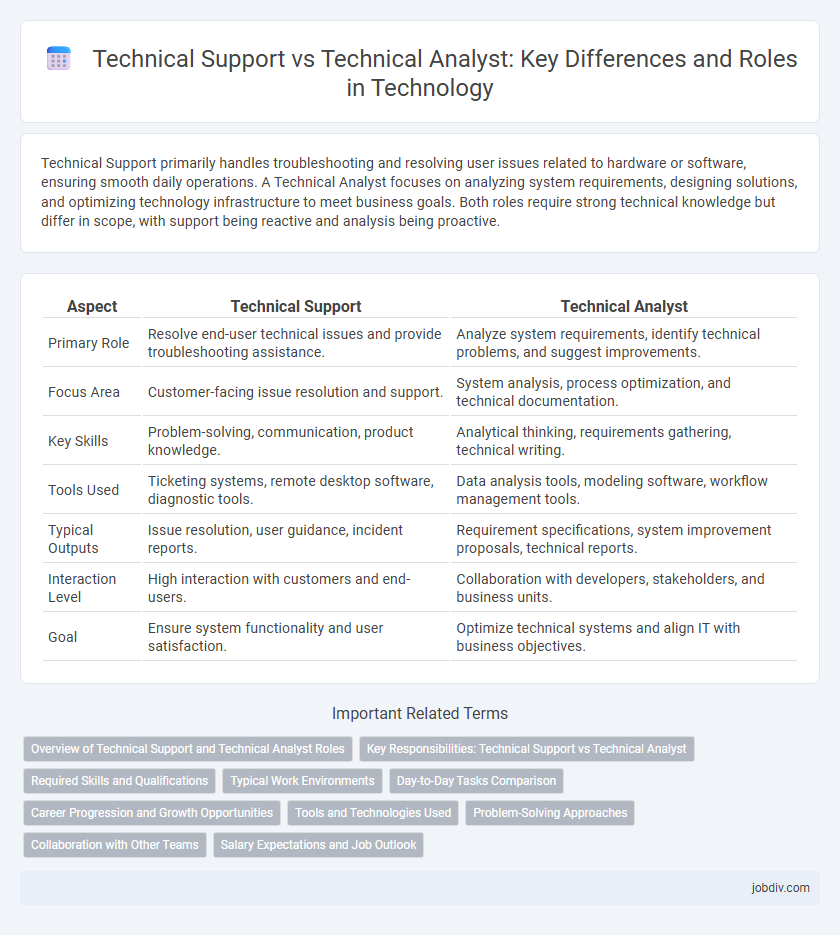
Technical Support primarily handles troubleshooting and resolving user issues related to hardware or software, ensuring smooth daily operations. A Technical Analyst focuses on analyzing system requirements, designing solutions, and optimizing technology infrastructure to meet business goals. Both roles require strong technical knowledge but differ in scope, with support being reactive and analysis being proactive.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Technical Support | Technical Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Resolve end-user technical issues and provide troubleshooting assistance. | Analyze system requirements, identify technical problems, and suggest improvements. |
| Focus Area | Customer-facing issue resolution and support. | System analysis, process optimization, and technical documentation. |
| Key Skills | Problem-solving, communication, product knowledge. | Analytical thinking, requirements gathering, technical writing. |
| Tools Used | Ticketing systems, remote desktop software, diagnostic tools. | Data analysis tools, modeling software, workflow management tools. |
| Typical Outputs | Issue resolution, user guidance, incident reports. | Requirement specifications, system improvement proposals, technical reports. |
| Interaction Level | High interaction with customers and end-users. | Collaboration with developers, stakeholders, and business units. |
| Goal | Ensure system functionality and user satisfaction. | Optimize technical systems and align IT with business objectives. |
Overview of Technical Support and Technical Analyst Roles
Technical Support professionals provide direct assistance to end-users by troubleshooting hardware, software, and network issues, ensuring system functionality and user satisfaction. Technical Analysts focus on analyzing IT systems and business processes, identifying technical requirements, and recommending solutions to improve operational efficiency. Both roles collaborate closely to maintain optimal system performance and address technical challenges within an organization.
