, their complementary roles enhance organizational success by balancing immediate problem-solving with long-term technological advancement.
Which Role is Right for Your Business Needs?
Technical Support professionals provide frontline assistance, troubleshooting hardware and software issues to ensure uninterrupted business operations, ideal for companies seeking immediate problem resolution. Technical Specialists possess deep expertise in specific technologies or systems, offering advanced solutions and strategic guidance that align with complex business requirements and long-term goals. Choosing between the two depends on whether your business prioritizes rapid issue resolution or in-depth technical proficiency for system optimization and innovation.
Technical Support vs Technical Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com