Key Responsibilities: Technical Support vs Technical Analyst
Technical Support primarily handles troubleshooting hardware and software issues, providing end-user assistance, and maintaining system functionality to ensure continuous operation. Technical Analysts focus on evaluating system performance, analyzing technical requirements, and designing solutions to optimize business processes and support strategic IT initiatives. Both roles require strong problem-solving skills but differ in scope, with Technical Support emphasizing immediate issue resolution and Technical Analysts driving long-term technical improvements.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Technical Support professionals require strong troubleshooting skills, customer service expertise, and proficiency with hardware and software systems. Technical Analysts need advanced analytical capabilities, experience in data interpretation, and knowledge of system design and development methodologies. Both roles demand a solid understanding of IT infrastructure, but Analysts typically require higher-level certifications such as CompTIA Security+ or ITIL.
Typical Work Environments
Technical support professionals typically operate in customer-facing environments such as call centers or help desks, assisting end-users with hardware, software, and network issues. Technical analysts usually work within corporate IT departments or consulting firms, analyzing system performance, troubleshooting complex problems, and implementing technology solutions. Both roles require collaboration with cross-functional teams but differ in the depth of technical problem-solving and strategic involvement.
Day-to-Day Tasks Comparison
Technical Support specialists primarily troubleshoot hardware and software issues, manage user inquiries, and maintain system functionality through direct problem resolution. Technical Analysts focus on data analysis, system performance evaluation, and process optimization by interpreting technical metrics to guide strategic improvements. While both roles require technical expertise, Technical Support emphasizes reactive problem-solving, whereas Technical Analysts engage in proactive system enhancement and reporting.
Career Progression and Growth Opportunities
Technical Support roles often serve as an entry point, providing foundational skills in troubleshooting and customer interaction, which are essential for career growth in IT. Technical Analysts typically require deeper analytical capabilities and experience in data interpretation, offering opportunities to evolve into strategic positions such as Systems Analyst or IT Consultant. Advancement pathways from Technical Support to Technical Analyst roles involve gaining certifications, enhancing problem-solving skills, and understanding complex system architectures.
Tools and Technologies Used
Technical Support professionals frequently utilize remote desktop tools, ticketing systems such as Zendesk or Jira, and diagnostic software to troubleshoot hardware and software issues efficiently. In contrast, Technical Analysts often employ advanced data analysis platforms like SQL, Power BI, and specialized monitoring tools to interpret system performance and recommend improvements. Both roles require proficiency in network protocols and operating systems, but Analysts focus more on data-driven decision-making while Support emphasizes problem resolution.
Problem-Solving Approaches
Technical Support professionals typically focus on immediate resolution of user issues through direct troubleshooting, using predefined scripts and knowledge bases to diagnose and solve problems efficiently. Technical Analysts approach problem-solving by conducting in-depth analysis of system data, identifying underlying patterns and root causes to develop strategic improvements and prevent recurring issues. Their methodologies emphasize proactive problem identification and long-term resolution strategies informed by data-driven insights.
Collaboration with Other Teams
Technical Support professionals facilitate seamless collaboration by addressing real-time user issues and communicating feedback to development and IT teams to improve product functionality. Technical Analysts bridge gaps between business objectives and technical teams by translating complex requirements into actionable plans, ensuring alignment across software developers, project managers, and stakeholders. Effective collaboration involves continuous knowledge sharing, joint problem-solving sessions, and integrated workflows to enhance overall system performance and user satisfaction.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Technical Support roles typically offer average salaries ranging from $45,000 to $60,000 annually, reflecting entry to mid-level experience in troubleshooting and user assistance. Technical Analysts command higher salaries, often between $65,000 and $85,000, due to their responsibilities in system analysis, data interpretation, and strategic IT improvements. Job outlook for Technical Analysts is projected to grow faster than Technical Support, driven by increasing demand for data-driven decision making and complex IT system optimization.
Technical Support vs Technical Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com